SPRS742L June 2011 – February 2021 F28M35E20B , F28M35H22C , F28M35H52C , F28M35H52C-Q1 , F28M35M22C , F28M35M52C
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 7.3 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for RFP PowerPAD Package
- 7.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 7.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.1 Power Sequencing
- 7.9.2
Clock Specifications
- 7.9.2.1 Changing the Frequency of the Main PLL
- 7.9.2.2
Input Clock Frequency and Timing Requirements, PLL Lock Times
- 7.9.2.2.1 Input Clock Frequency
- 7.9.2.2.2 Crystal Oscillator Electrical Characteristics
- 7.9.2.2.3 X1 Timing Requirements - PLL Enabled (1)
- 7.9.2.2.4 X1 Timing Requirements - PLL Disabled
- 7.9.2.2.5 XCLKIN Timing Requirements - PLL Enabled
- 7.9.2.2.6 XCLKIN Timing Requirements - PLL Disabled
- 7.9.2.2.7 PLL Lock Times
- 7.9.2.3 Output Clock Frequency and Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.2.4 Internal Clock Frequencies
- 7.9.3 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 7.9.4 Flash Timing – Master Subsystem
- 7.9.5 Flash Timing – Control Subsystem
- 7.9.6
GPIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.9.6.1 GPIO - Output Timing
- 7.9.6.2 GPIO - Input Timing
- 7.9.6.3 Sampling Window Width for Input Signals
- 7.9.6.4
Low-Power Mode Wakeup Timing
- 7.9.6.4.1 IDLE Mode Timing Requirements
- 7.9.6.4.2 IDLE Mode Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.6.4.3 IDLE Entry and Exit Timing Diagram
- 7.9.6.4.4 STANDBY Mode Timing Requirements
- 7.9.6.4.5 STANDBY Mode Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.6.4.6 STANDBY Entry and Exit Timing Diagram
- 7.9.6.4.7 HALT Mode Timing Requirements
- 7.9.6.4.8 HALT Mode Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.6.4.9 HALT Entry and Exit Timing Diagram
- 7.9.7 External Interrupt Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.10
Analog and Shared Peripherals
- 7.10.1 Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 7.10.2 Comparator + DAC Units
- 7.10.3 Interprocessor Communications
- 7.10.4
External Peripheral Interface
- 7.10.4.1 EPI General-Purpose Mode
- 7.10.4.2 EPI SDRAM Mode
- 7.10.4.3 EPI Host Bus Mode
- 7.10.4.4
EPI Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.10.4.4.1 EPI SDRAM Interface Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) (see Figure 1-1 , Figure 1-1 , and Figure 1-1 )
- 7.10.4.4.2 EPI SDRAM Timing Diagrams
- 7.10.4.4.3 EPI Host-Bus 8 and Host-Bus 16 Interface Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) (see Figure 1-1 , Figure 1-1 , Figure 1-1 , and Figure 1-1 )
- 7.10.4.4.4 EPI Host-Bus 8 and Host-Bus 16 Interface Timing Requirements (1) (see Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-1 )
- 7.10.4.4.5 EPI Host-Bus 8/16 Mode Timing Diagrams
- 7.10.4.4.6 EPI General-Purpose Interface Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) (see Figure 1-1 )
- 7.10.4.4.7 EPI General-Purpose Interface Timing Requirements (see Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-1 )
- 7.10.4.4.8 EPI General-Purpose Interface Timing Diagrams
- 7.11
Master Subsystem Peripherals
- 7.11.1 Synchronous Serial Interface
- 7.11.2 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
- 7.11.3 Cortex-M3 Inter-Integrated Circuit
- 7.11.4 Cortex-M3 Controller Area Network
- 7.11.5 Cortex-M3 Universal Serial Bus Controller
- 7.11.6
Cortex-M3 Ethernet Media Access Controller
- 7.11.6.1 Functional Overview
- 7.11.6.2 MII Signals
- 7.11.6.3
EMAC Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.11.6.3.1 Timing Requirements for MIITXCK (see Figure 1-1 )
- 7.11.6.3.2 MIITXCK Timing Diagrams
- 7.11.6.3.3 Timing Requirements for MIIRXCK (see Figure 1-1 )
- 7.11.6.3.4 MIIRXCK Timing Diagram
- 7.11.6.3.5 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) for EMAC MII Transmit (see Figure 1-1 )
- 7.11.6.3.6 EMAC MII Transmit Timing Diagram
- 7.11.6.3.7 Timing Requirements for EMAC MII Receive (see Figure 1-1 )
- 7.11.6.3.8 EMAC MII Receive Timing Diagram
- 7.11.6.4
MDIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.11.6.4.1 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) for MDIO_CK (see Figure 1-1 )
- 7.11.6.4.2 MDIO_CK Timing Diagram
- 7.11.6.4.3 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) for MDIO as Output (see Figure 1-1 )
- 7.11.6.4.4 MDIO as Output Timing Diagram
- 7.11.6.4.5 Timing Requirements for MDIO as Input (see Figure 1-1 )
- 7.11.6.4.6 MDIO as Input Timing Diagram
- 7.12
Control Subsystem Peripherals
- 7.12.1 High-Resolution PWM and Enhanced PWM Modules
- 7.12.2 Enhanced Capture Module
- 7.12.3 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Module
- 7.12.4 C28x Inter-Integrated Circuit Module
- 7.12.5 C28x Serial Communications Interface
- 7.12.6 C28x Serial Peripheral Interface
- 7.12.7
C28x Multichannel Buffered Serial Port
