SNOSBH0D May 2000 – November 2015 LF156 , LF256 , LF356
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 AC Electrical Characteristics, TA = TJ = 25°C, VS = ±15 V
- 6.6 DC Electrical Characteristics, TA = TJ = 25°C, VS = ±15 V
- 6.7 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 Power Dissipation Ratings
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | LF155x, LF256x, LF356B | ±22 | V | |||
| LF35x | ±18 | |||||
| Differential input voltage | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | ±40 | V | |||
| LF35x | ±30 | |||||
| Input voltage(2) | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | ±20 | V | |||
| LF35x | ±16 | |||||
| Output short circuit duration | Continuous | — | ||||
| TJMAX | LMC package | LF15x | 150 | °C | ||
| LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 115 | |||||
| P package | LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 100 | ||||
| D package | LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 100 | ||||
| Soldering information (lead temp.) |
TO-99 package | Soldering (10 sec.) | 300 | °C | ||
| PDIP package | Soldering (10 sec.) | 260 | ||||
| SOIC package | Vapor phase (60 sec.) | LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 215 | |||
| Infrared (15 sec.) | LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 220 | ||||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | −65 | 150 | °C | |||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, contact the TI Sales Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1)(2) | ±1000 | V |
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) 100 pF discharged through 1.5-kΩ resistor
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VS | LF15x | ±15 | VS | ±20 | V |
| LF25x | ±15 | VS | ±20 | ||
| LF356B | ±15 | VS | ±20 | ||
| LF35x | ±15 | ||||
| TA | LF15x | –55 | TA | 125 | °C |
| LF25x | –25 | TA | 85 | ||
| LF356B | 0 | TA | 70 | ||
| LF35x | 0 | TA | 70 | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LF155, LF156, LF355, LF357 | LF356 | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (PDIP) | D (SOIC) | LMC (TO-99) | P (PDIP) | ||||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | ||||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 130 | 195 | — | 55.2 | °C/W | |
| Still Air | — | — | 160 | — | |||
| 400 LF/Min Air Flow | — | — | 65 | — | |||
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | — | — | 23 | 44.5 | °C/W | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | — | — | — | 32.4 | °C/W | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | — | — | — | 21.7 | °C/W | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | — | — | — | 32.3 | °C/W | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 AC Electrical Characteristics, TA = TJ = 25°C, VS = ±15 V
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | Slew Rate | LF15x: AV = 1 | LFx55 | 5 | V/μs | |||
| LFx56, LF356B | 7.5 | |||||||
| LFx56, LF356B | 12 | |||||||
| LF357: AV = 5 | LFx57 | 50 | ||||||
| GBW | Gain Bandwidth Product | LFx55 | 2.5 | MHz | ||||
| LFx56, LF356B | 5 | |||||||
| LFx57 | 20 | |||||||
| ts | Settling Time to 0.01%(1) | LFx55 | 4 | μs | ||||
| LFx56, LF356B | 1.5 | |||||||
| LFx57 | 1.5 | |||||||
| en | Equivalent Input Noise Voltage | RS = 100 Ω | f = 100 Hz | LFx55 | 25 | nV/√Hz | ||
| LFx56, LF356B | 15 | |||||||
| LFx57 | 15 | |||||||
| f = 1000 Hz | LFx55 | 20 | nV/√Hz | |||||
| LFx56, LF356B | 12 | |||||||
| LFx57 | 12 | |||||||
| in | Equivalent Input Current Noise | f = 100 Hz | LFx55 | 0.01 | pA/√Hz | |||
| LFx56, LF356B | ||||||||
| LFx57 | ||||||||
| f = 1000 Hz | LFx55 | 0.01 | pA/√Hz | |||||
| LFx56, LF356B | ||||||||
| LFx57 | ||||||||
| CIN | Input Capacitance | LFx55 | 3 | pF | ||||
| LFx56, LF356B | ||||||||
| LFx57 | ||||||||
(1) Settling time is defined here, for a unity gain inverter connection using 2-kΩ resistors for the LF15x. It is the time required for the error voltage (the voltage at the inverting input pin on the amplifier) to settle to within 0.01% of its final value from the time a 10-V step input is applied to the inverter. For the LF357, AV = −5, the feedback resistor from output to input is 2 kΩ and the output step is 10 V (See Settling Time Test Circuit).
6.6 DC Electrical Characteristics, TA = TJ = 25°C, VS = ±15 V
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply current | LF155 | 2 | 4 | mA | |
| LF355 | 2 | 4 | |||
| LFx56, LF356B | 5 | 7 | |||
| LF356 | 5 | 10 | |||
| LF357 | 5 | 10 |
6.7 DC Electrical Characteristics
See (1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOS | Input offset voltage | RS = 50 Ω | TA = 25°C | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | 3 | 5 | mV | |
| LF35x | 3 | 10 | ||||||
| Over temperature | LF15x | 7 | ||||||
| LF25x, LF356B | 6.5 | |||||||
| LF35x | 13 | |||||||
| ΔVOS/ΔT | Average TC of input offset voltage |
RS = 50 Ω | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 5 | μV/°C | |||
| ΔTC/ΔVOS | Change in average TC with VOS adjust | RS = 50 Ω(3) | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 0.5 | μV/°C per mV |
|||
| IOS | Input offset current | TJ = 25°C(1) (4) | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | 3 | 20 | pA | ||
| LF35x | 3 | 50 | ||||||
| TJ ≤ THIGH | LF15x | 20 | nA | |||||
| LF25x, LF356B | 1 | |||||||
| LF35x | 2 | |||||||
| IB | Input bias current | TJ = 25°C(1) (4) | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | 30 | 100 | pA | ||
| LF35x | 30 | 200 | ||||||
| TJ ≤ THIGH | LF15x | 50 | nA | |||||
| LF25x, LF356B | 5 | |||||||
| LF35x | 8 | |||||||
| RIN | Input resistance | TJ = 25°C | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 1012 | Ω | |||
| AVOL | Large signal voltage gain | VS = ±15 V, VO = ±10 V, RL = 2 kΩ |
TA = 25°C | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | 50 | 200 | V/mV | |
| LF35x | 25 | 200 | ||||||
| Over temperature | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | 25 | ||||||
| LF35x | 15 | |||||||
| VO | Output voltage swing | VS = ±15 V, RL = 10 kΩ | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | ±12 | ±13 | V | ||
| VS = ±15 V, RL= 2 kΩ | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | ±10 | ±12 | |||||
| VCM | Input common-mode voltage range |
VS = ±15 V | VCM, High | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | 11 | 15.1 | V | |
| LF35x | 10 | 15.1 | ||||||
| VCM, Low | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | −12 | –11 | |||||
| LF35x | −12 | –10 | ||||||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | 85 | 100 | dB | |||
| LF35x | 80 | 100 | ||||||
| PSRR | Supply voltage rejection ratio(5) | LF15x, LF25x, LF356B | 85 | 100 | dB | |||
| LF35x | 80 | 100 | ||||||
(1) Unless otherwise stated, these test conditions apply:
and VOS, IB and IOS are measured at VCM = 0.
| LF15x | LF25x | LF356B | LF35x | |
| Supply Voltage, VS | ±15 V ≤ VS ≤ ±20 V | ±15 V ≤ VS ≤ ±20 V | ±15 V ≤ VS ≤ ±20 V | VS = ±15 V |
| TA | −55°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C | −25°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C | 0°C ≤ TA ≤ +70°C | 0°C ≤ TA ≤ +70°C |
| THIGH | +125°C | +85°C | +70°C | +70°C |
(2) Unless otherwise specified the absolute maximum negative input voltage is equal to the negative power supply voltage.
