SBOS014A September 2000 – January 2024 INA114
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Application and Implementation
- 7 Typical Applications
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- P|8
- DW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
Orderable Information
6.1 Application Information
Figure 6-1 shows the basic connections required for operation of the INA114. Applications with noisy or high-impedance power supplies can require decoupling capacitors close to the device pins as shown.
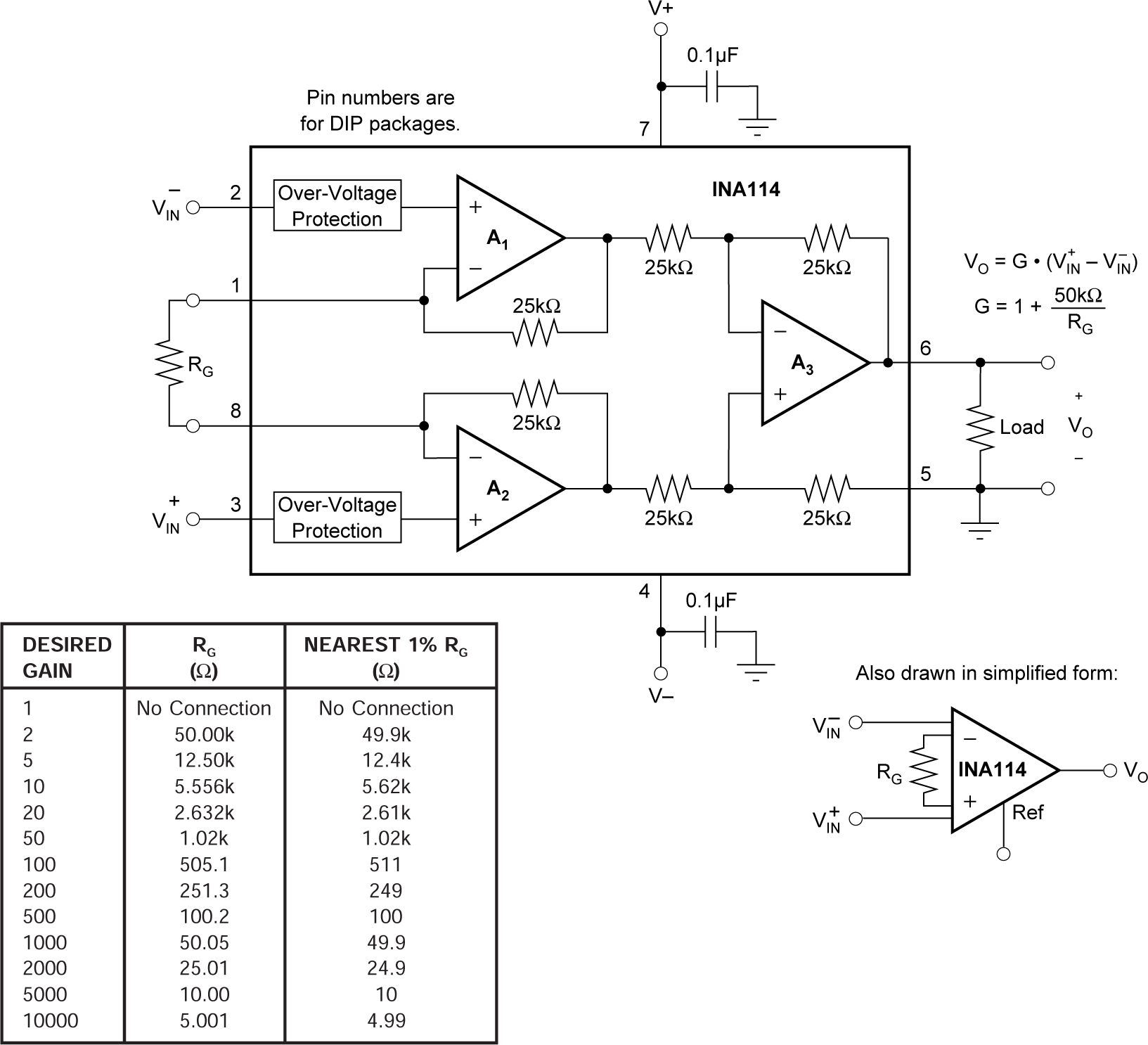 Figure 6-1 Basic Connections.
Figure 6-1 Basic Connections.The output is referred to the output reference (Ref) pin, which is normally grounded. This connection must be low-impedance to provide good common-mode rejection. A resistance of 5Ω in series with the Ref pin causes a typical device to degrade to approximately 80dB CMR (G = 1).