- 7.12.7.1
McBSP Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.12.7.1.1 McBSP Transmit and Receive Timing
- 7.12.7.1.2
McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing
- 7.12.7.1.2.1 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.12.7.1.2.2 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.12.7.1.2.3 McBSP Timing as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0 Timing Diagram
- 7.12.7.1.2.4 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.12.7.1.2.5 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.12.7.1.2.6 McBSP Timing as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0 Timing Diagram
- 7.12.7.1.2.7 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.12.7.1.2.8 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.12.7.1.2.9 McBSP Timing as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1 Timing Diagram
- 7.12.7.1.2.10 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.12.7.1.2.11 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions (Unless Otherwise Noted) (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.12.7.1.2.12 McBSP Timing as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1 Timing Diagram
- 7.12.7.1
McBSP Electrical Data and Timing
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Memory Maps
- 8.2 Identification
- 8.3 Master Subsystem
- 8.4 Control Subsystem
- 8.5 Analog Subsystem
- 8.6 Master Subsystem NMIs
- 8.7 Control Subsystem NMIs
- 8.8 Resets
- 8.9 Internal Voltage Regulation and Power-On-Reset Functionality
- 8.10 Input Clocks and PLLs
- 8.11 Master Subsystem Clocking
- 8.12 Control Subsystem Clocking
- 8.13 Analog Subsystem Clocking
- 8.14 Shared Resources Clocking
- 8.15 Loss of Input Clock (NMI Watchdog Function)
- 8.16 GPIOs and Other Pins
- 8.17 Emulation/JTAG
- 8.18 Code Security Module
- 8.19 µCRC Module
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RFP|144
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RFP|144
Orderable Information
8.16.1 GPIO_MUX1
Sixty-six pins of the GPIO_MUX1 block can be selectively mapped through corresponding sets of registers to all Cortex-M3 peripherals, to all C28x peripherals, to 66General-Purpose Inputs, to 66 General-Purpose Outputs, or a mixture of all of the above. Sixty-two pins of GPIO_MUX1 (GPIO0–GPIO63 minus GPIO39 and GPIO44) can also be mapped to 12 ePWM Trip Inputs, 6 eCAP inputs, 3 External Interrupts to the C28x PIE, and the C28x STANDBY Mode Wakeup signal (LMPWAKE). Additionally, each GPIO_MUX1 pin can have a pullup enabled or disabled. By default, all pullups and outputs are disabled on reset, and all pins of the GPIO_MUX1 block are mapped to Cortex-M3 peripherals (and not to C28x peripherals).
Figure 8-15 shows the internal structure of GPIO_MUX1. The blue blocks represent the Master Subsystem side of GPIO_MUX1, and the green blocks are the Control Subsystem side. The grey block in the center, Pin-Level Mux, is where the GPIO_MUX1 pins are individually assigned between the two subsystems, based on how the configuration registers are programmed in the blue and green blocks (see Figure 8-16 for the configuration registers).
Pin-Level Mux assigns Master Subsystem peripheral signals, Control Subsystem peripheral signals, or GPIOs to the 66 GPIO_MUX1 pins. In addition to connecting peripheral I/Os of the two subsystems to pins, the Pin-Level Mux also provides other signals to the subsystems: XCLKIN and GPIO[A:J] IRQ signals to the Master Subsystem, plus GPTRIP[12:1] and GPI[63:0] signals to the Control Subsystem. XCLKIN carries a clock from an external pin to USB PLL and CAN modules. The nine GPIO[A:J] IRQ signals are interrupt requests from selected external pins to the NVIC interrupt controller. The 12 GPTRIP[12:1] signals carry trip events from selected external pins to C28x control peripherals—ePWM, eCAP, and eQEP. Sixty-four GPI signals go to the C28x LPM GPIO Select block where one of them can be selected to wake up the C28x CPU from Low-Power Mode. Sixty-six (66) GPI signals go to the C28x QUAL block where they can be configured with a qualification sampling period (see Figure 8-16).
The configuration registers for the muxing of Master Subsystem peripherals are organized in nine sets (A–J), with each set being responsible for eight pins. These nine sets of registers are programmable by the Cortex-M3 CPU through the AHB bus or the APB bus. The configuration register for the muxing of Control Subsystem peripherals are organized in three sets (A–C), with each set being responsible for up to 32 pins. These registers are programmable by the C28x CPU through the C28x CPU bus. Figure 8-16 shows set A of the Master Subsystem GPIO configuration registers, set A of the Control Subsystem registers, and the muxing logic for one GPIO pin as driven by these registers.
