SNLS685 December 2020 DS160PR412
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Layout Example
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RUA|42
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RUA|42
Orderable Information
8.2.1.3 Pin-to-pin Passive versus Redriver Option
For eight lane PCIe lane muxing application a topology is illustrated where two DS160PR412 and two DS160PR421 are used. There are system use cases where the PCIe link loss is low enough that a signal conditioner such as linear redrivers may not be needed. In such use cases system engineers may consider passive mux to achieve same lane muxing topology. The four channel passive mux/demux TMUXHS4412 is pin-to-pin (p2p) compatible with the DS160PR412 and DS160PR421. This p2p component availability provides great flexibility for system implementation engineers where the need for redriver is not completely clear. Figure 8-2 illustrates p2p passive vs redriver option to implement PCIe lane switching.
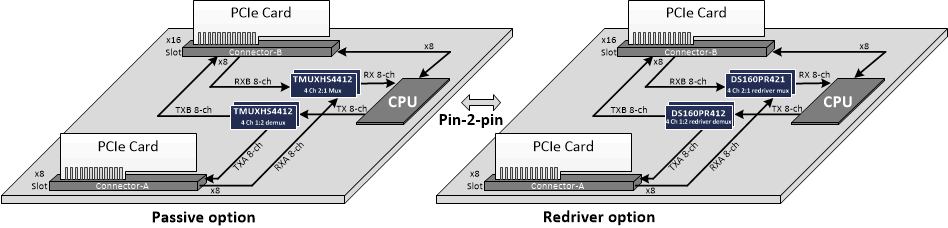 Figure 8-2 Pin-to-pin passive vs redriver option for PCIe lane switching
Figure 8-2 Pin-to-pin passive vs redriver option for PCIe lane switching