SBOSAD5D December 2022 – November 2024 INA351
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
7.3.3 EMI Rejection
The INA351 uses integrated electromagnetic interference (EMI) filtering to reduce the effects of EMI from sources such as wireless communications and densely-populated boards with a mix of analog signal chain and digital components. EMI immunity can be improved with circuit design techniques; the INA351 benefits from these design improvements. Texas Instruments has developed the ability to accurately measure and quantify the immunity of an operational amplifier over a broad frequency spectrum extending from 10 MHz to 6 GHz. Figure 7-3 shows the results of this testing on the INA351. Table 7-2 provides the EMIRR IN+ values for the INA351 at particular frequencies commonly encountered in real-world applications. The EMI Rejection Ratio of Operational Amplifiers application report contains detailed information on the topic of EMIRR performance relating to op amps and is available for download from www.ti.com.
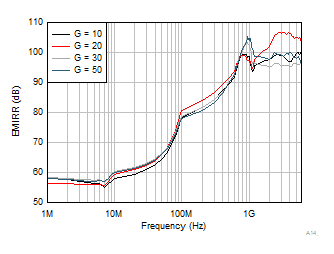 Figure 7-3 EMIRR Testing
Figure 7-3 EMIRR Testing| FREQUENCY | APPLICATION OR ALLOCATION | EMIRR IN+ |
|---|---|---|
| 400 MHz | Mobile radio, mobile satellite, space operation, weather, radar, ultra-high frequency (UHF) applications | 92 dB |
| 900 MHz | Global system for mobile communications (GSM) applications, radio communication, navigation, GPS (to 1.6 GHz), GSM, aeronautical mobile, UHF applications | 96 dB |
| 1.8 GHz | GSM applications, mobile personal communications, broadband, satellite, L-band (1 GHz to 2 GHz) | 100 dB |
| 2.4 GHz | 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, Bluetooth®, mobile personal communications, industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio band, amateur radio and satellite, S-band (2 GHz to 4 GHz) | 108 dB |
| 3.6 GHz | Radiolocation, aero communication and navigation, satellite, mobile, S-band | 106.5 dB |
| 5 GHz | 802.11a, 802.11n, aero communication and navigation, mobile communication, space and satellite operation, C-band (4 GHz to 8 GHz) | 105 dB |