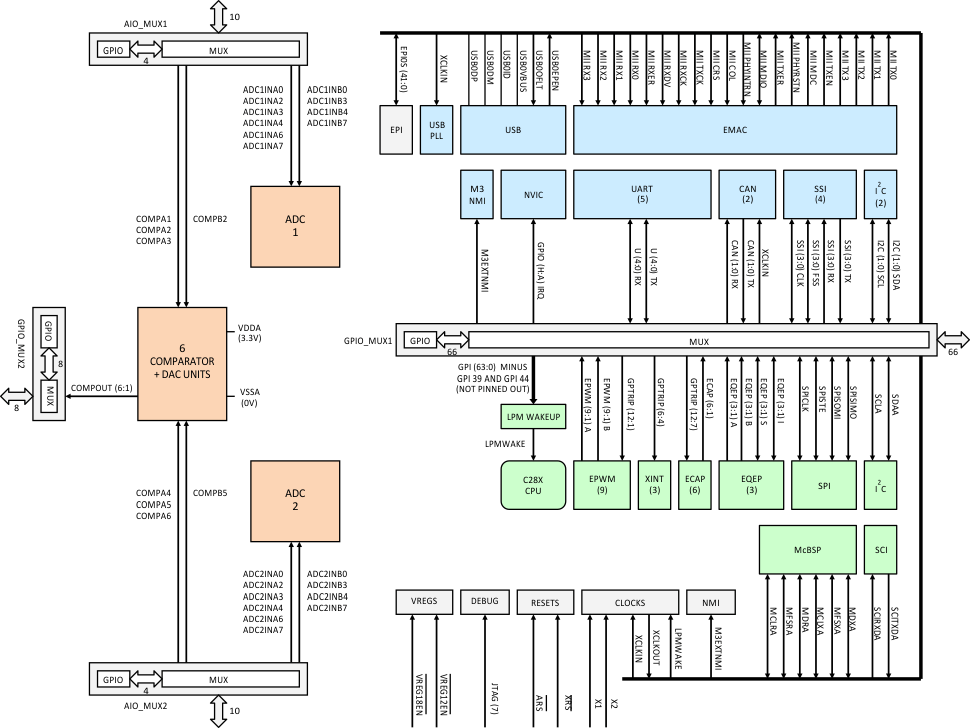 Figure 8-14 GPIOs and Other Pins
Figure 8-14 GPIOs and Other Pins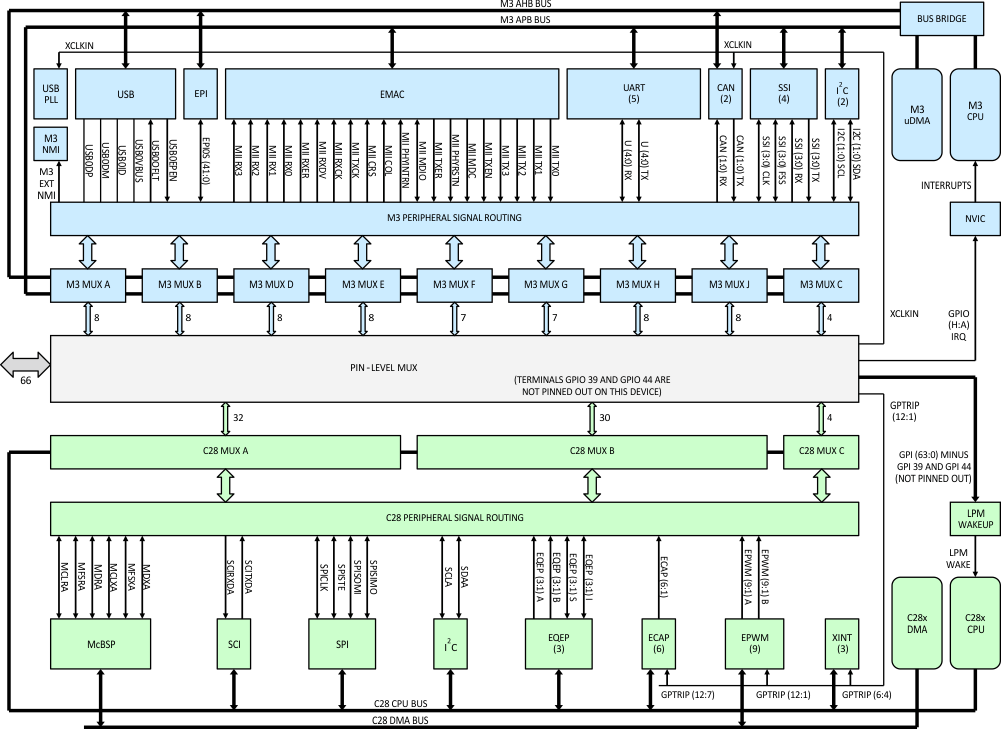 Figure 8-15 GPIO_MUX1 Block
Figure 8-15 GPIO_MUX1 Block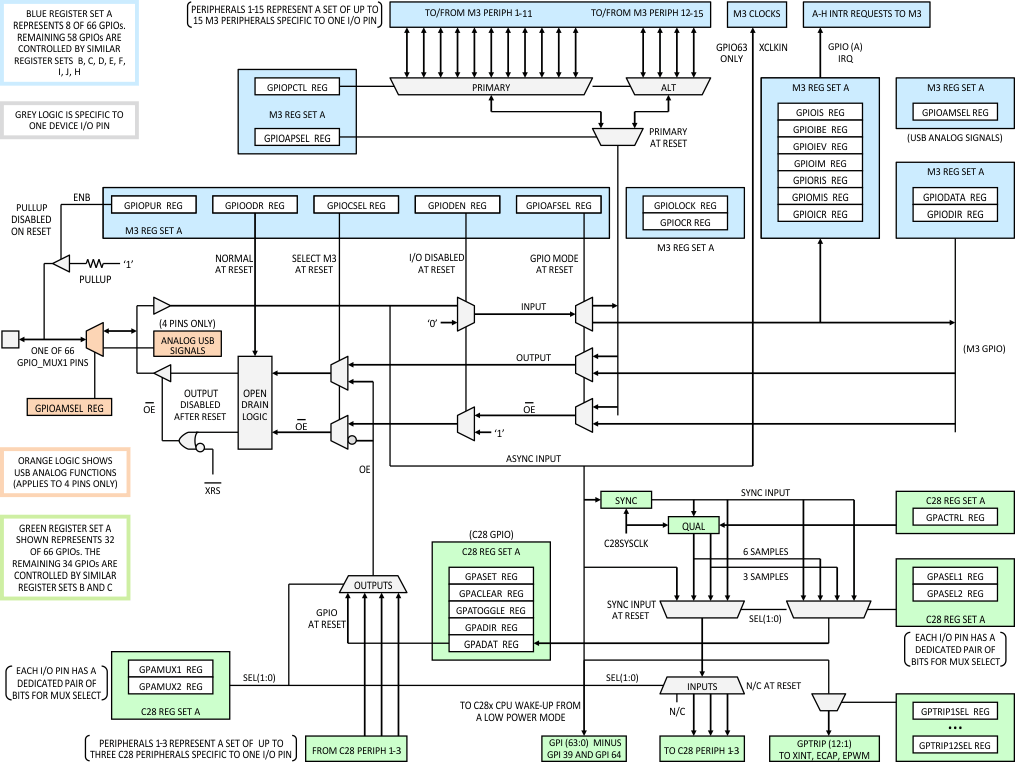 Figure 8-16 GPIO_MUX1 Pin Mapping Through Register Set
A
Figure 8-16 GPIO_MUX1 Pin Mapping Through Register Set
AFor each of the 8 pins in set A of the Cortex-M3 GPIO registers, register GPIOPCTL selects between 1 of 11 possible primary Cortex-M3 peripheral signals, or 1 of 4 possible alternate peripheral signals. Register GPIOAPSEL then picks one output to propagate further along the muxing chain towards a given pin. The input takes the reverse path. See Table 8-27 and Table 8-28 for the mapping of Cortex-M3 peripheral signals to GPIO_MUX1 pins.
Similarly, on the C28x side, GPAMUX1 and GPAMUX2 registers select 1 of 4 possible C28x peripheral signals for each of 32 pins of set A. The selected C28x peripheral output then propagates further along the muxing chain towards a given pin. The input takes the reverse path. See Table 8-29 for the mapping of C28x peripheral signals to GPIO_MUX1 pins.
In addition to passing mostly digital signals, four GPIO_MUX1 pins can also be assigned to analog signals. The GPIO Analog Mode Select (GPIOAMSEL) Register is used to assign four pins to analog USB signals. PF6_GPIO38 becomes USB0VBUS, PG2_GPIO42 becomes USB0DM, PG5_GPIO45 becomes USB0DP, and PG6_GPIO46 becomes USB0ID. When analog mode is selected, these four pins are not available for digital GPIO_MUX1 options as described above.
Another special case is the External Oscillator Input signal (XCLKIN). This signal, available through pin PJ7_GPIO63, is directly tied to USBPLLCLK (clock input to USB PLL) and two CAN modules. XCLKIN is always available at these modules where it can be selected through local registers.
