SLES242H December 2009 – July 2024 DRV8412
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
- 6Detailed Description
-
Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2 Typical Applications
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Revision History
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDW|44
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDW|44
Orderable Information
7.4.2.1 Current Shunt Resistor
If current shunt resistor is connected between GND_X to GND or PVDD_X to PVDD, make sure there is only one single path to connect each GND_X or PVDD_X pin to shunt resistor, and the path is short and symmetrical on each sense path to minimize the measurement error due to additional resistance on the trace.
An example of the schematic and PCB layout of DRV8412 are shown in Figure 7-13, Figure 7-14, and Figure 7-15.
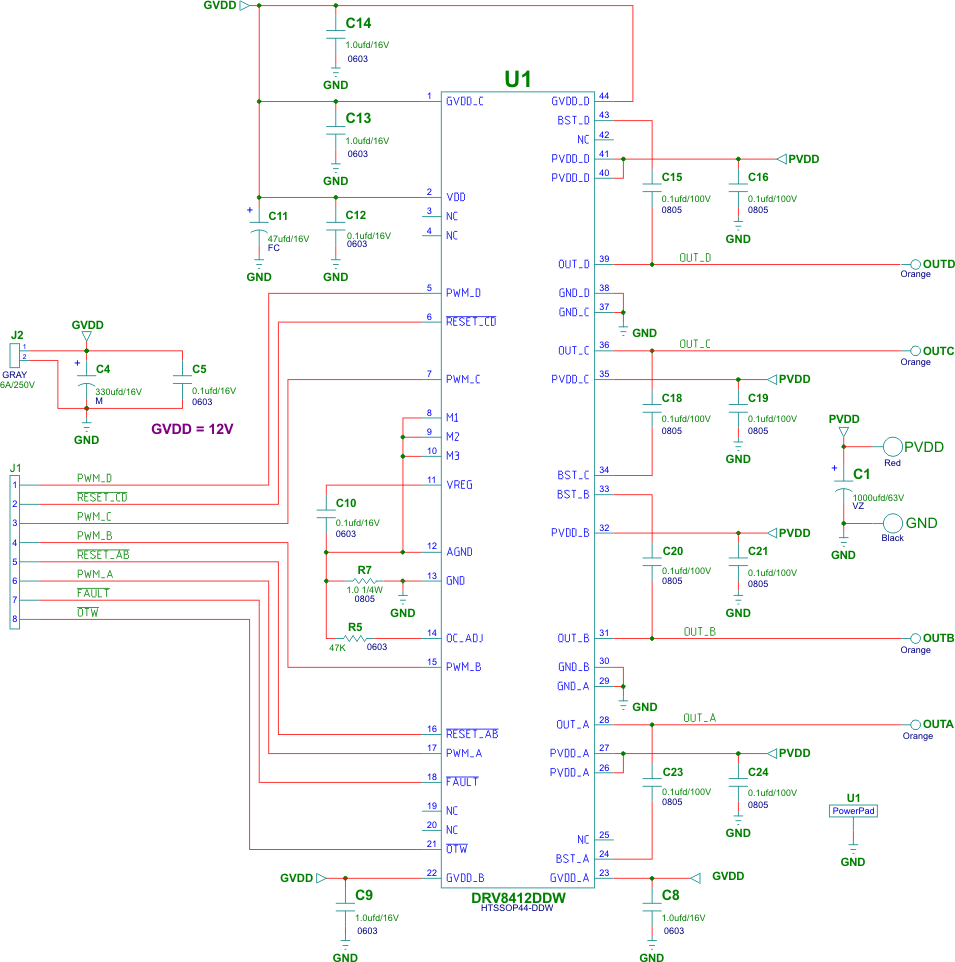 Figure 7-13 DRV8412
Schematic Example
Figure 7-13 DRV8412
Schematic Example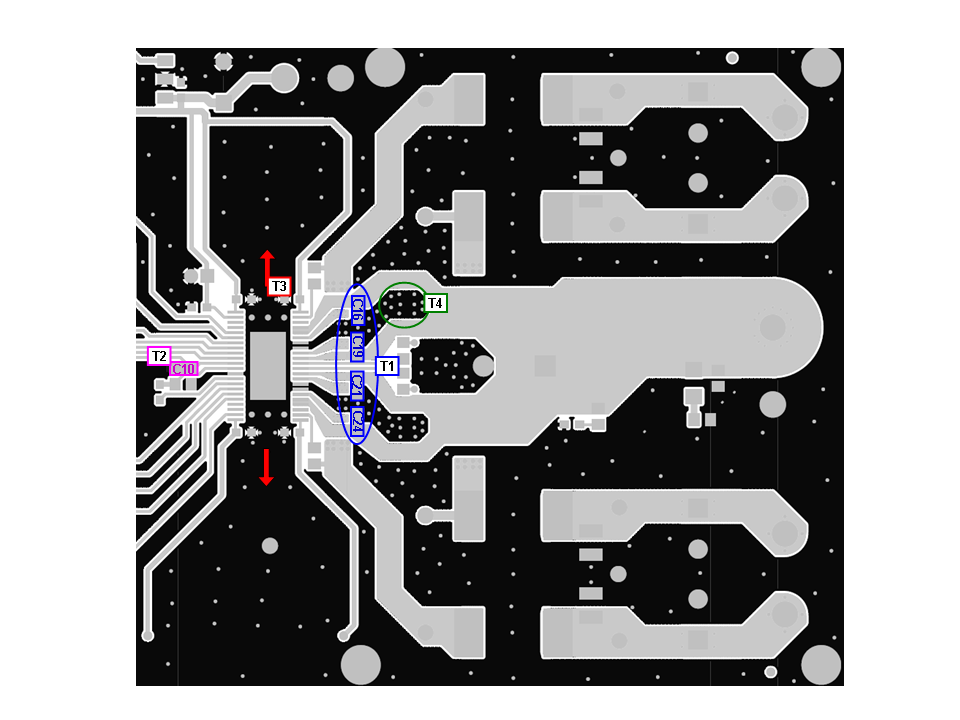
T1: PVDD decoupling capacitors C16, C19, C21, and C24 should be placed very close to PVDD_X pins and ground return path.
T2: VREG decoupling capacitor C10 should be placed very close to VREG abd AGND pins.
T3: Clear the space above and below the device as much as possible to improve the thermal spreading.
T4: Add many vias to reduce the impedance of ground path through top to bottom side. Make traces as wide as possible for ground path such as GND_X path.
Figure 7-14 Printed Circuit Board – Top Layer
B1: Do not block the heat transfer path at bottom side. Clear as much space as possible for better heat spreading.
Figure 7-15 Printed Circuit Board – Bottom Layer