(3) The Temperature Coefficient of the adjusted input offset voltage changes only a small amount (0.5 μV/°C typically) for each mV of adjustment from its original unadjusted value. Common-mode rejection and open-loop voltage gain are also unaffected by offset adjustment.
(4) The input bias currents are junction leakage currents which approximately double for every 10°C increase in the junction temperature, TJ. Due to limited production test time, the input bias currents measured are correlated to junction temperature. In normal operation the junction temperature rises above the ambient temperature as a result of internal power dissipation, Pd. TJ = TA + θJA Pd where θJA is the thermal resistance from junction to ambient. Use of a heat sink is recommended if input bias current is to be kept to a minimum.
(5) Supply Voltage Rejection is measured for both supply magnitudes increasing or decreasing simultaneously, in accordance with common practice.
6.8 Power Dissipation Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Dissipation at TA = 25°C (1) (2) |
LMC Package (Still Air) | LF15x | 560 | mW | |
| LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 400 | ||||
| LMC Package (400 LF/Min Air Flow) |
LF15x | 1200 | |||
| LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 1000 | ||||
| P Package | LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 670 | |||
| D Package | LF25x, LF356B, LF35x | 380 | |||
(1) The maximum power dissipation for these devices must be derated at elevated temperatures and is dictated by TJMAX, θJA, and the ambient temperature, TA. The maximum available power dissipation at any temperature is PD = (TJMAX − TA) / θJA or the 25°C PdMAX, whichever is less.
(2) Maximum power dissipation is defined by the package characteristics. Operating the part near the maximum power dissipation may cause the part to operate outside specified limits.
6.9 Typical Characteristics
6.9.1 Typical DC Performance Characteristics