For GPIO_MUX1 pins PF6_GPIO38 and PG6_GPIO46, only the corresponding USB function is available on silicon revision 0 devices (GPIO and other functions listed in Section 6.2.1 are not available).
| ANALOG MODE (USB PINS)(1) |
DEVICE PIN NAME |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 1 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 2 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 3 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 4 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 5 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 6 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 7 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 8 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 9 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 10 |
M3 PRIMARY MODE 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| – | PA0_GPIO0 | U0RX | – | – | – | – | – | – | I2C1SCL | U1RX | – | – |
| – | PA1_GPIO1 | U0TX | – | – | – | – | – | – | I2C1SDA | U1TX | – | – |
| – | PA2_GPIO2 | SSI0CLK | – | MIITXD2 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PA3_GPIO3 | SSI0FSS | – | MIITXD1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PA4_GPIO4 | SSI0RX | – | MIITXD0 | – | CAN0RX | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PA5_GPIO5 | SSI0TX | – | MIIRXDV | – | CAN0TX | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PA6_GPIO6 | I2C1SCL | CCP1 | MIIRXCK | – | – | CAN0RX | – | USB0EPEN | – | – | – |
| – | PA7_GPIO7 | I2C1SDA | CCP4 | MIIRXER | – | – | CAN0TX | CCP3 | USB0PFLT | – | – | – |
| – | PB0_GPIO8 | CCP0 | – | – | – | U1RX | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PB1_GPIO9 | CCP2 | – | – | CCP1 | U1TX | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PB2_GPIO10 | I2C0SCL | – | – | CCP3 | CCP0 | – | – | USB0EPEN | – | – | – |
| – | PB3_GPIO11 | I2C0SDA | – | – | – | – | – | – | USB0PFLT | – | – | – |
| – | PB4_GPIO12 | – | – | – | U2RX | CAN0RX | – | U1RX | EPI0S23 | – | – | – |
| – | PB5_GPIO13 | – | CCP5 | CCP6 | CCP0 | CAN0TX | CCP2 | U1TX | EPI0S22 | – | – | – |
| – | PB6_GPIO14 | CCP1 | CCP7 | – | – | – | CCP5 | – | EPI0S37(2) | – | – | – |
| – | PB7_GPIO15 | – | – | – | EXTNMI | – | – | MIIRXD1 | EPI0S36(2) | – | – | – |
| – | PD0_GPIO16 | – | CAN0RX | – | U2RX | U1RX | CCP6 | MIIRXDV | – | – | – | – |
| – | PD1_GPIO17 | – | CAN0TX | – | U2TX | U1TX | CCP7 | MIITXER | – | – | CCP2 | – |
| – | PD2_GPIO18 | U1RX | CCP6 | – | CCP5 | – | – | – | EPI0S20 | – | – | – |
| – | PD3_GPIO19 | U1TX | CCP7 | – | CCP0 | – | – | – | EPI0S21 | – | – | – |
| – | PD4_GPIO20 | CCP0 | CCP3 | – | MIITXD3 | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S19 | – |
| – | PD5_GPIO21 | CCP2 | CCP4 | – | MIITXD2 | – | – | – | – | U2RX | EPI0S28 | – |
| – | PD6_GPIO22 | – | – | – | MIITXD1 | – | – | – | – | U2TX | EPI0S29 | – |
| – | PD7_GPIO23 | – | – | CCP1 | MIITXD0 | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S30 | – |
| – | PE0_GPIO24 | – | SSI1CLK | CCP3 | – | – | – | – | EPI0S8 | USB0PFLT | – | – |
| – | PE1_GPIO25 | – | SSI1FSS | – | CCP2 | CCP6 | – | – | EPI0S9 | – | – | – |
| – | PE2_GPIO26 | CCP4 | SSI1RX | – | – | CCP2 | – | – | EPI0S24 | – | – | – |
| – | PE3_GPIO27 | CCP1 | SSI1TX | – | – | CCP7 | – | – | EPI0S25 | – | – | – |
| – | PE4_GPIO28 | CCP3 | – | – | – | U2TX | CCP2 | MIIRXD0 | EPI0S34(2) | – | – | – |
| – | PE5_GPIO29 | CCP5 | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S35(2) | – | – | – |
