SLLSFC2D December 2020 – September 2021 ISO1640 , ISO1641 , ISO1642 , ISO1643 , ISO1644
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Ratings
- 6.6 Insulation Specifications
- 6.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 6.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.10 Supply Current Characteristics
- 6.11 Timing Requirements
- 6.12 I2C Switching Characteristics
- 6.13 GPIO Switching Characteristics
- 6.14 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 6.15 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DW|16
Orderable Information
9.3 Insulation Lifetime
Insulation lifetime projection data is collected by using the industry-standard Time Dependent Dielectric Breakdown (TDDB) test method. In this test, all pins on each side of the barrier are tied together creating a two-terminal device and high voltage is applied between the two sides; see Figure 9-10 for TDDB test setup. The insulation breakdown data is collected at various high voltages switching at 60 Hz over temperature. For basic insulation, VDE standard requires the use of a TDDB projection line with failure rate of less than 1000 part per million (ppm). For reinforced insulation, VDE standard requires the use of a TDDB projection line with failure rate of less than 1 part per million (ppm).
Even though the expected minimum insulation lifetime is 20 years, at the specified working isolation voltage, VDE basic and reinforced certifications require additional safety margin of 20% for working voltage. For basic certification, device lifetime requires a safety margin of 30% translating to a minimum required insulation lifetime of 26 years at a working voltage that is 20% higher than the specified value. For reinforced insulation, device lifetime requires a safety margin of 87.5% translating to a minimum required insulation lifetime of 37.5 years at a working voltage that is 20% higher than the specified value.
Insulation Lifetime Projection Data for ISO164x in 8-D Package and Insulation Lifetime Projection Data for ISO164x in 16-DW Package show the intrinsic capability of the isolation barrier to withstand high voltage stress over its lifetime. Based on the TDDB data, the intrinsic capability of the insulation is 450 VRMS with a lifetime in excess of 100 years in the 8-D package and 1500 VRMS with a lifetime in excess of 135 years in the 16-DW package. Other factors, such as package size, pollution degree, material group, etc. can further limit the working voltage of the component. At the lower working voltages, the corresponding insulation lifetime is much longer than 100 years in the 8-D package and 135 years in the 16-DW package.
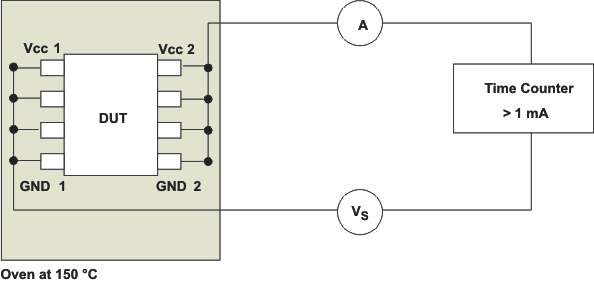 Figure 9-10 Test Setup for Insulation Lifetime Measurement
Figure 9-10 Test Setup for Insulation Lifetime Measurement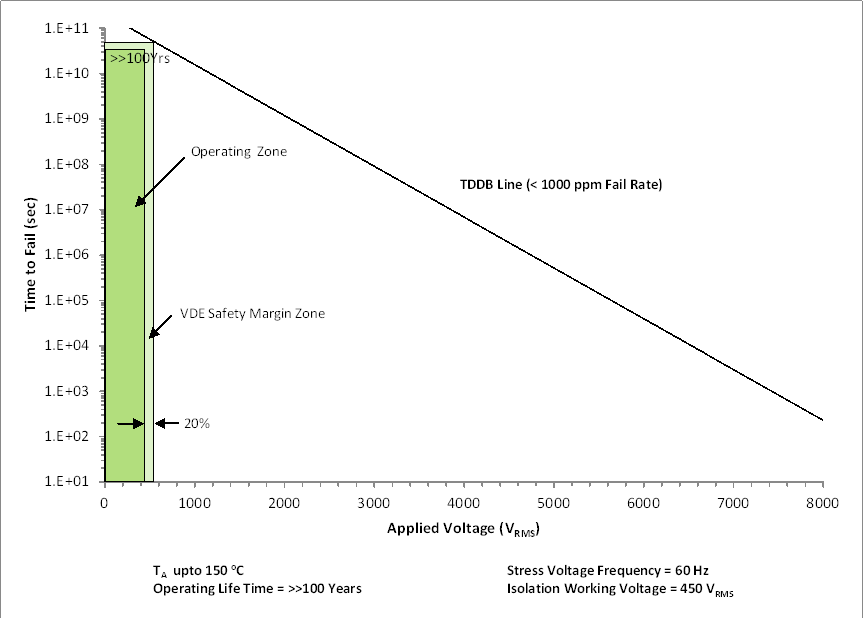 Figure 9-11 Insulation Lifetime Projection Data for ISO164x in 8-D Package
Figure 9-11 Insulation Lifetime Projection Data for ISO164x in 8-D Package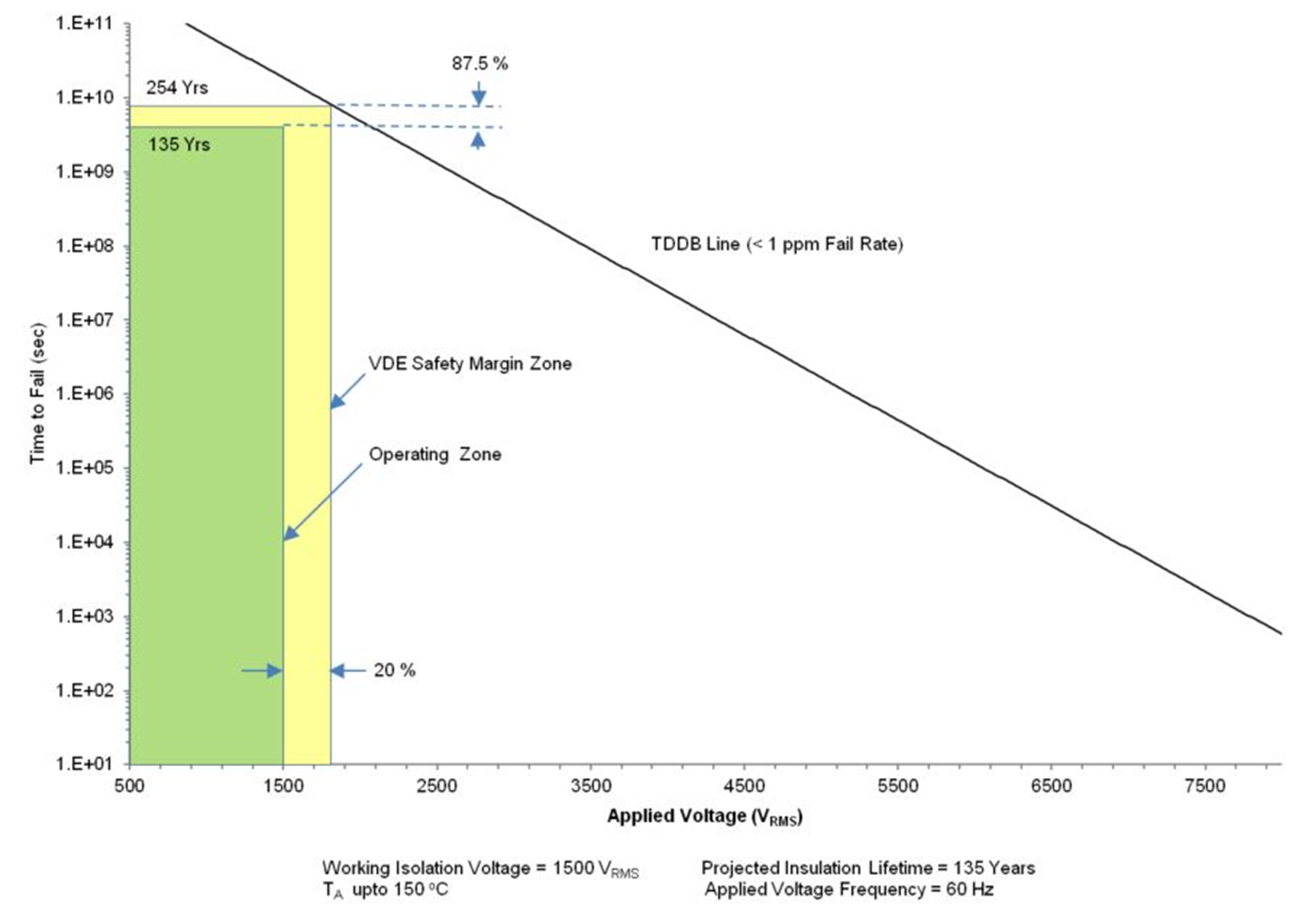 Figure 9-12 Insulation Lifetime Projection Data for ISO164x in 16-DW Package
Figure 9-12 Insulation Lifetime Projection Data for ISO164x in 16-DW Package