SBOS154B September 2000 – April 2024 INA117
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- P|8
- LMC|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.1.4 Noise Performance
The noise performance of the INA117 is dominated by the internal resistor network. The thermal or Johnson noise of these resistors produces approximately 550nV/√Hz noise. The internal op amp contributes virtually no excess noise at frequencies above 100Hz.
Many applications can be satisfied with less than the full 200kHz bandwidth of the INA117. In these cases, the noise can be reduced with a low-pass filter on the output. The two- pole filter shown in Figure 7-9 limits bandwidth to 1kHz and reduces noise by more than 15:1. Since the INA117 has a 1/f noise corner frequency of approximately 100Hz, a cutoff frequency below 100Hz does not further reduce noise.
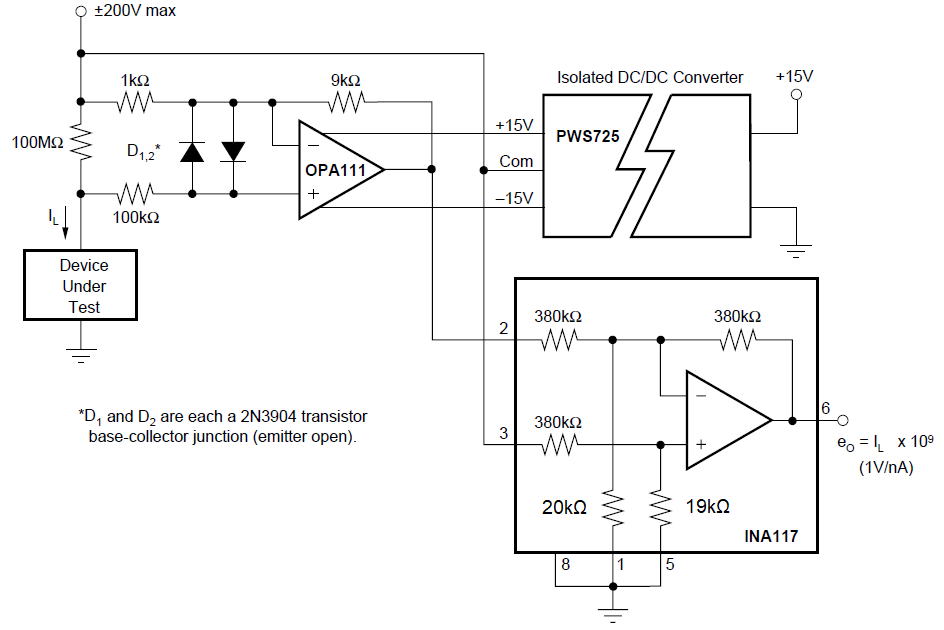 Figure 7-8 Leakage Current Measurement
Circuit
Figure 7-8 Leakage Current Measurement