| – | PE6_GPIO30 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PE7_GPIO31 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PF0_GPIO32 | CAN1RX | – | – | MIIRXCK | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PF1_GPIO33 | CAN1TX | – | – | MIIRXER | – | – | – | – | – | CCP3 | – |
| – | PF2_GPIO34 | – | – | MIIPHYINTR | – | – | – | – | EPI0S32(2) | SSI1CLK | – | – |
| – | PF3_GPIO35 | – | – | MIIMDC | – | – | – | – | EPI0S33(2) | SSI1FSS | – | – |
| – | PF4_GPIO36 | CCP0 | – | MIIMDIO | – | – | – | – | EPI0S12 | SSI1RX | – | – |
| – | PF5_GPIO37 | CCP2 | – | MIIRXD3 | – | – | – | – | EPI0S15 | SSI1TX | – | – |
| USB0VBUS | PF6_GPIO38 | CCP1 | – | MIIRXD2 | – | – | – | – | EPI0S38(2) | – | – | – |
| – | PF7_GPIO39 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PG0_GPIO40 | U2RX | – | I2C1SCL | – | – | – | USB0EPEN | EPI0S13 | – | – | – |
| – | PG1_GPIO41 | U2TX | – | I2C1SDA | – | – | – | – | EPI0S14 | – | – | – |
| USB0DM | PG2_GPIO42 | – | – | MIICOL | – | – | – | – | EPI0S39(2) | – | – | – |
| – | PG3_GPIO43 | – | – | MIICRS | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PG4_GPIO44 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| USB0DP | PG5_GPIO45 | CCP5 | – | MIITXEN | – | – | – | – | EPI0S40(2) | – | – | – |
| USB0ID | PG6_GPIO46 | – | – | MIITXCK | – | – | – | – | EPI0S41(2) | – | – | – |
| – | PG7_GPIO47 | – | – | MIITXER | – | – | – | – | CCP5 | EPI0S31 | – | – |
| – | PH0_GPIO48 | CCP6 | – | MIIPHYRST | – | – | – | – | EPI0S6 | – | – | – |
| – | PH1_GPIO49 | CCP7 | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S7 | – | – | – |
| – | PH2_GPIO50 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S1 | MIITXD3 | – | – |
| – | PH3_GPIO51 | – | – | – | USB0EPEN | – | – | – | EPI0S0 | MIITXD2 | – | – |
| – | PH4_GPIO52 | – | – | – | USB0PFLT | – | – | – | EPI0S10 | MIITXD1 | – | SSI1CLK |
| – | PH5_GPIO53 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S11 | MIITXD0 | – | SSI1FSS |
| – | PH6_GPIO54 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S26 | MIIRXDV | – | SSI1RX |
| – | PH7_GPIO55 | – | – | MIIRXCK | – | – | – | – | EPI0S27 | – | – | SSI1TX |
| – | PJ0_GPIO56 | – | – | MIIRXER | – | – | – | – | EPI0S16 | – | – | I2C1SCL |
| – | PJ1_GPIO57 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S17 | USB0PFLT | – | I2C1SDA |
| – | PJ2_GPIO58 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S18 | CCP0 | – | – |
| – | PJ3_GPIO59 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S19 | – | CCP6 | – |
| – | PJ4_GPIO60 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S28 | – | CCP4 | – |
| – | PJ5_GPIO61 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S29 | – | CCP2 | – |
| – | PJ6_GPIO62 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | EPI0S30 | – | CCP1 | – |
| – | PJ7_GPIO63 XCLKIN |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | CCP0 | – |
| – | PC0_GPIO64 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PC1_GPIO65 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PC2_GPIO66 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PC3_GPIO67 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| – | PC4_GPIO68 | CCP5 | – | MIITXD3 | – | CCP2 | CCP4 | – | EPI0S2 | CCP1 | – | – |
| – | PC5_GPIO69 | CCP1 | – | – | – | CCP3 | USB0EPEN | – | EPI0S3 | – | – | – |
| – | PC6_GPIO70 | CCP3 | – | – | – | U1RX | CCP0 | USB0PFLT | EPI0S4 | – | – | – |
| – | PC7_GPIO71 | CCP4 | – | – | CCP0 | U1TX | USB0PFLT | – | EPI0S5 | – | – | – |
| ANALOG MODE (USB PINS)(1) |
DEVICE PIN NAME | M3 ALTERNATE MODE 12 |
M3 ALTERNATE MODE 13 |
M3 ALTERNATE MODE 14 |
M3 ALTERNATE MODE 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| – | PA0_GPIO0 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PA1_GPIO1 | – | – | – | SSI1FSS |
