SLVSC40H June 2013 – May 2020 DRV8711
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Control Registers
- 7.6.2 CTRL Register (Address = 0x00)
- 7.6.3 TORQUE Register (Address = 0x01)
- 7.6.4 OFF Register (Address = 0x02)
- 7.6.5 BLANK Register (Address = 0x03)
- 7.6.6 DECAY Register (Address = 0x04)
- 7.6.7 STALL Register (Address = 0x05)
- 7.6.8 DRIVE Register (Address = 0x06)
- 7.6.9 STATUS Register (Address = 0x07)
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DCP|38
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DCP|38
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 Calculate Current Regulation
In a stepper motor, the set full-scale current (IFS) is the maximum current driven through either winding. For the DRV8711, this quantity will depend on the analog voltage, the programmed torque and gain values, and the sense resistor value (RSENSE). During stepping, IFS defines the current chopping threshold (ITRIP) for the maximum current step. The gain of DRV8711 is set for 5 V/V.
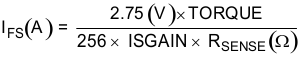
To achieve IFS = 1.25 A with RSENSE of 0.2 Ω with a gain of 5, TORQUE should be set to 116(dec).
IFS is set by a comparator which compares the voltage across RSENSE to a reference voltage. There is a current sense amplifier built in with programmable gain through ISGAIN. Note that IFS must also follow Equation 8 in order to avoid saturating the motor. VM is the motor supply voltage, and RL is the motor winding resistance.
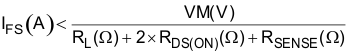
TORQUE is a register used to scale the output. If TORQUE = 0xFF, then the SIN DAC is scaled by 1. As TORQUE is decreased, the reference is decreased as well.
As an example, the torque register can be reduced when the motor has been stopped. Reducing torque at this point could reduce the current required to hold the motor.
| TORQUE Register | Address = 0x01h |
| Bit | Name | Size | R/W | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | TORQUE | 8 | R/W | 0xFFh | Sets full-scale output current for both H-bridges |
ISGAIN controls the gain of the current sense amplifier. Note that from Equation 7, increasing this gain will decrease IFS since it is used in the feedback path.
| CTRL Register | Address = 0x00h |
| Bit | Name | Size | R/W | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9-8 | ISGAIN | 2 | R/W | 00 | ISENSE amplifier gain set
00: Gain of 5 01: Gain of 10 10: Gain of 20 11: Gain of 40 |