SNLS689 December 2020 DS160PR822
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NJX|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.5.1.3 SMBus/I2C Master Mode Configuration (EEPROM Self Load)
The DS160PR822 can also be configured by reading from EEPROM. To enter into this mode MODE pin must be set to L1. The EEPROM load operation only happens once after device's initial power-up. If the device is configured for SMBus master mode, it will remain in the SMBus IDLE state until the READ_EN_N pin is asserted to LOW. After the READ_EN_N pin is driven LOW, the device becomes an SMBus master and attempts to self-configure by reading device settings stored in an external EEPROM (SMBus 8-bit address 0xA0). When the device has finished reading from the EEPROM successfully, it will drive the ALL_DONE_N pin LOW. SMBus/I2C slave operation is available in this mode before, during or after EEPROM reading. Note during EEPROM reading if the external SMBus/I2C master wants to access the device registers it must support arbitration. Refer to the Understanding EEPROM Programming for PCI-Express 4.0 Redrivers (SNLA342) application report for more information.
When designing a system for using the external EEPROM, the user must follow these specific guidelines:
- EEPROM size of 2 kb (256 × 8-bit) is recommended.
- Set MODE = L1, configure for SMBus master mode
- The external EEPROM device address byte must be 0xA0 and capable of 400 kHz operation at 3.3 V supply
- In SMBus/I2C modes the SCL, SDA pins must be pulled up to a 3.3 V supply with a pull-up resistor. The value of the resistor depends on total bus capacitance. 4.7 kΩ is a good first approximation for a bus capacitance of 10 pF.
Figure 7-2 shows a use case with four DS160PR822 to implement a 2x2 crosspoint for a x8 link configuration, but the user can cascade any number of DS160PR822 devices in a similar way. Tie first device’s READ_EN_N pin low to automatically initiate EEPROM read at power up. Alternately the READ_EN_N pin of the first device can also be controlled by a microcontroller to initiate the EEPROM read manually. Leave the final device’s ALL_DONE_N pin floating, or connect the pin to a microcontroller input to monitor the completion of the final EEPROM read.
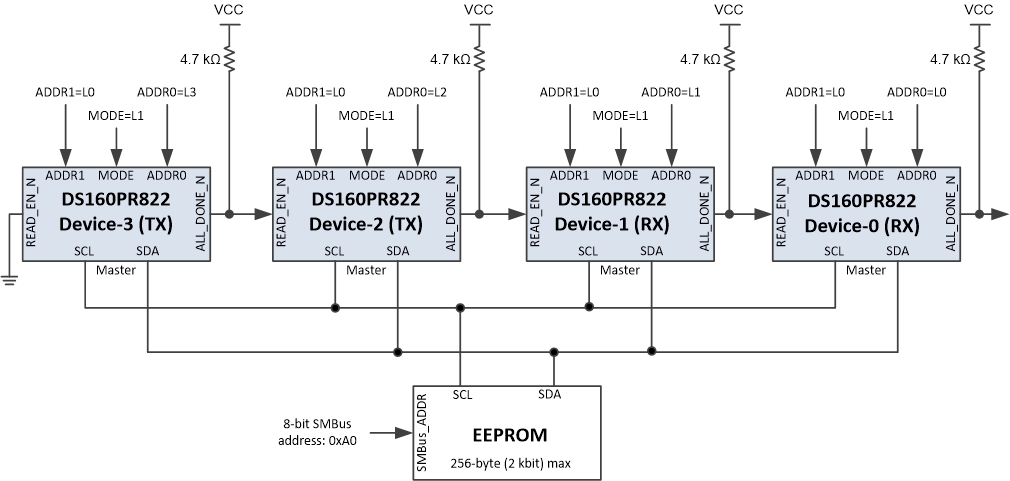 Figure 7-2 Daisy Chain Four DS160PR822 Devices to Read from
Single EEPROM
Figure 7-2 Daisy Chain Four DS160PR822 Devices to Read from
Single EEPROM