| – | PA2_GPIO2 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PA3_GPIO3 | – | – | – | SSI1CLK |
| – | PA4_GPIO4 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PA5_GPIO5 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PA6_GPIO6 | MIITXD3 | – | – | – |
| – | PA7_GPIO7 | MIIRXD1 | – | – | – |
| – | PB0_GPIO8 | – | SSI2TX | CAN1TX | U4TX |
| – | PB1_GPIO9 | – | SSI2RX | – | – |
| – | PB2_GPIO10 | – | SSI2CLK | CAN1RX | U4RX |
| – | PB3_GPIO11 | – | SSI2FSS | U1RX | – |
| – | PB4_GPIO12 | – | – | CAN1TX | SSI1TX |
| – | PB5_GPIO13 | – | – | CAN1RX | SSI1RX |
| – | PB6_GPIO14 | MIICRS | I2C0SDA | U1TX | SSI1CLK |
| – | PB7_GPIO15 | – | I2C0SCL | U1RX | SSI1FSS |
| – | PD0_GPIO16 | MIIRXD2 | SSI0TX | CAN1TX | USB0EPEN |
| – | PD1_GPIO17 | MIICOL | SSI0RX | CAN1RX | USB0PFLT |
| – | PD2_GPIO18 | – | SSI0CLK | U1TX | CAN0RX |
| – | PD3_GPIO19 | – | SSI0FSS | U1RX | CAN0TX |
| – | PD4_GPIO20 | – | – | U3TX | CAN1TX |
| – | PD5_GPIO21 | – | – | U3RX | CAN1RX |
| – | PD6_GPIO22 | – | – | I2C1SDA | U1TX |
| – | PD7_GPIO23 | – | – | I2C1SCL | U1RX |
| – | PE0_GPIO24 | – | SSI3TX | CAN0RX | SSI1TX |
| – | PE1_GPIO25 | – | SSI3RX | CAN0TX | SSI1RX |
| – | PE2_GPIO26 | – | SSI3CLK | U2RX | SSI1CLK |
| – | PE3_GPIO27 | – | SSI3FSS | U2TX | SSI1FSS |
| – | PE4_GPIO28 | – | U0RX | EPI0S38(2) | USB0EPEN |
| – | PE5_GPIO29 | MIITXER | U0TX | – | USB0PFLT |
| – | PE6_GPIO30 | MIIMDIO | CAN0RX | – | – |
| – | PE7_GPIO31 | MIIRXD3 | CAN0TX | – | – |
| – | PF0_GPIO32 | – | I2C0SDA | TRACED2 | – |
| – | PF1_GPIO33 | – | I2C0SCL | TRACED3 | – |
| – | PF2_GPIO34 | – | – | TRACECLK | XCLKOUT |
| – | PF3_GPIO35 | – | U0TX | TRACED0 | – |
| – | PF4_GPIO36 | – | U0RX | – | – |
| – | PF5_GPIO37 | – | – | – | – |
| USB0VBUS | PF6_GPIO38 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PF7_GPIO39 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PG0_GPIO40 | MIIRXD2 | U4RX | – | – |
| – | PG1_GPIO41 | MIIRXD1 | U4TX | – | – |
| USB0DM | PG2_GPIO42 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PG3_GPIO43 | MIIRXDV | – | TRACED1 | – |
| – | PG4_GPIO44 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| USB0DP | PG5_GPIO45 | – | – | – | – |
| USB0ID | PG6_GPIO46 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PG7_GPIO47 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PH0_GPIO48 | – | SSI3TX | – | – |
| – | PH1_GPIO49 | MIIRXD0 | SSI3RX | – | – |
| – | PH2_GPIO50 | – | SSI3CLK | – | – |
| – | PH3_GPIO51 | – | SSI3FSS | – | – |
| – | PH4_GPIO52 | – | U3TX | – | – |
| – | PH5_GPIO53 | – | U3RX | – | – |
| – | PH6_GPIO54 | MIITXEN | SSI0TX | – | – |
| – | PH7_GPIO55 | MIITXCK | SSI0RX | – | – |
| – | PJ0_GPIO56 | – | SSI0CLK | – | – |
| – | PJ1_GPIO57 | MIIRXDV | SSI0FSS | – | – |
| – | PJ2_GPIO58 | MIIRXCK | SSI0CLK | U0TX | – |
| – | PJ3_GPIO59 | MIIMDC | SSI0FSS | U0RX | – |
| – | PJ4_GPIO60 | MIICOL | SSI1CLK | – | – |
| – | PJ5_GPIO61 | MIICRS | SSI1FSS | – | – |
| – | PJ6_GPIO62 | MIIPHYINTR | U2RX | – | – |
| – | PJ7_GPIO63/ XCLKIN |
MIIPHYRST | U2TX | – | – |
| – | PC0_GPIO64 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PC1_GPIO65 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PC2_GPIO66 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PC3_GPIO67 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PC4_GPIO68 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PC5_GPIO69 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PC6_GPIO70 | – | – | – | – |
| – | PC7_GPIO71 | – | – | – | – |
| ANALOG MODE (USB PINS)(1) |
DEVICE PIN NAME | C28x PERIPHERAL MODE 0 |