Curves are for LF155 and LF156 unless otherwise specified.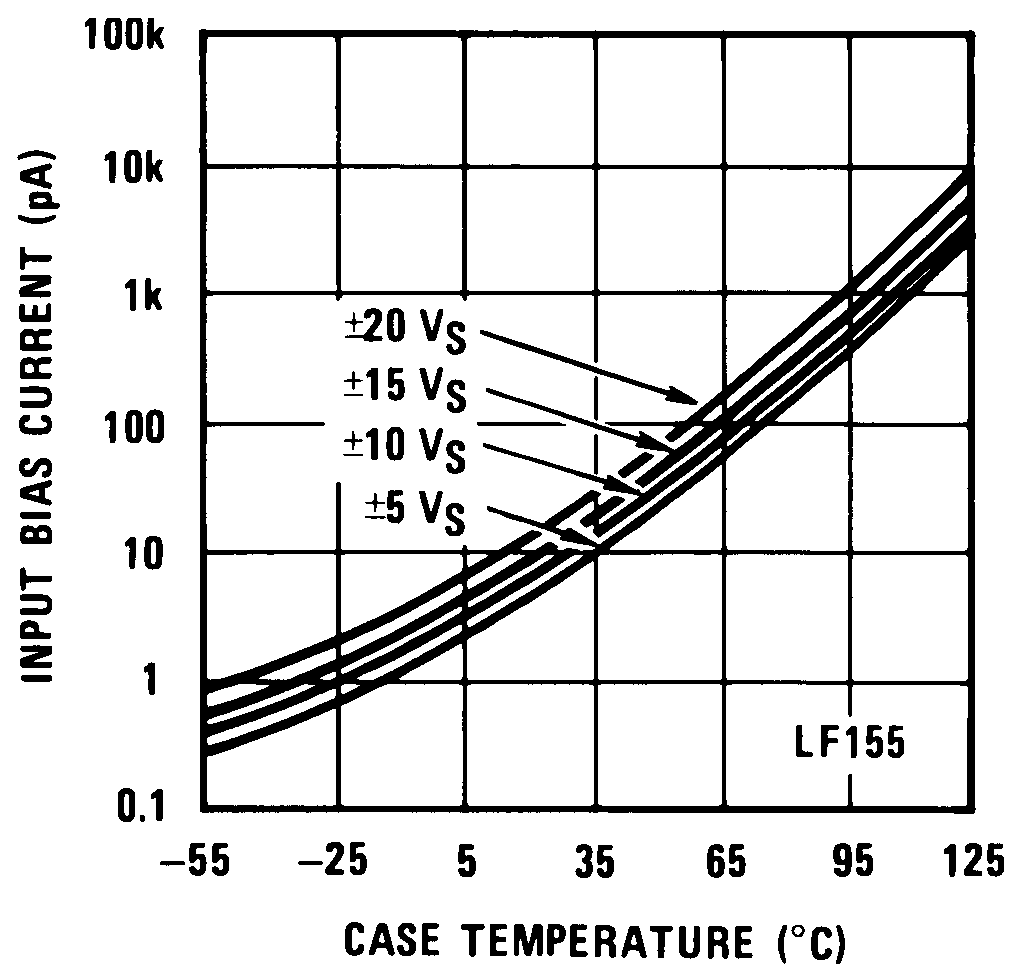 Figure 1. Input Bias Current
Figure 1. Input Bias Current
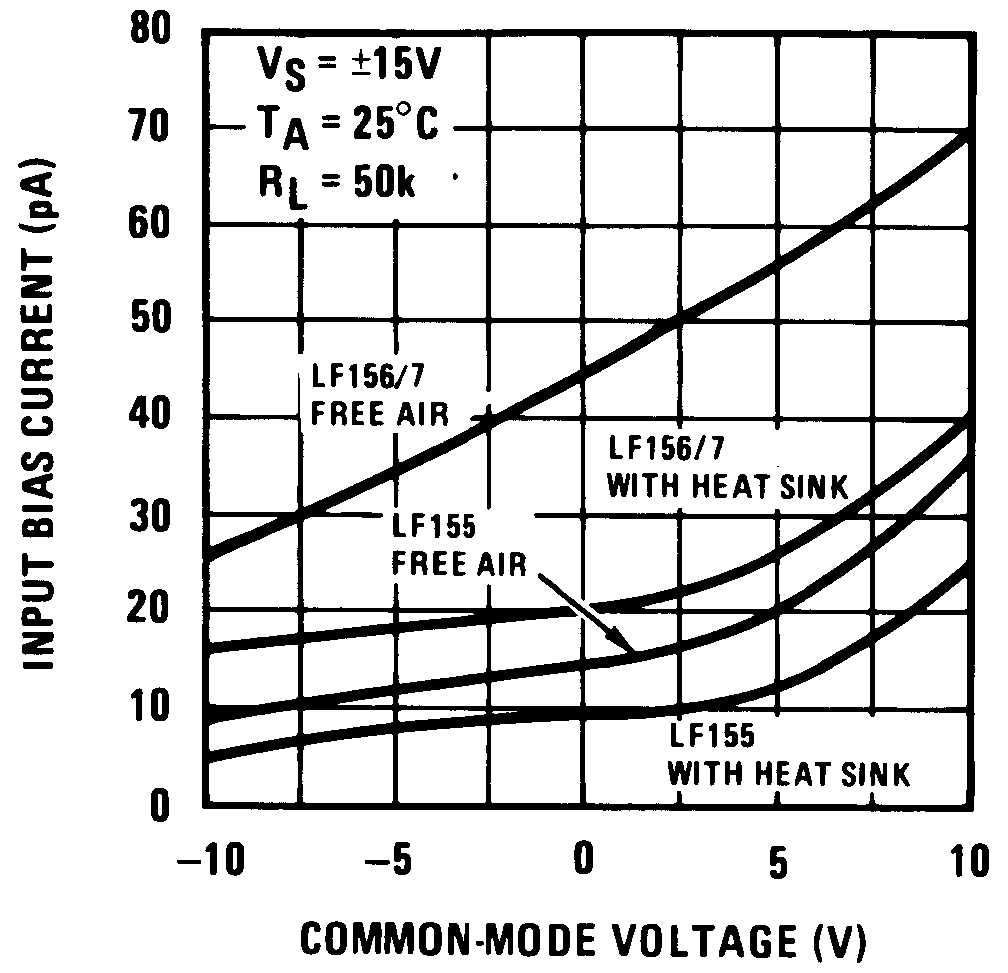 Figure 3. Input Bias Current
Figure 3. Input Bias Current
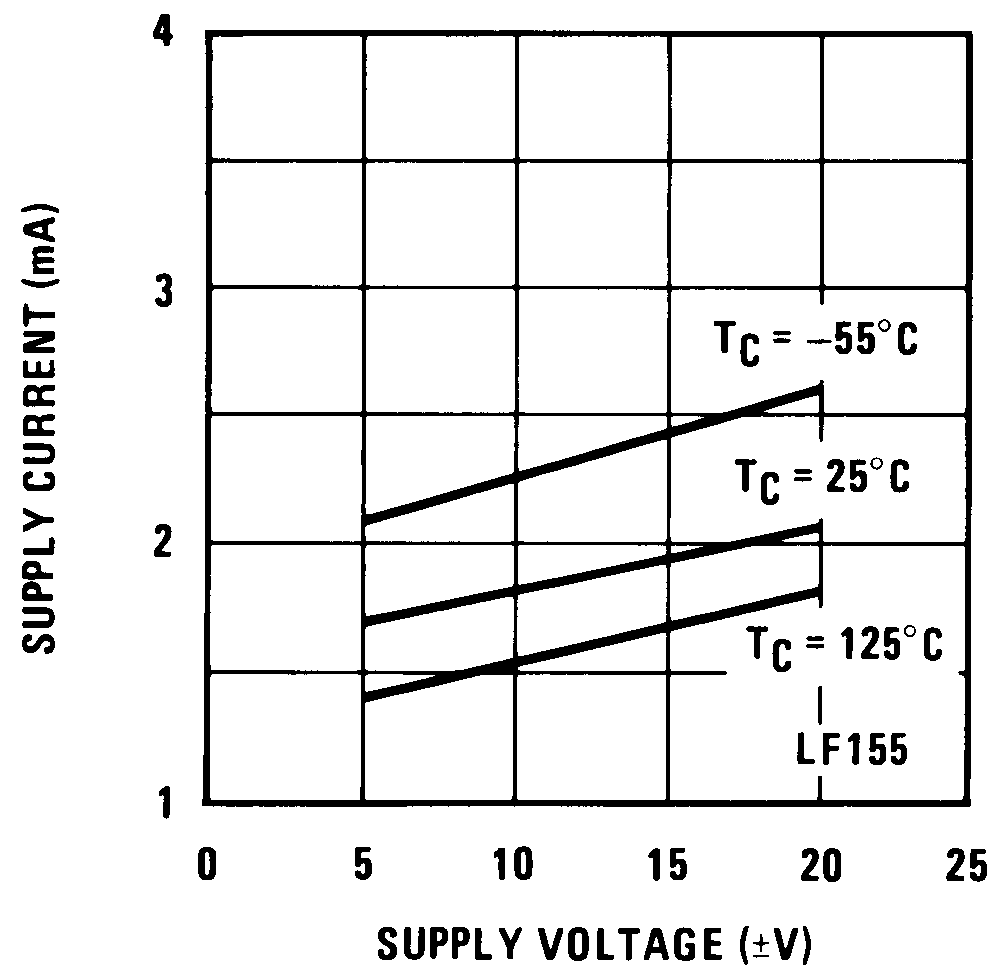 Figure 5. Supply Current
Figure 5. Supply Current
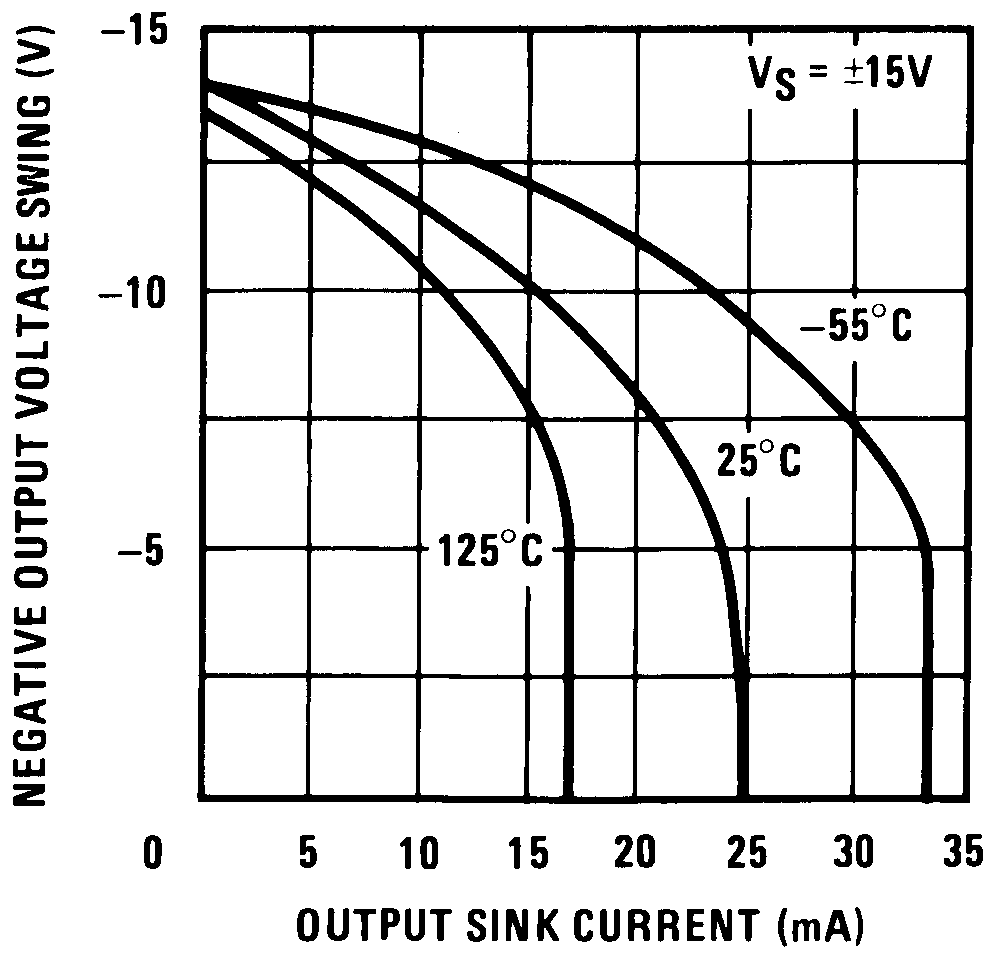 Figure 7. Negative Current Limit
Figure 7. Negative Current Limit