Circuit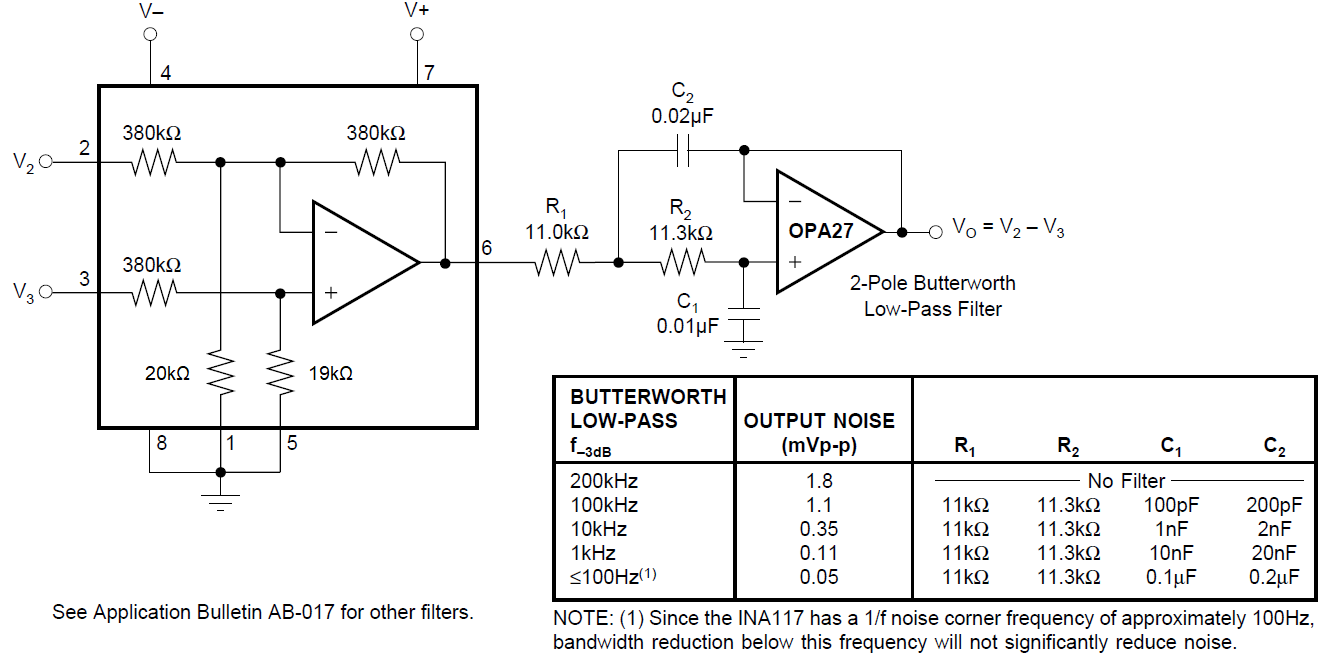 Figure 7-9 Output Filter for Noise
Reduction
Figure 7-9 Output Filter for Noise
Reduction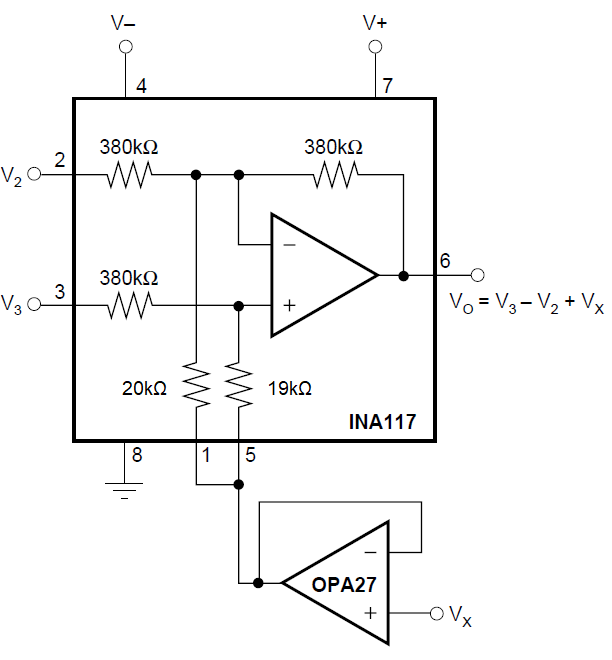 Figure 7-10 Summing VX in
Output
Figure 7-10 Summing VX in
Output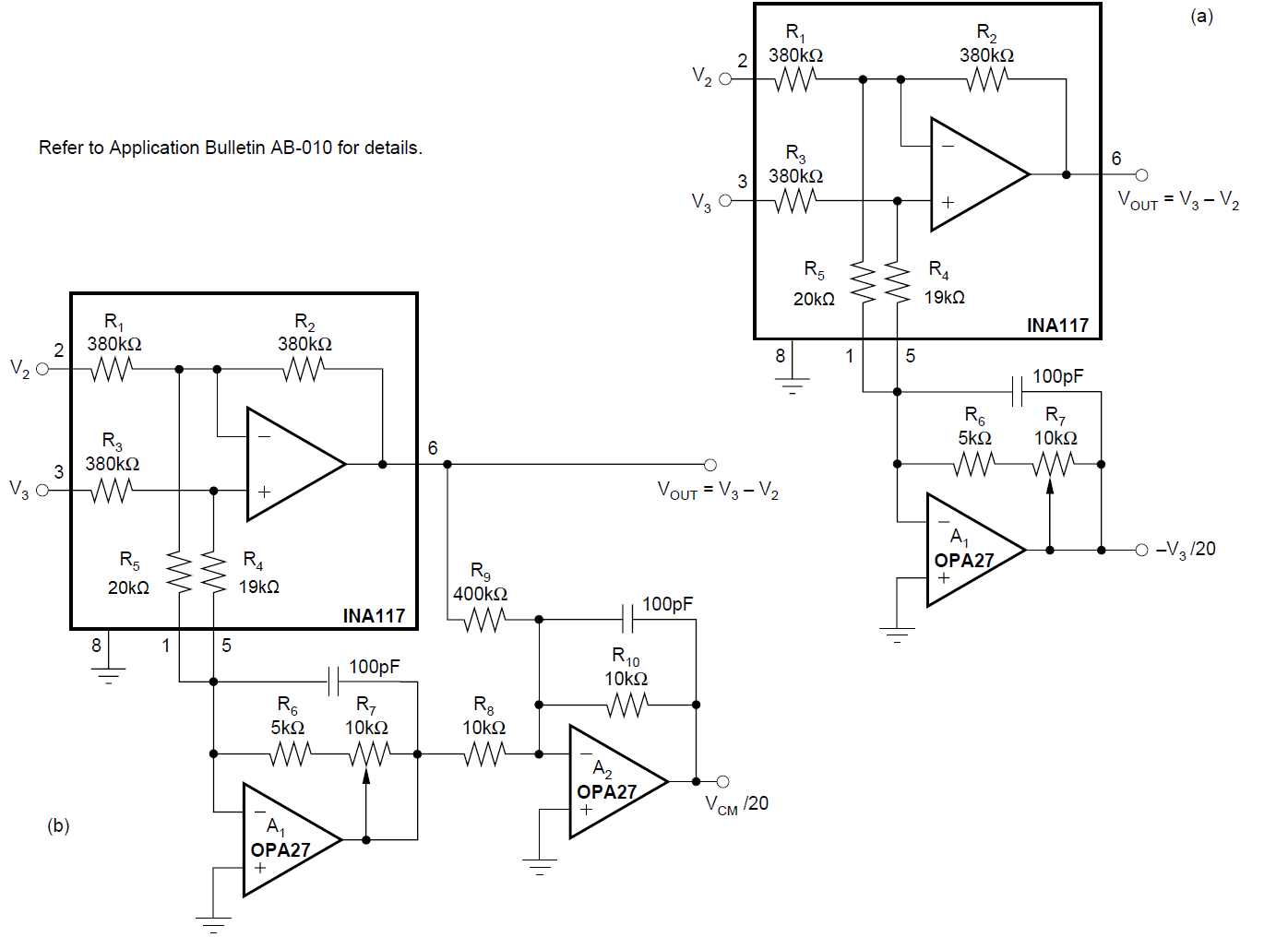 Figure 7-11 Common-mode Voltage
