SBOS601A February 2012 – December 2021 INA230
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Related Products
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 Configuration Register (00h, Read/Write)
- 8.6.2 AVG Bit Settings [11:9]
- 8.6.3 VBUS CT Bit Settings [8:6]
- 8.6.4 VSH CT Bit Settings [5:3]
- 8.6.5 Mode Settings [2:0]
- 8.6.6
Data Output Register
- 8.6.6.1 Shunt Voltage Register (01h, Read-Only)
- 8.6.6.2 Bus Voltage Register (02h, Read-Only) (1)
- 8.6.6.3 Power Register (03h, Read-Only)
- 8.6.6.4 Current Register (04h, Read-Only)
- 8.6.6.5 Calibration Register (05h, Read/Write)
- 8.6.6.6 Mask/Enable Register (06h, Read/Write)
- 8.6.6.7 Alert Limit Register (07h, Read/Write)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
- DGS|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Orderable Information
8.5 Programming
An important aspect of the INA230 is that it does not necessarily measure current or power. The INA230 measures both the differential voltage applied between the IN+ and IN– input pins and the voltage applied to the BUS pin. For the INA230 to report both current and power values, both the Current register resolution and the value of the shunt resistor present in the application that resulted in the differential voltage being developed must be programmed. The Power register is internally set to be 25 times the programmed least significant bit of the current register (Current_LSB). Both the Current_LSB and shunt resistor value are used when calculating the Calibration register value. The INA230 uses this value to calculate the corresponding current and power values based on the measured shunt and bus voltages.
The Calibration register is calculated based on Equation 1. This equation includes the term Current_LSB, the programmed value for the LSB for the Current register. This is the value used to convert the value in the Current register to the actual current in amps. The highest resolution for the Current register can be obtained by using the smallest allowable Current_LSB based on the maximum expected current, as shown in Equation 2. While this value yields the highest resolution, it is common to select a value for the Current_LSB to the nearest round number above this value to simplify the conversion of the Current register and Power register to amps and watts respectively. RSHUNT is the value of the external shunt used to develop the differential voltage across the input pins. The 0.00512 value in Equation 1 is an internal fixed value used to ensure scaling is maintained properly.
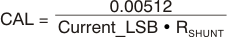

After the Calibration register has been programmed, the Current register and Power register are updated accordingly based on the corresponding shunt voltage and bus voltage measurements. Until the Calibration register is programmed, the Current and Power registers remain at zero.