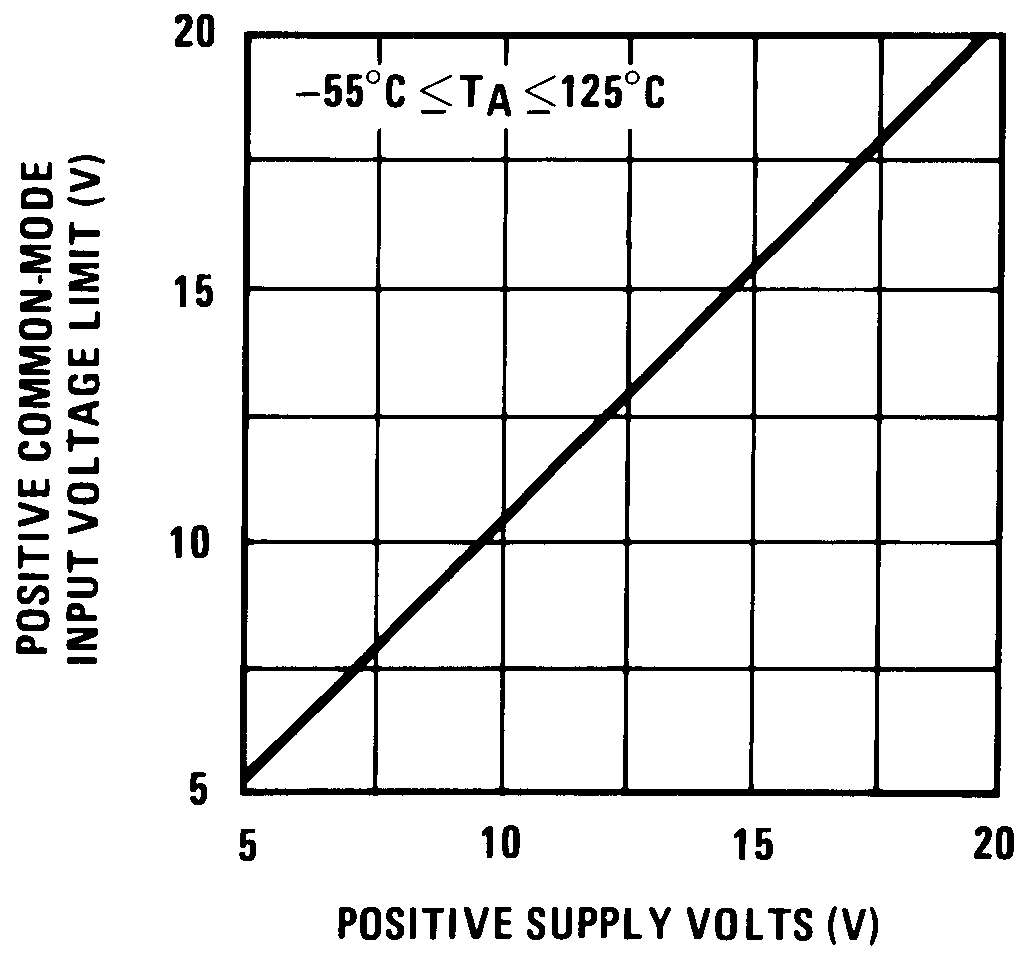 Figure 9. Positive Common-Mode Input Voltage Limit
Figure 9. Positive Common-Mode Input Voltage Limit
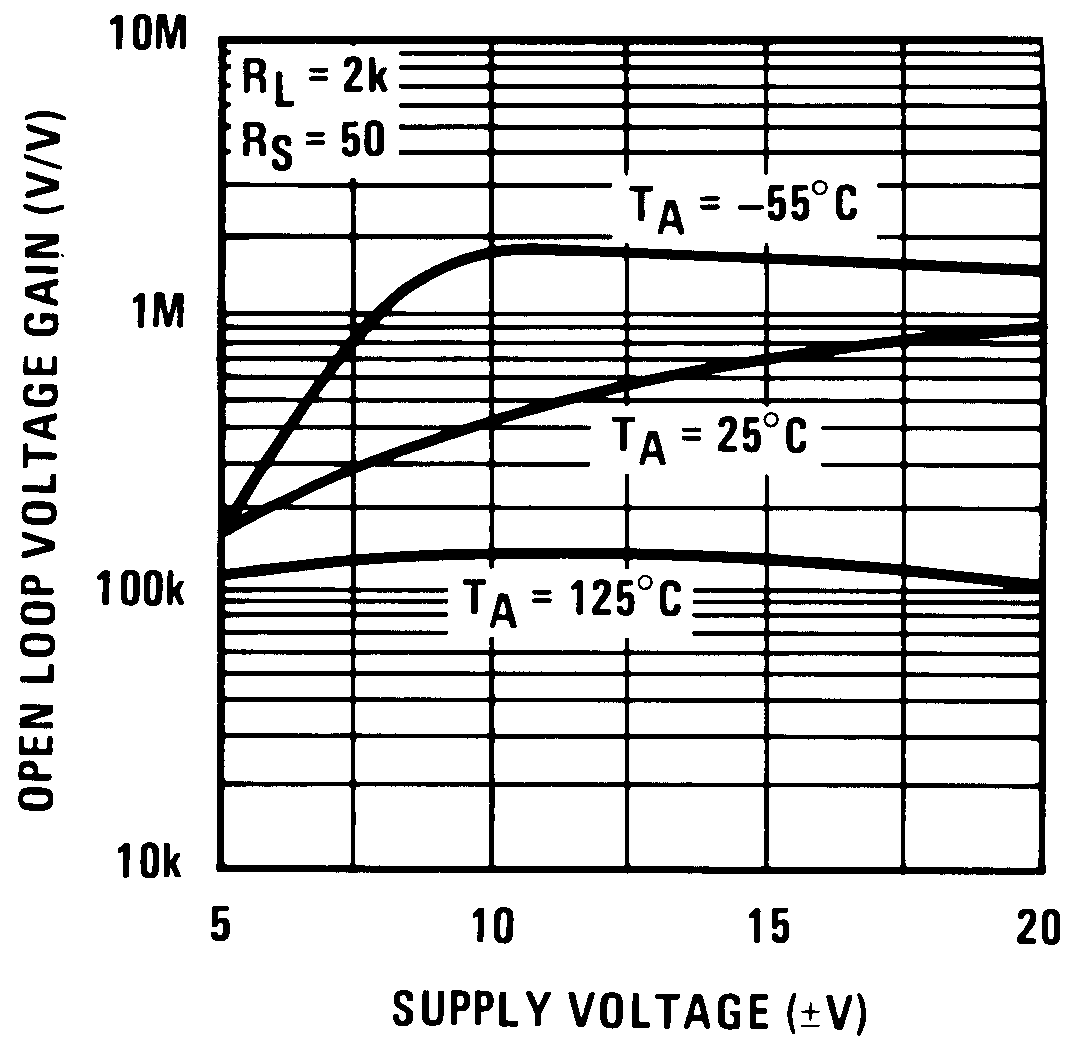 Figure 11. Open-Loop Voltage Gain
Figure 11. Open-Loop Voltage Gain
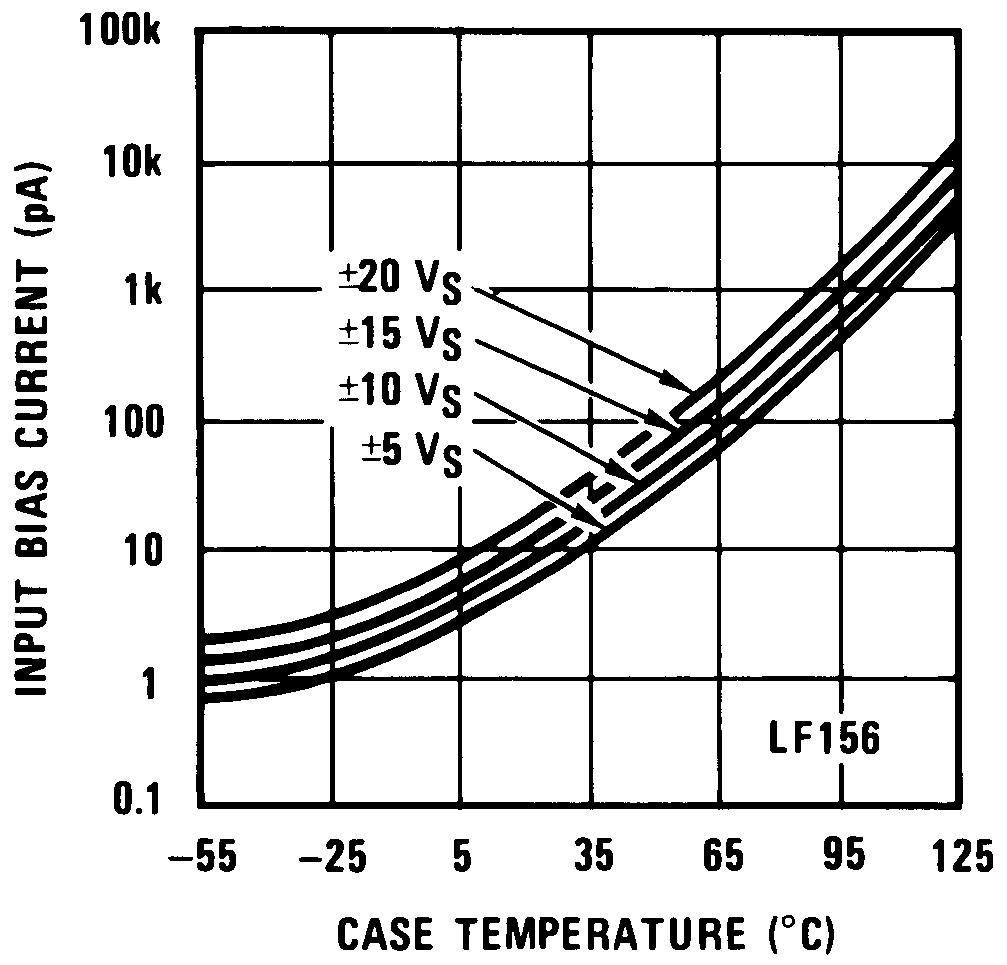 Figure 2. Input Bias Current
Figure 2. Input Bias Current
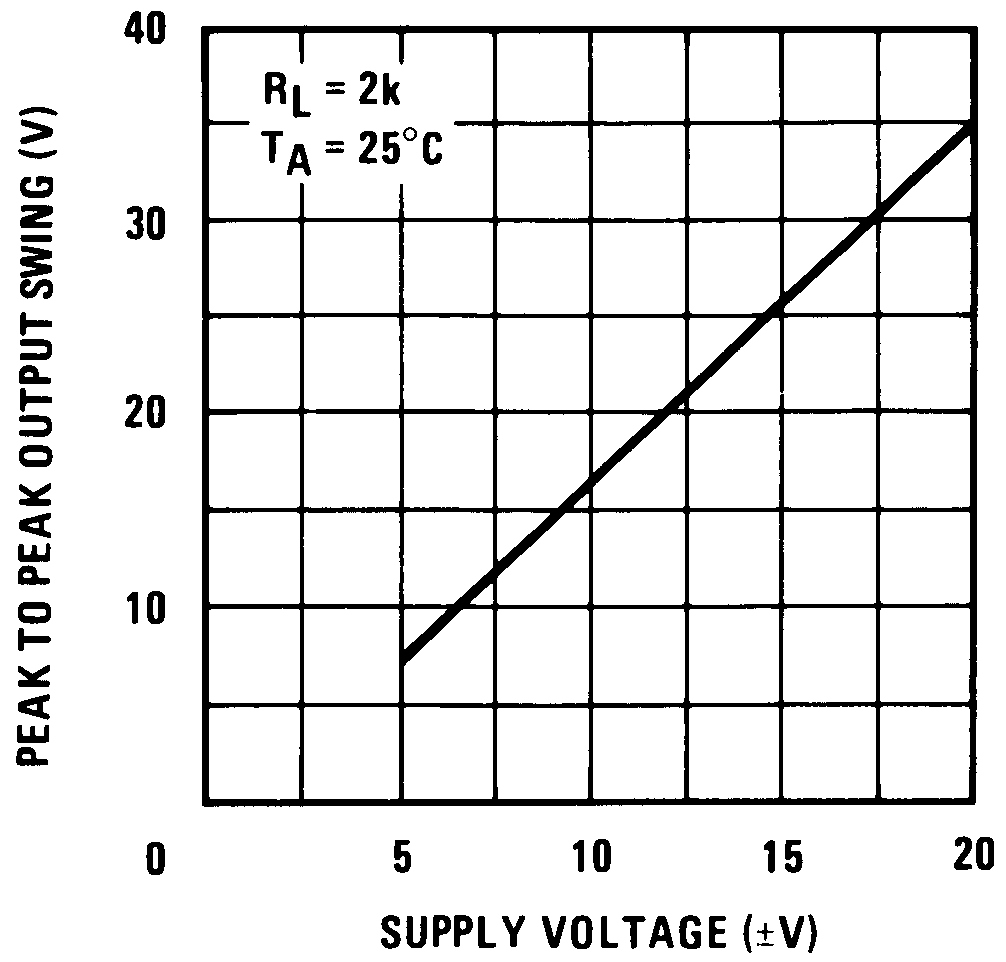 Figure 4. Voltage Swing
Figure 4. Voltage Swing
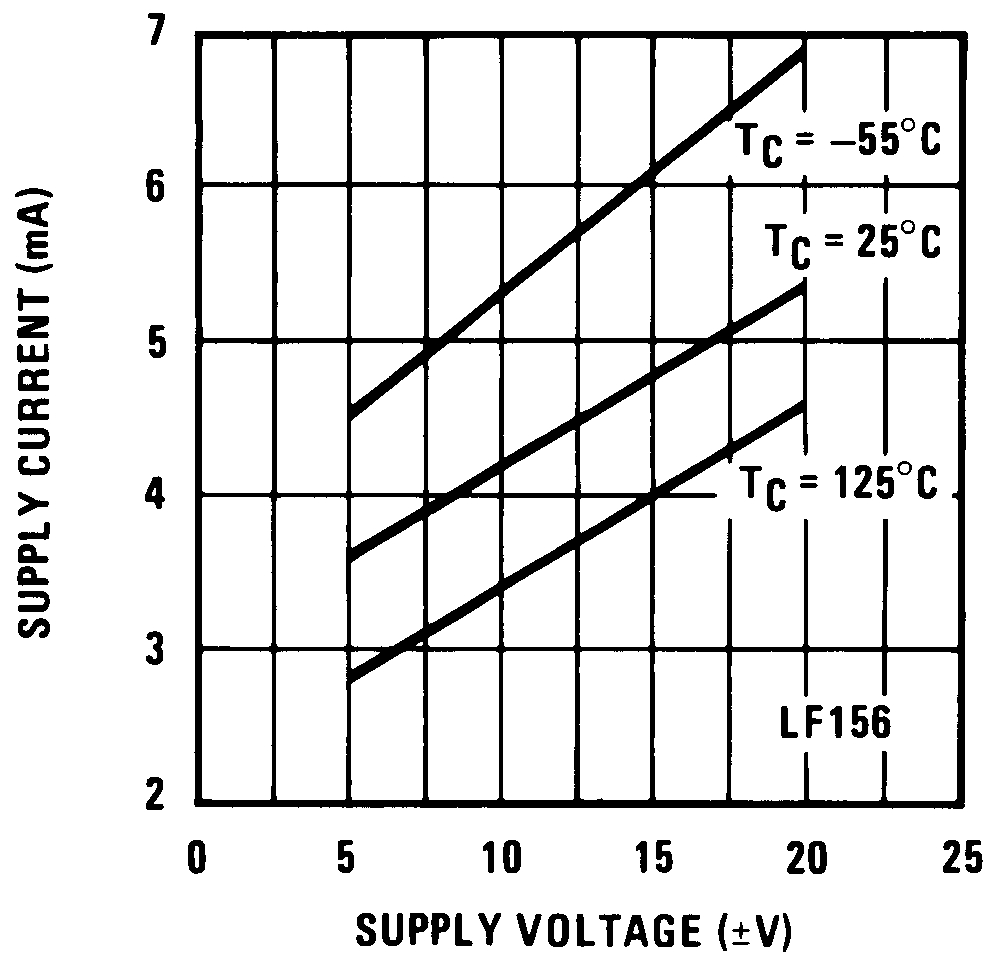 Figure 6. Supply Current
Figure 6. Supply Current