Monitoring
Figure 7-11 Common-mode Voltage
Monitoring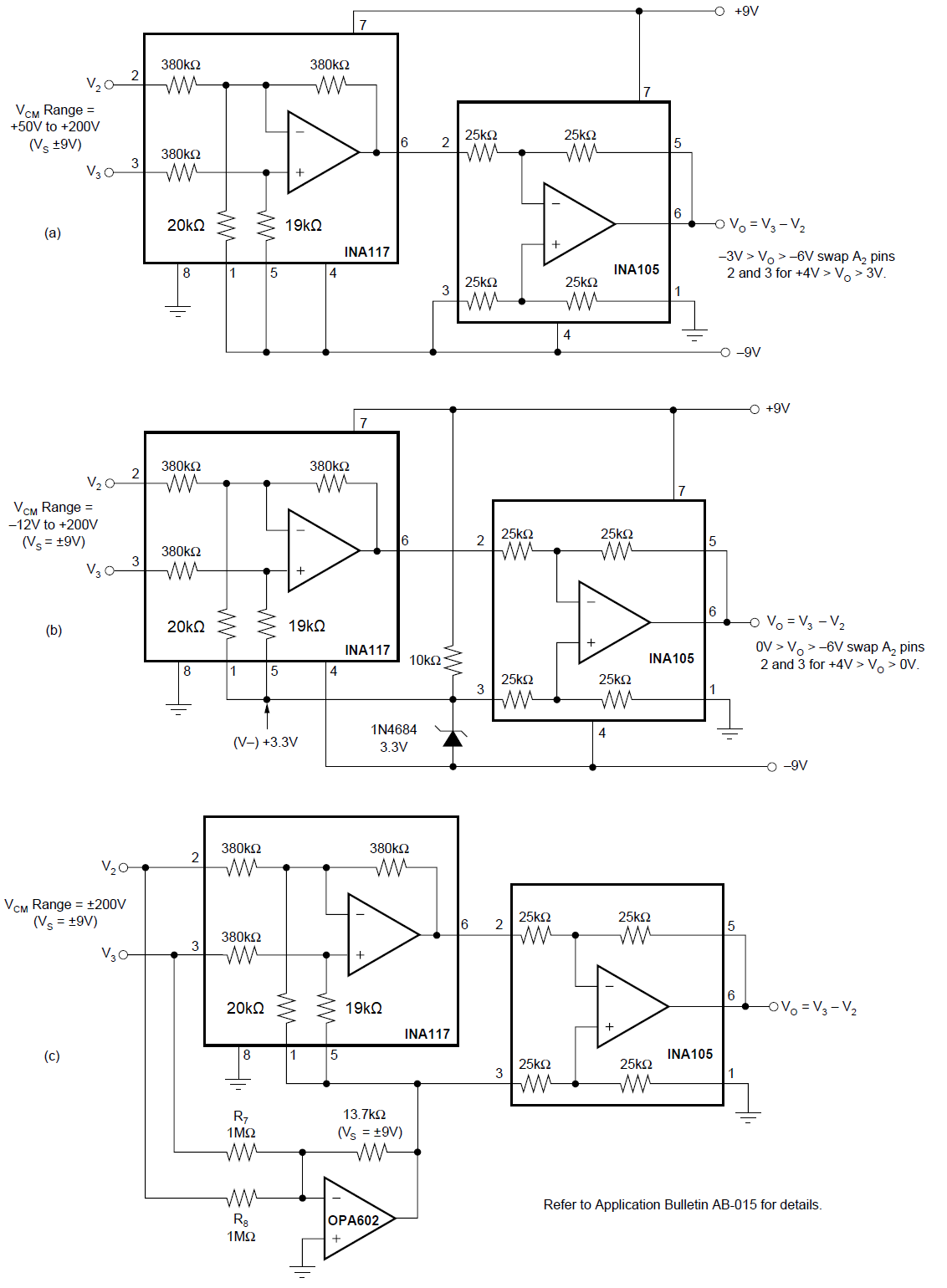 Figure 7-12 Offsetting or Boosting
Common-mode Voltage Range for Reduced Power-supply Voltage Operation
Figure 7-12 Offsetting or Boosting
Common-mode Voltage Range for Reduced Power-supply Voltage Operation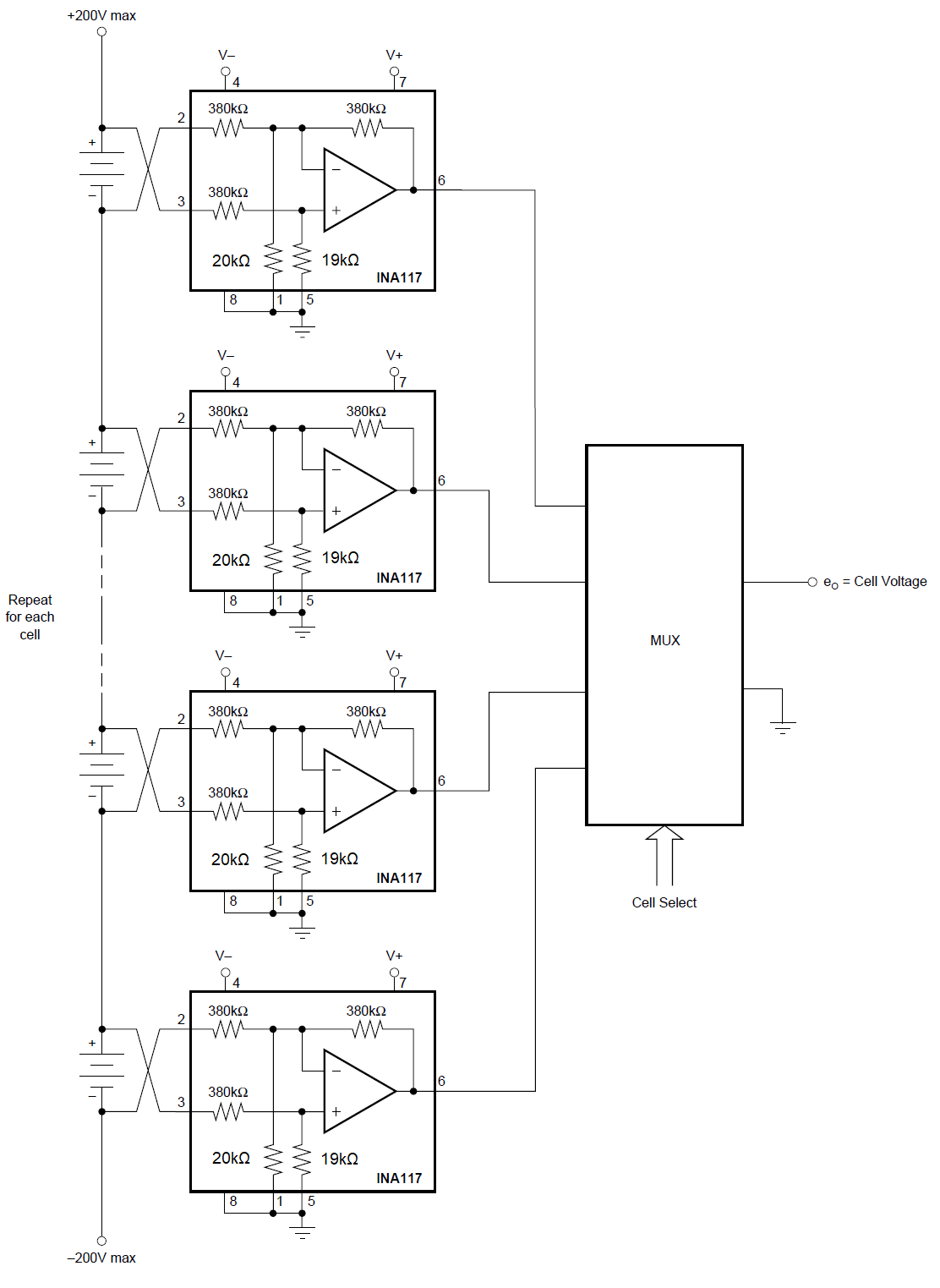 Figure 7-13 Battery Cell Voltage
