SLLSEL7B October 2014 – April 2024 DRV8848
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
6.3.5 Current Recirculation and Decay Modes
During PWM current chopping, the H-bridge is enabled to drive current through the motor winding until the PWM current chopping threshold is reached (see case 1 in Figure 6-3).
After the chopping current threshold is reached, the drive current is interrupted, but due to the inductive nature of the motor, current must continue to flow for some period of time. This is called recirculation current. To handle this recirculation current, the DRV8848 H-bridge operates in mixed decay mode.
Mixed decay is a combination of fast and slow decay modes. In fast decay mode, the opposite drivers are turned on to allow the current to decay (see case 2 in Figure 6-3). If the winding current approaches zero, while in fast decay, the bridge is disabled to prevent any reverse current flow. In slow decay mode, winding current is recirculated by enabling both of the low-side FETs in the bridge (see case 3 in Figure 6-3). Mixed decay starts with fast decay, then goes to slow decay. In DRV8848, the mixed decay ratio is 25% fast decay and 75% slow decay (as shown in Figure 6-4).
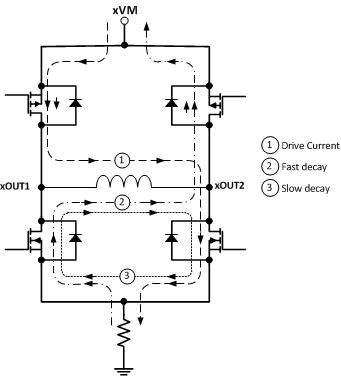 Figure 6-3 Decay Modes
Figure 6-3 Decay Modes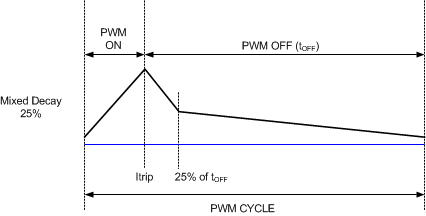 Figure 6-4 Mixed Decay
Figure 6-4 Mixed Decay