C28x PERIPHERAL MODE 1 |
C28x PERIPHERAL MODE 2 |
C28x PERIPHERAL MODE 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| – | PA0_GPIO0 | GPIO0 | EPWM1A | – | – |
| – | PA1_GPIO1 | GPIO1 | EPWM1B | ECAP6 | – |
| – | PA2_GPIO2 | GPIO2 | EPWM2A | – | – |
| – | PA3_GPIO3 | GPIO3 | EPWM2B | ECAP5 | – |
| – | PA4_GPIO4 | GPIO4 | EPWM3A | – | – |
| – | PA5_GPIO5 | GPIO5 | EPWM3B | MFSRA | ECAP1 |
| – | PA6_GPIO6 | GPIO6 | EPWM4A | – | EPWMSYNCO |
| – | PA7_GPIO7 | GPIO7 | EPWM4B | MCLKRA | ECAP2 |
| – | PB0_GPIO8 | GPIO8 | EPWM5A | – | ADCSOCAO |
| – | PB1_GPIO9 | GPIO9 | EPWM5B | – | ECAP3 |
| – | PB2_GPIO10 | GPIO10 | EPWM6A | – | ADCSOCBO |
| – | PB3_GPIO11 | GPIO11 | EPWM6B | – | ECAP4 |
| – | PB4_GPIO12 | GPIO12 | EPWM7A | – | – |
| – | PB5_GPIO13 | GPIO13 | EPWM7B | – | – |
| – | PB6_GPIO14 | GPIO14 | EPWM8A | – | – |
| – | PB7_GPIO15 | GPIO15 | EPWM8B | – | – |
| – | PD0_GPIO16 | GPIO16 | SPISIMOA | – | – |
| – | PD1_GPIO17 | GPIO17 | SPISOMIA | – | – |
| – | PD2_GPIO18 | GPIO18 | SPICLKA | – | – |
| – | PD3_GPIO19 | GPIO19 | SPISTEA | – | – |
| – | PD4_GPIO20 | GPIO20 | EQEP1A | MDXA | – |
| – | PD5_GPIO21 | GPIO21 | EQEP1B | MDRA | – |
| – | PD6_GPIO22 | GPIO22 | EQEP1S | MCLKXA | – |
| – | PD7_GPIO23 | GPIO23 | EQEP1I | MFSXA | – |
| – | PE0_GPIO24 | GPIO24 | ECAP1 | EQEP2A | – |
| – | PE1_GPIO25 | GPIO25 | ECAP2 | EQEP2B | – |
| – | PE2_GPIO26 | GPIO26 | ECAP3 | EQEP2I | – |
| – | PE3_GPIO27 | GPIO27 | ECAP4 | EQEP2S | – |
| – | PE4_GPIO28 | GPIO28 | SCIRXDA | – | – |
| – | PE5_GPIO29 | GPIO29 | SCITXDA | – | – |
| – | PE6_GPIO30 | GPIO30 | – | – | EPWM9A |
| – | PE7_GPIO31 | GPIO31 | – | – | EPWM9B |
| – | PF0_GPIO32 | GPIO32 | I2CASDA | SCIRXDA | ADCSOCAO |
| – | PF1_GPIO33 | GPIO33 | I2CASCL | EPWMSYNCO | ADCSOCBO |
| – | PF2_GPIO34 | GPIO34 | ECAP1 | SCIRXDA | XCLKOUT |
| – | PF3_GPIO35 | GPIO35 | SCITXDA | – | – |
| – | PF4_GPIO36 | GPIO36 | SCIRXDA | – | – |
| – | PF5_GPIO37 | GPIO37 | ECAP2 | – | – |
| USB0VBUS | PF6_GPIO38 | GPIO38 | – | – | – |
| – | PF7_GPIO39 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PG0_GPIO40 | GPIO40 | – | – | – |
| – | PG1_GPIO41 | GPIO41 | – | – | – |
| USB0DM | PG2_GPIO42 | GPIO42 | – | – | – |
| – | PG3_GPIO43 | GPIO43 | – | – | – |
| – | PG4_GPIO44 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| USB0DP | PG5_GPIO45 | GPIO45 | – | – | – |
| USB0ID | PG6_GPIO46 | GPIO46 | – | – | – |
| – | PG7_GPIO47 | GPIO47 | – | – | – |
| – | PH0_GPIO48 | GPIO48 | ECAP5 | – | – |
| – | PH1_GPIO49 | GPIO49 | ECAP6 | – | – |
| – | PH2_GPIO50 | GPIO50 | EQEP1A | – | – |
| – | PH3_GPIO51 | GPIO51 | EQEP1B | – | – |
| – | PH4_GPIO52 | GPIO52 | EQEP1S | – | – |
| – | PH5_GPIO53 | GPIO53 | EQEP1I | – | – |
| – | PH6_GPIO54 | GPIO54 | SPISIMOA | – | EQEP3A |
| – | PH7_GPIO55 | GPIO55 | SPISOMIA | – | EQEP3B |
| – | PJ0_GPIO56 | GPIO56 | SPICLKA | – | EQEP3S |
| – | PJ1_GPIO57 | GPIO57 | SPISTEA | – | EQEP3I |
| – | PJ2_GPIO58 | GPIO58 | MCLKRA | – | EPWM7A |
| – | PJ3_GPIO59 | GPIO59 | MFSRA | – | EPWM7B |
| – | PJ4_GPIO60 | GPIO60 | – | – | EPWM8A |
| – | PJ5_GPIO61 | GPIO61 | – | – | EPWM8B |
| – | PJ6_GPIO62 | GPIO62 | – | – | EPWM9A |
| – | PJ7_GPIO63/ XCLKIN |
GPIO63 | – | – | EPWM9B |
| – | PC0_GPIO64 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PC1_GPIO65 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PC2_GPIO66 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PC3_GPIO67 (no pin) |
– | – | – | – |
| – | PC4_GPIO68 | GPIO68 | – | – | – |
| – | PC5_GPIO69 | GPIO69 | – | – | – |
| – | PC6_GPIO70 | GPIO70 | – | – | – |
| – | PC7_GPIO71 | GPIO71 | – | – | – |