SBOS914F October 2018 – April 2021 INA592
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.3 Input Voltage Range
The INA592 is able to measure input voltages beyond the supply rails. The internal resistors divide down the voltage before the voltage reaches the internal op amp, and provide protection to the op amp inputs. Figure 9-3 shows an example of how the voltage division works in a difference-amplifier configuration. For the INA592 to measure correctly, the input voltages at the input nodes of the internal op amp must stay less than 0.1 V of the positive supply rail, and can exceed the negative supply rail by 0.1 V. See Section 10 for more details.
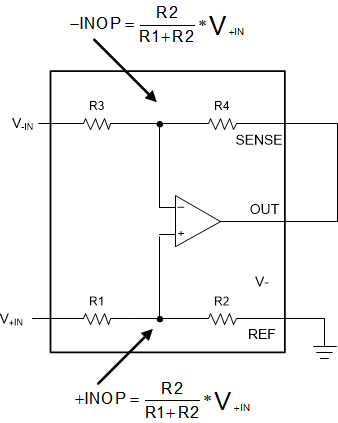 Figure 9-3 Voltage Division in the
Difference Amplifier Configuration
Figure 9-3 Voltage Division in the
Difference Amplifier ConfigurationThe INA592 has integrated ESD diodes at the inputs that provide overvoltage protection. This feature simplifies system design by eliminating the need for additional external protection circuitry, and enables a more robust system. The voltages at any of the inputs of the devices in G = ½ configuration with ±18-V supplies can safely range from +VS − 54 V up to −VS + 54 V. For example, on ±10-V supplies, input voltages can go as high as ±30 V.