SLES256F May 2010 – May 2022 DRV8312 , DRV8332
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DKD|36
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DKD|36
Orderable Information
10.2.1.1
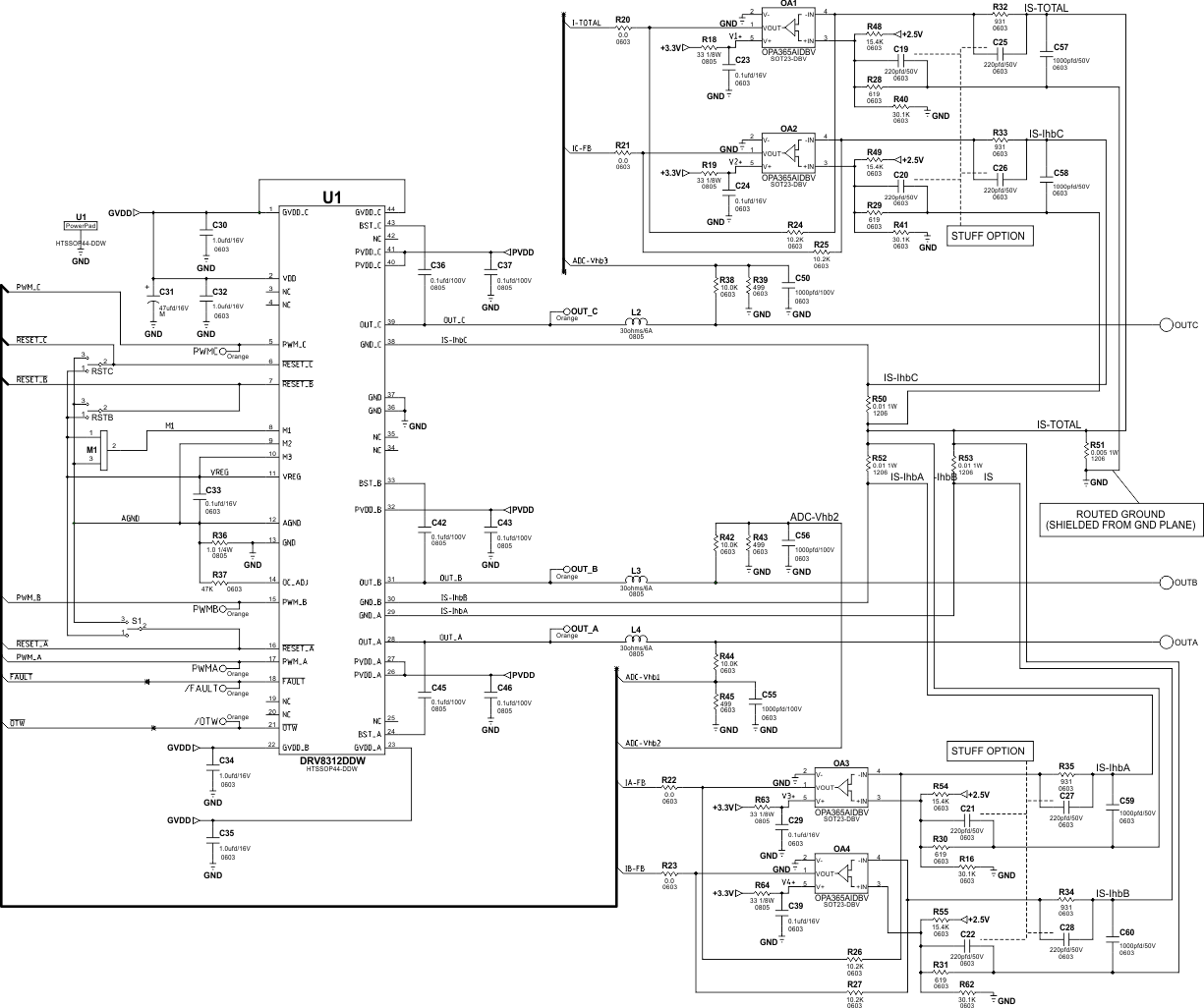 Figure 10-1 DRV8312 Schematic Example
Figure 10-1 DRV8312 Schematic Example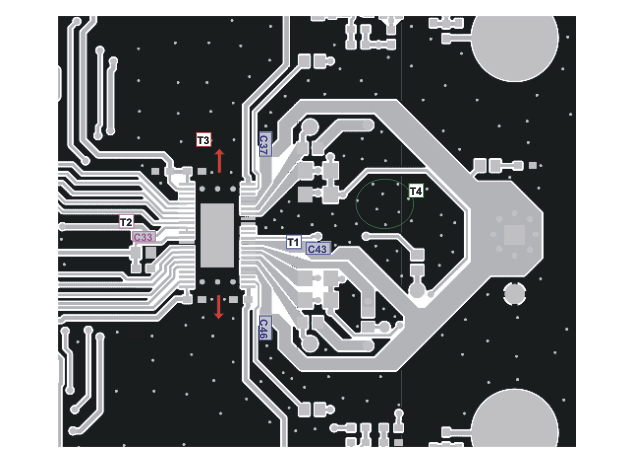
T1: PVDD decoupling capacitors C37, C43, and C46 should be placed very close to PVDD_X pins and ground return path.
T2: VREG decoupling capacitor C33 should be placed very close to VREG abd AGND pins.
T3: Clear the space above and below the device as much as possible to improve the thermal spreading.
T4: Add many vias to reduce the impedance of ground path through top to bottom side. Make traces as wide as possible for ground path such as GND_X path.
Figure 10-2 Printed Circuit Board – Top Layer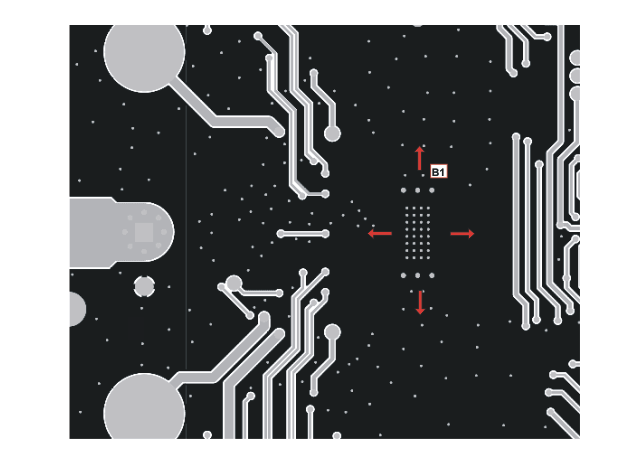
B1: Do not block the heat transfer path at bottom side. Clear as much space as possible for better heat spreading.
Figure 10-3 Printed Circuit Board – Bottom Layer