Monitor
Figure 7-13 Battery Cell Voltage
Monitor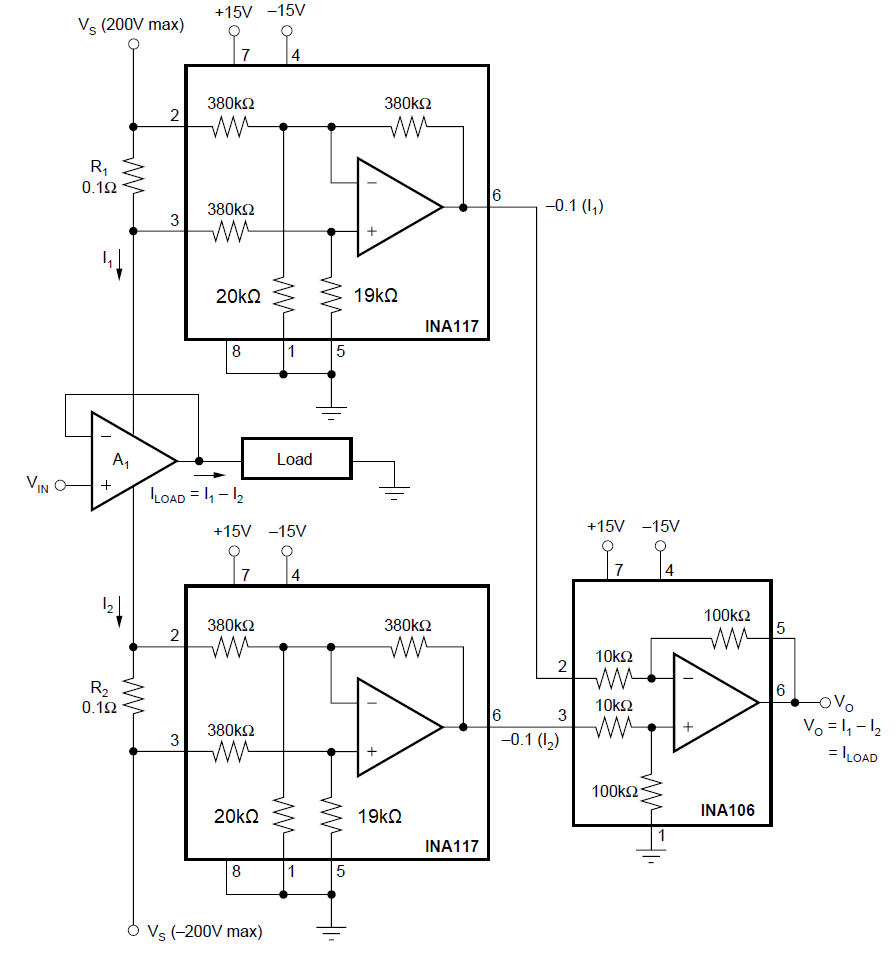 Figure 7-14 Measuring Amplifier Load
Current
Figure 7-14 Measuring Amplifier Load
Current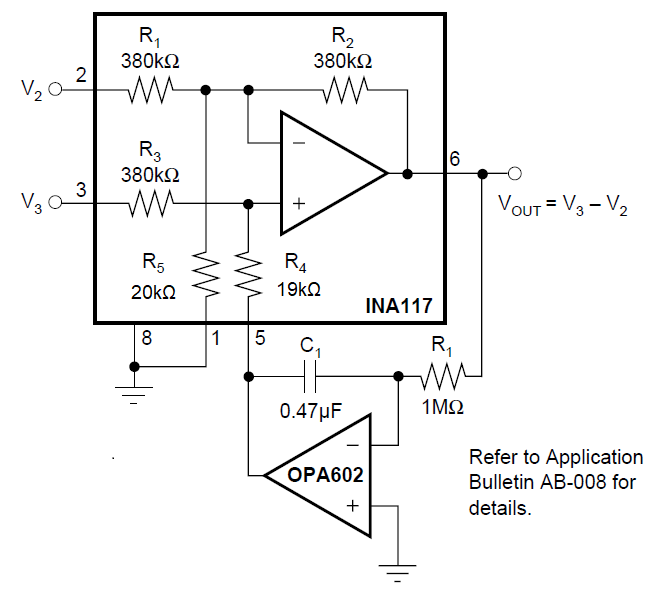 Figure 7-15 AC-coupled INA117
Figure 7-15 AC-coupled INA117