SLOSE37B June 2020 – May 2022 DRV8436
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Stepper Motor Driver Current Ratings
- 7.3.2 PWM Motor Drivers
- 7.3.3 Microstepping Indexer
- 7.3.4 Controlling VREF with an MCU DAC
- 7.3.5 Current Regulation
- 7.3.6
Decay Modes
- 7.3.6.1 Slow Decay for Increasing and Decreasing Current
- 7.3.6.2 Slow Decay for Increasing Current, Mixed Decay for Decreasing Current
- 7.3.6.3 Mixed Decay for Increasing and Decreasing Current
- 7.3.6.4 Smart tune Dynamic Decay
- 7.3.6.5 Smart tune Ripple Control
- 7.3.6.6 PWM OFF Time
- 7.3.6.7 Blanking time
- 7.3.7 Charge Pump
- 7.3.8 Linear Voltage Regulators
- 7.3.9 Logic Level, tri-level and quad-level Pin Diagrams
- 7.3.10 Protection Circuits
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Thermal Application
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
7.3.6 Decay Modes
During PWM current chopping, the H-bridge is enabled to drive through the motor winding until the PWM current chopping threshold is reached. This is shown in Figure 7-7, Item 1.
Once the chopping current threshold is reached, the H-bridge can operate in two different states, fast decay or slow decay. In fast decay mode, once the PWM chopping current level has been reached, the H-bridge reverses state to allow winding current to flow in a reverse direction. Fast decay mode is shown in Figure 7-7, item 2. In slow decay mode, winding current is re-circulated by enabling both of the low-side FETs in the bridge. This is shown in Figure 7-7, Item 3.
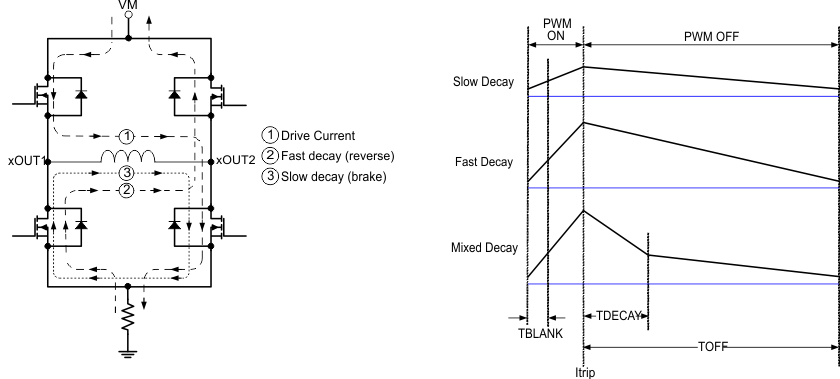 Figure 7-7 Decay Modes
Figure 7-7 Decay ModesThe decay mode of the DRV8436 is selected by the DECAY0 and DECAY1 pins as shown in Table 7-6. The decay modes can be changed on the fly.
| DECAY0 | DECAY1 | INCREASING STEPS | DECREASING STEPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Smart tune Dynamic Decay | Smart tune Dynamic Decay |
| 0 | 1 | Smart tune Ripple Control | Smart tune Ripple Control |
| 1 | 0 | Mixed decay: 30% fast | Mixed decay: 30% fast |
| 1 | 1 | Slow decay | Mixed decay: 30% fast |
| Hi-Z | 0 | Mixed decay: 60% fast | Mixed decay: 60% fast |
| Hi-Z | 1 | Slow decay | Slow decay |
Figure 7-8 defines increasing and decreasing current. For the slow-mixed decay mode, the decay mode is set as slow during increasing current steps and mixed decay during decreasing current steps. In full step and noncircular 1/2-step operation, the decay mode corresponding to decreasing steps is always used.
 Figure 7-8 Definition of Increasing and Decreasing Steps
Figure 7-8 Definition of Increasing and Decreasing Steps