SBOSA30C March 2022 – October 2023 INA241A , INA241B
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.4.3.4 Output Set Using Resistor Divider
The INA241x reference pins allow for the mid-point of the output voltage to be adjusted for system circuitry connections to analog to digital converters (ADCs) or other amplifiers. The reference pins are designed to be connected directly to supply, ground, or a low-impedance reference voltage. The reference pins can be connected together and biased using a resistor divider to achieve a custom output voltage. If the amplifier is used in this configuration, as shown in Figure 8-8, use the output as a differential signal with respect to the resistor divider voltage. Use of the amplifier output as a single-ended signal in this configuration is not recommended because the internal impedance shifts can adversely affect device performance specifications. If single-ended measurement is required, TI recommends to use an external op amp to buffer the resistor divider voltage (see Figure 8-9).
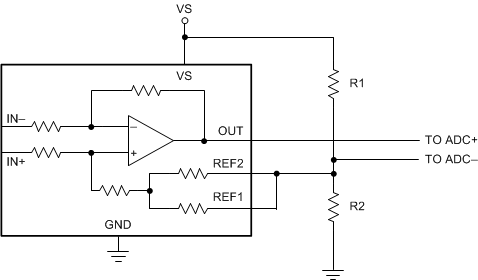 Figure 8-8 Setting the Reference Using a
Resistor Divider
Figure 8-8 Setting the Reference Using a
Resistor Divider Figure 8-9 Setting the Reference Using a
Resistor Divider and an Op Amp buffer
Figure 8-9 Setting the Reference Using a
Resistor Divider and an Op Amp buffer