SBOSA30D March 2022 – December 2024 INA241A , INA241B
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4.1 Adjusting the Output With the Reference Pins
Figure 7-2 shows a test circuit for reference-divider accuracy. The INA241x output is configurable to allow for unidirectional or bidirectional operation.
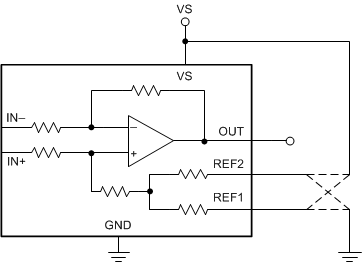 Figure 7-2 Test Circuit For Reference Divider Accuracy
Figure 7-2 Test Circuit For Reference Divider AccuracyThe output voltage is set by applying a voltage or voltages to the reference voltage inputs, REF1 and REF2. The reference inputs are connected to an internal gain network. There is no operational difference between the two reference pins. The resistor network connected to the two reference pins are designed with ultra-precision and matching. Output is set accurately at the mid-point voltage between the voltages applied to reference voltage inputs, when current-sense input voltage is 0V as shown in Equation 1. In most bidirectional applications, one reference input is connected to the positive supply and the other reference input is connected to the negative supply (GND pin) to set the output voltage to mid-supply.