SBOSA20A February 2021 – May 2022 INA237
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGS|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.2 Power Calculation
The current and power are calculated after a shunt voltage and bus voltage measurement as shown in Figure 7-2. Power is calculated based on the previous current calculation and the latest bus voltage measurement. If the value loaded into the SHUNT_CAL register is zero, the power value reported is also zero. The current and power values are considered intermediate results (unless the averaging is set to 1) and are stored in an internal accumulation register. Following every measured sample, the newly-calculated values for current and power are appended to this accumulation register until all of the samples have been measured and averaged. After all of the samples have been measured and the corresponding current and power calculations have been made, the accumulated average for each of these parameters is then loaded to the corresponding output registers where they can then be read. These calculations are performed in the background and do not add to the overall conversion time.
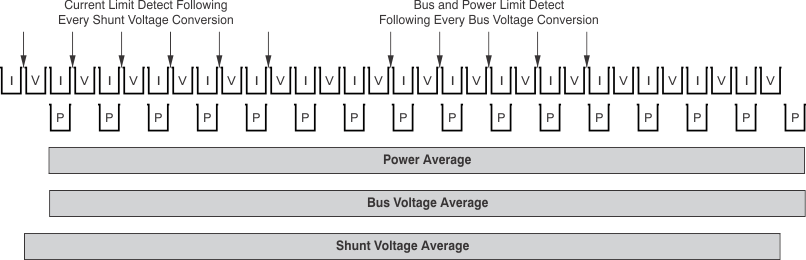 Figure 7-2 Power Calculation
Scheme
Figure 7-2 Power Calculation
Scheme