SLVSE65C July 2018 – December 2023 DRV8847
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 PWM Motor Drivers
- 7.3.2 Bridge Operation
- 7.3.3 Bridge Control
- 7.3.4 Current Regulation
- 7.3.5 Current Recirculation and Decay Modes
- 7.3.6 Torque Scalar
- 7.3.7 Stepping Modes
- 7.3.8 Motor Driver Protection Circuits
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Map
- 7.6.1 Slave Address Register (Address = 0x00) [reset = 0x60]
- 7.6.2 IC1 Control Register (Address = 0x01) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.3 IC2 Control Register (Address = 0x02) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.4 Slew-Rate and Fault Status-1 Register (Address = 0x03) [reset = 0x40]
- 7.6.5 Fault Status-2 Register (Address = 0x04) [reset = 0x00]
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Stepper Motor Application
- 8.2.2 Dual BDC Motor Application
- 8.2.3 Open Load Implementation
- Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|16
- PWP|16
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
7.3.4 Current Regulation
The current through the motor windings is regulated by a fixed off-time PWM current regulation circuit. With brushed DC motors, current regulation can be used to limit the stall current (which is also the start-up current) of the motor.
Current regulation works as follows: When an H-bridge is enabled, current rises through the winding at a rate dependent on the supply voltage and inductance of the winding. If the current reaches the current trip threshold, the bridge disables the current for a time tOFF before starting the next PWM cycle.
Immediately after the current is enabled, the voltage on the ISENxx pin is ignored for a while (tBLANK) before enabling the current sense circuitry. This blanking time also sets the minimum on-time of the PWM cycle.
The PWM trip current is set by a comparator which compares the voltage across a current sense resistor connected to the ISENxx pin with a reference voltage. This reference voltage (VTRIP) is generated on-chip and decides the current trip level.
The full-scale trip current in a winding is calculated as shown in Equation 1.
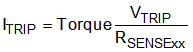
where
- ITRIP is the regulated current.
- VTRIP is the internally generated trip voltage.
- RSENSExx is the resistance of the sense resistor.
- Torque is the torque scalar, the value of which depends on the input on the TRQ pin. TRQ = 100% for TRQ pin connected to GND (DRV8847) or TRQ bit set to 0 (DRV8847S) and TRQ = 50% connected to VEXT (DRV8847) or TRQ bit set to 1 (DRV8847S).
For example, if the VTRIP voltage is 150 mV and the value of the sense resistor is 150 mΩ, the full-scale trip current is 1 A (150 mV / (150 mΩ) = 1 A).
If the current control is not needed, connect the ISENxx pins directly to the ground.