-
DRV8833 Dual H-Bridge Motor Driver
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|16
- RTY|16
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
DRV8833 Dual H-Bridge Motor Driver
1 Features
- Dual-H-Bridge Current-Control Motor Driver
- Can Drive Two DC Motors or One Stepper Motor
- Low MOSFET ON-Resistance: HS + LS 360 mΩ
- Output Current (at VM = 5 V, 25°C)
- Outputs can be in Parallel for
- 3-A RMS, 4-A Peak (PWP and RTY)
- 1-A RMS, 4-A Peak (PW)
- Wide Power Supply Voltage Range:
2.7 to 10.8 V - PWM Winding Current Regulation and Current Limiting
- Thermally Enhanced Surface-Mount Packages
2 Applications
- Battery-Powered Toys
- POS Printers
- Video Security Cameras
- Office Automation Machines
- Gaming Machines
- Robotics
3 Description
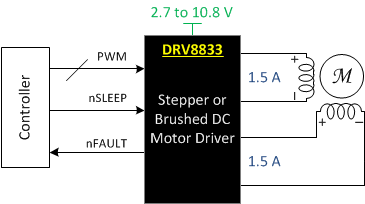
The DRV8833 device provides a dual bridge motor driver solution for toys, printers, and other mechatronic applications.
The device has two H-bridge drivers, and can drive two DC brush motors, a bipolar stepper motor, solenoids, or other inductive loads.
The output driver block of each H-bridge consists of N-channel power MOSFETs configured as an H-bridge to drive the motor windings. Each H-bridge includes circuitry to regulate or limit the winding current.
Internal shutdown functions with a fault output pin are provided for overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, undervoltage lockout, and overtemperature. A low-power sleep mode is also provided.
The DRV8833 is packaged in a 16-pin WQFN package with PowerPAD™ (Eco-friendly: RoHS & no Sb/Br).
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| DRV8833 | TSSOP (16) | 5.00 mm × 4.40 mm |
| HTSSOP (16) | 5.00 mm × 4.40 mm | |
| WQFN (16) | 4.00 mm × 4.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Simplified Schematic
4 Revision History
Changes from D Revision (March 2015) to E Revision
- Updated Features bullets to include specifications for other packagesGo
- Added note back to Pin Functions regarding the different I/O types Go
- Corrected the device name and current regulation description in OverviewGo
- Corrected output current to 1.5-A RMS from 700-mA RMS Go
Changes from C Revision (January 2013) to D Revision
- Added ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions



Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | EXTERNAL COMPONENTS OR CONNECTIONS |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | WQFN | HTSSOP, TSSOP |
|||
| POWER AND GROUND | |||||
| GND | 11 PPAD |
13 | — | Device ground. HTSSOP package has PowerPAD. | Both the GND pin and device PowerPAD must be connected to ground. |
| VINT | 12 | 14 | — | Internal supply bypass | Bypass to GND with 2.2-μF, 6.3-V capacitor. |
| VM | 10 | 12 | — | Device power supply | Connect to motor supply. A 10-µF (minimum) ceramic bypass capacitor to GND is recommended. |
| VCP | 9 | 11 | IO | High-side gate drive voltage | Connect a 0.01-μF, 16-V (minimum) X7R ceramic capacitor to VM. |
| CONTROL | |||||
| AIN1 | 14 | 16 | I | Bridge A input 1 | Logic input controls state of AOUT1. Internal pulldown. |
| AIN2 | 13 | 15 | I | Bridge A input 2 | Logic input controls state of AOUT2. Internal pulldown. |
| BIN1 | 7 | 9 | I | Bridge B input 1 | Logic input controls state of BOUT1. Internal pulldown. |
| BIN2 | 8 | 10 | I | Bridge B input 2 | Logic input controls state of BOUT2. Internal pulldown. |
| nSLEEP | 15 | 1 | I | Sleep mode input | Logic high to enable device, logic low to enter low-power sleep mode and reset all internal logic. Internal pulldown. |
| STATUS | |||||
| nFAULT | 6 | 8 | OD | Fault output | Logic low when in fault condition (overtemperature, overcurrent) |
| OUTPUT | |||||
| AISEN | 1 | 3 | IO | Bridge A ground / ISENSE | Connect to current sense resistor for bridge A, or GND if current control not needed |
| BISEN | 4 | 6 | IO | Bridge B ground / ISENSE | Connect to current sense resistor for bridge B, or GND if current control not needed |
| AOUT1 | 16 | 2 | O | Bridge A output 1 | Connect to motor winding A |
| AOUT2 | 2 | 4 | O | Bridge A output 2 | |
| BOUT1 | 5 | 7 | O | Bridge B output 1 | Connect to motor winding B |
| BOUT2 | 3 | 5 | O | Bridge B output 2 | |