SLLSED3C June 2013 – July 2015 ISO7420FCC
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 = 5 V ± 10%
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 = 3.3 V ± 10%
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 = 2.7 V
- 6.8 Power Dissipation Characteristics
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 = 5 V ± 10%
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 = 3.3 V ± 10%
- 6.11 Switching Characteristics: VCC1 and VCC2 = 2.7 V
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
ISO7420FCC utilize single-ended TTL-logic switching technology. Its supply voltage range is from 2.7 V to 5.5 V for both supplies, VCC1 and VCC2. When designing with digital isolators, it is important to keep in mind that due to the single-ended design structure, digital isolators do not conform to any specific interface standard and are only intended for isolating single-ended CMOS or TTL digital signal lines. The isolator is typically placed between the data controller (i.e. μC or UART), and a data converter or a line transceiver, regardless of the interface type or standard.
9.2 Typical Application
ISO7420FCC can be used to isolate power MOSFETs from sensitive logic circuitry in Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) as shown in Figure 18. Low default output of ISO7420FCC is critical for proper operation of power MOSFETs in such applications.
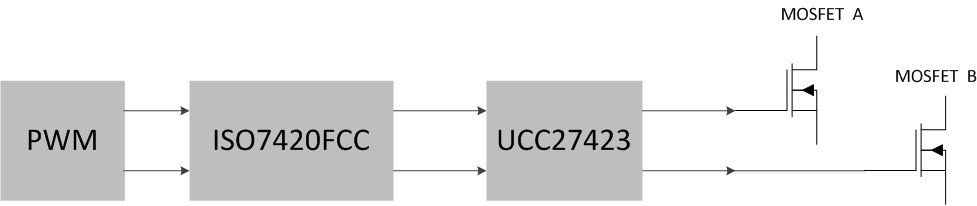 Figure 18. Isolated Switch Mode Power Supply
Figure 18. Isolated Switch Mode Power Supply
9.2.1 Design Requirements
Unlike optocouplers, which require external components to improve performance, provide bias, or limit current, the ISO7420FCC only requires two external bypass capacitors to operate.
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
9.2.2.1 Supply Current Equations
9.2.2.1.1 Maximum Supply Current Equations
(Calculated over recommended operating temperature range and Silicon process variation).
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 5 V ±10%:
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 3.3 V ± 10%:
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 2.7 V:
f is data rate of each channel measured in Mbps; CL is the capacitive load of each channel measured in pF; ICC1(maximum) and ICC2(max) are measured in mA.
9.2.2.1.2 Typical Supply Current Equations
(Calculated for TA = 25°C and nominal Silicon process material).
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 5 V:
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 3.3 V:
At VCC1 = VCC2 = 2.7 V:
f is Data Rate of each channel measured in Mbps; CL is the Capacitive Load of each channel measured in pF; ICC1(typ) and ICC2(typ) are measured in mA.
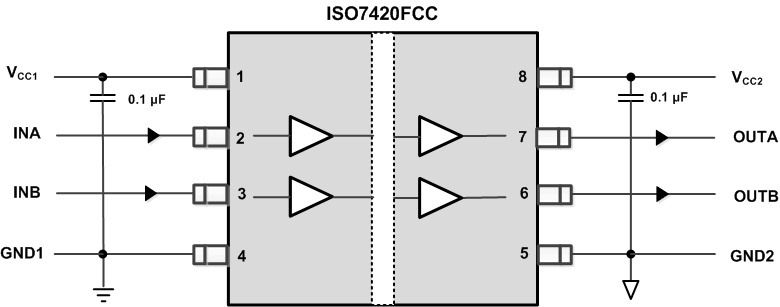 Figure 19. ISO7420FCC Typical Circuit Hook-Up
Figure 19. ISO7420FCC Typical Circuit Hook-Up
9.2.3 Application Curves
Figure 20 shows the INA input on Channel 1 and OUTA output on Channel 2 of an oscilloscope.
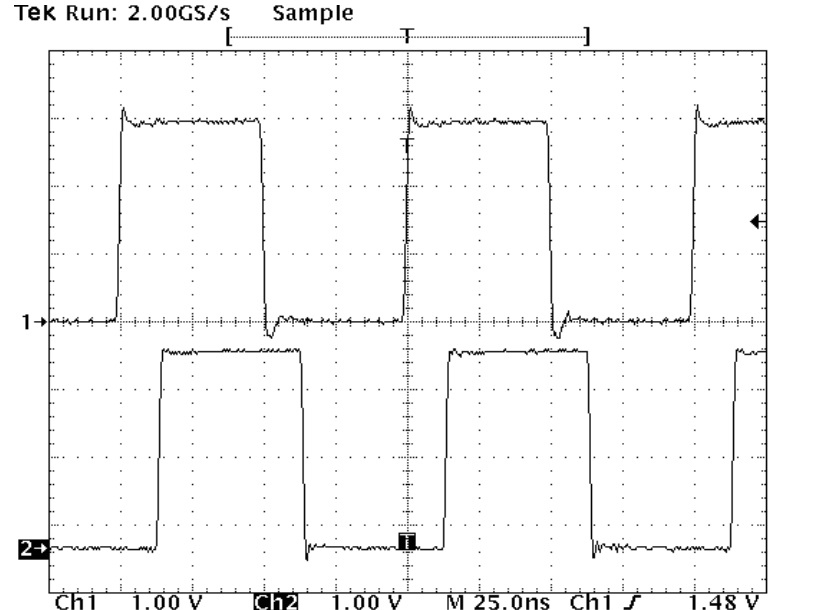 Figure 20. Typical Input and Output Waveforms
Figure 20. Typical Input and Output Waveforms