SLLSFA7A July 2020 – April 2021 DRV8706-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Descriptions
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 External Components
- 7.3.2 Device Interface Variants
- 7.3.3 Input PWM Modes
- 7.3.4 Smart Gate Driver
- 7.3.5 Doubler (Single-Stage) Charge Pump
- 7.3.6 Wide Common Mode Differential Current Shunt Amplifier
- 7.3.7 Pin Diagrams
- 7.3.8
Protection and Diagnostics
- 7.3.8.1 Gate Driver Disable and Enable (DRVOFF and EN_DRV)
- 7.3.8.2 Fault Reset (CLR_FLT)
- 7.3.8.3 DVDD Logic Supply Power on Reset (DVDD_POR)
- 7.3.8.4 PVDD Supply Undervoltage Monitor (PVDD_UV)
- 7.3.8.5 PVDD Supply Overvoltage Monitor (PVDD_OV)
- 7.3.8.6 VCP Charge Pump Undervoltage Lockout (VCP_UV)
- 7.3.8.7 MOSFET VDS Overcurrent Protection (VDS_OCP)
- 7.3.8.8 Gate Driver Fault (VGS_GDF)
- 7.3.8.9 Thermal Warning (OTW)
- 7.3.8.10 Thermal Shutdown (OTSD)
- 7.3.8.11 Offline Short Circuit and Open Load Detection (OOL and OSC)
- 7.3.8.12 Fault Detection and Response Summary Table
- 7.4 Device Function Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
7.3.3.1 Half-Bridge Control
In half-bridge control, each half-bridge gate driver can be individually controlled through the corresponding IN1/EN, IN2/PH, and nHIZx input pins. The nHIZx signals have priority over the IN1/EN and IN2/PH signals. For half-bridge control, you can refer to the INx designator. The DRV8706-Q1 internally handles the dead-time generation between high-side and low-side switching so that a single PWM input can control each half-bridge.
The DRV8706-Q1 provides the ability to independently Hi-Z each half-bridge gate driver through the nHIZx pins. The nHIZx pins should be tied to DVDD if this function is not required.
On SPI device variants, the IN1/EN, IN2/PH, HIZ1, and HIZ2 signals can also be controlled through the SPI registers. The IN1/EN and IN2/PH SPI control can be enabled through the IN1/EN_MODE and IN2/PH_MODE register settings. The signals are controlled through S_IN1/EN and S_IN2/PH register settings. The HIZ1 signal is the logic OR of the nHIZ1 pin and S_HIZ1 register setting. The HIZ2 signal is the logic OR of the nHIZ2 pin and S_HIZ2 register setting.
| nHIZx | INx | GHx | GLx | SHx |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | X | L | L | Z |
| 1 | 0 | L | H | L |
| 1 | 1 | H | L | H |
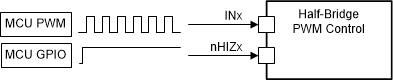 Figure 7-3 Half-Bridge Control
Figure 7-3 Half-Bridge Control