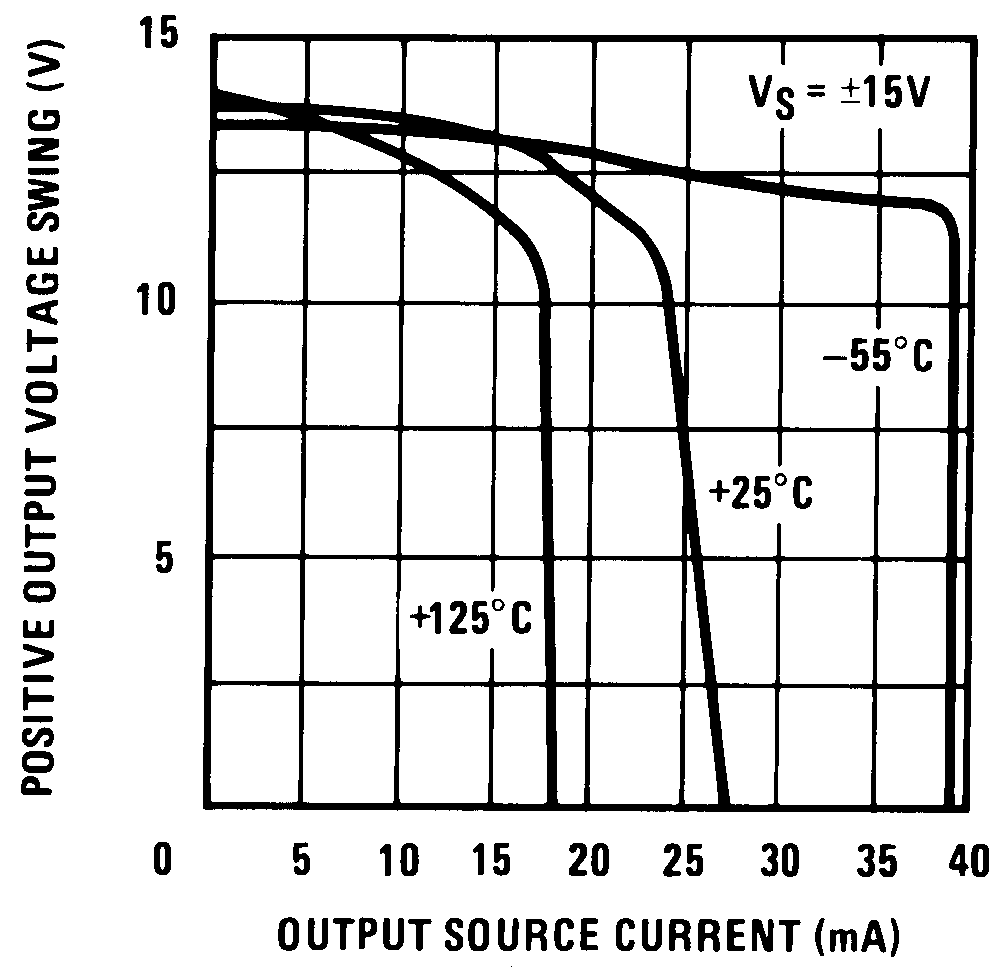 Figure 8. Positive Current Limit
Figure 8. Positive Current Limit
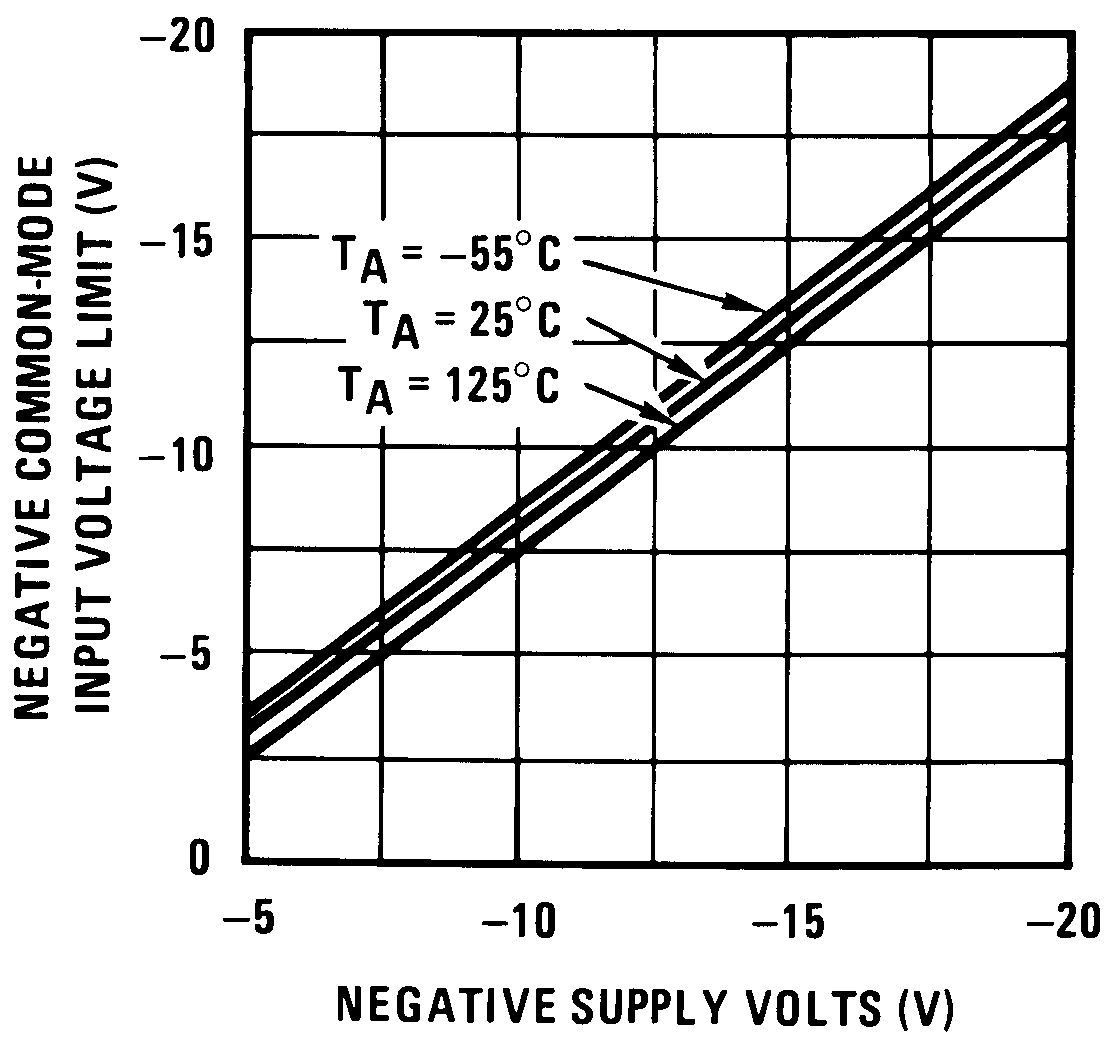 Figure 10. Negative Common-Mode Input Voltage Limit
Figure 10. Negative Common-Mode Input Voltage Limit
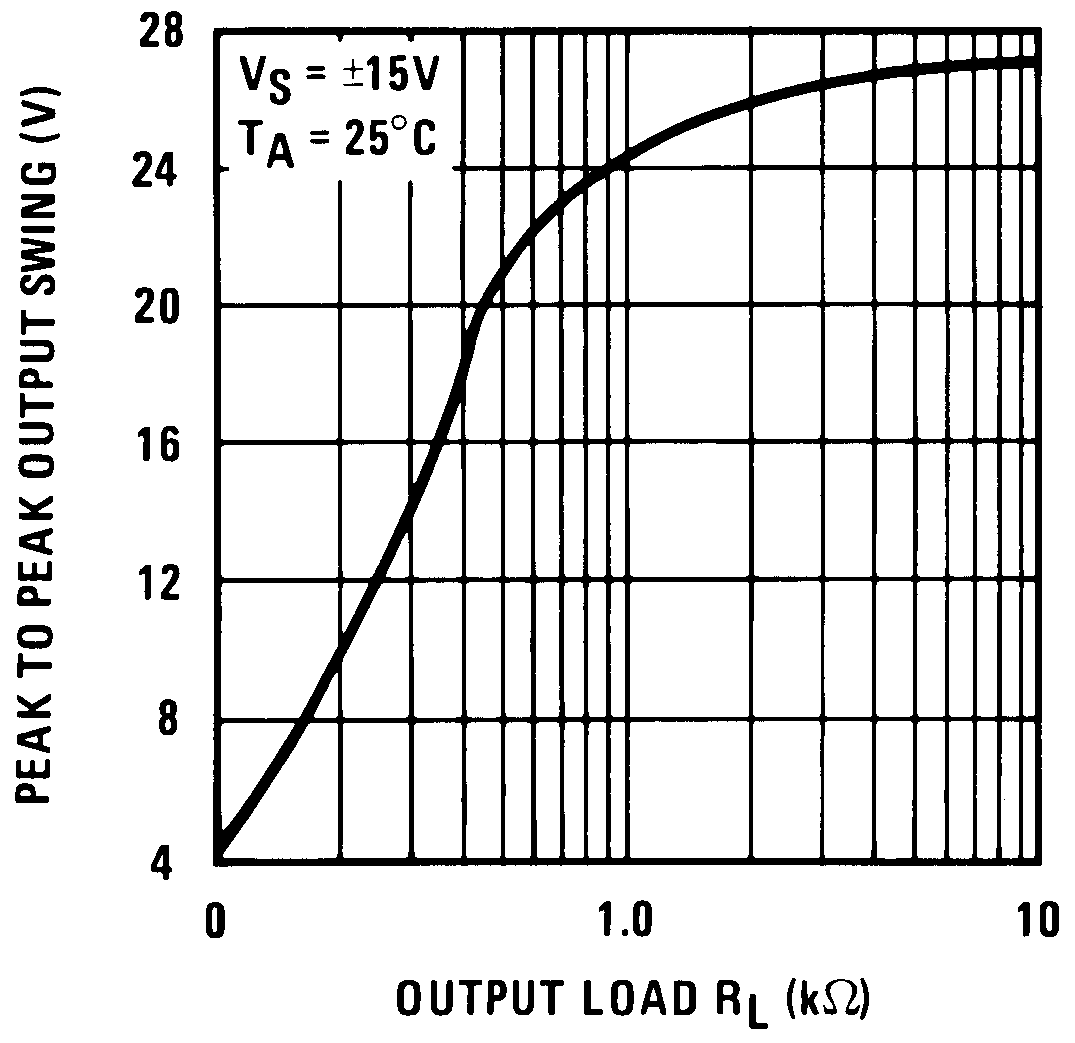 Figure 12. Output Voltage Swing
Figure 12. Output Voltage Swing
6.9.2 Typical AC Performance Characteristics
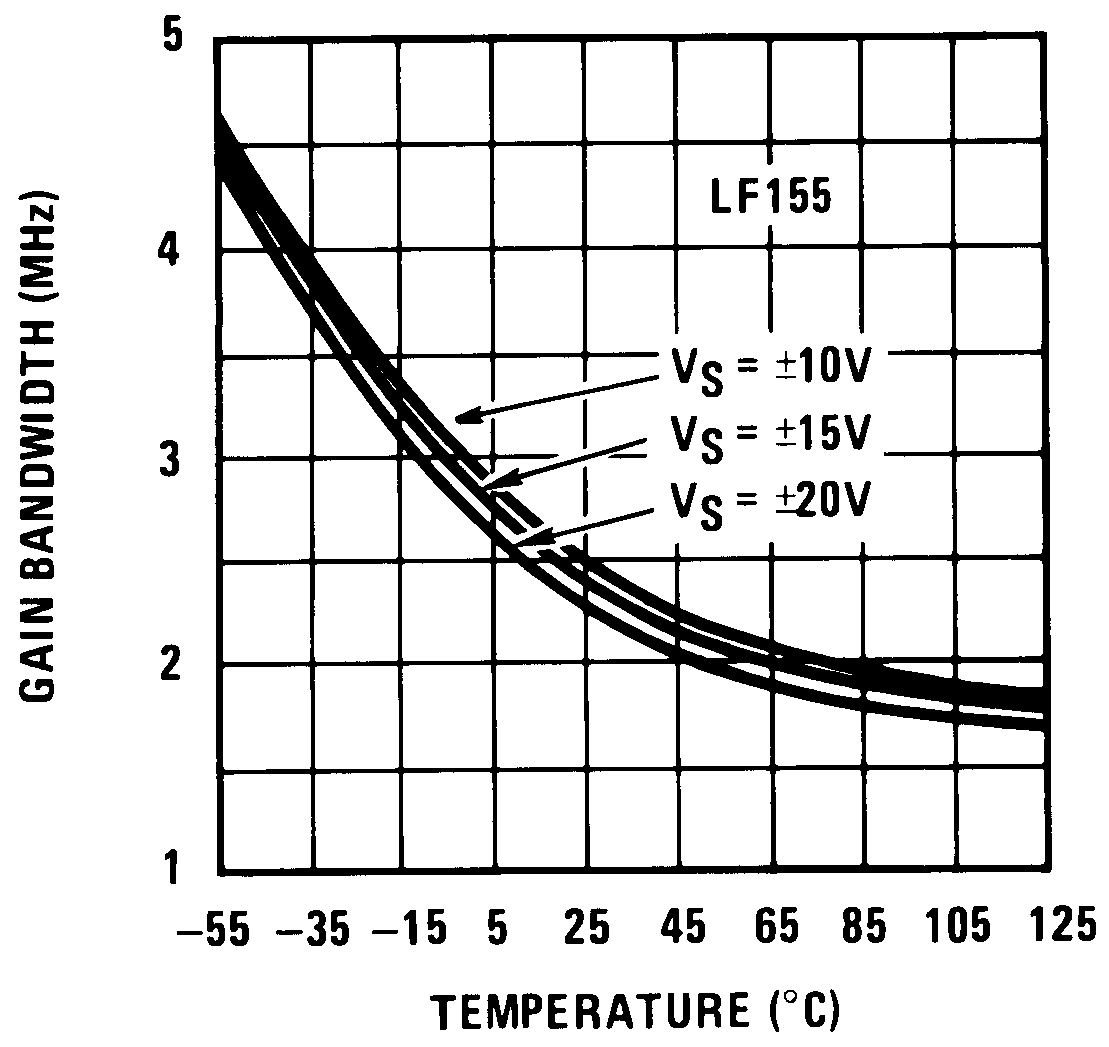 Figure 13. Gain Bandwidth
Figure 13. Gain Bandwidth
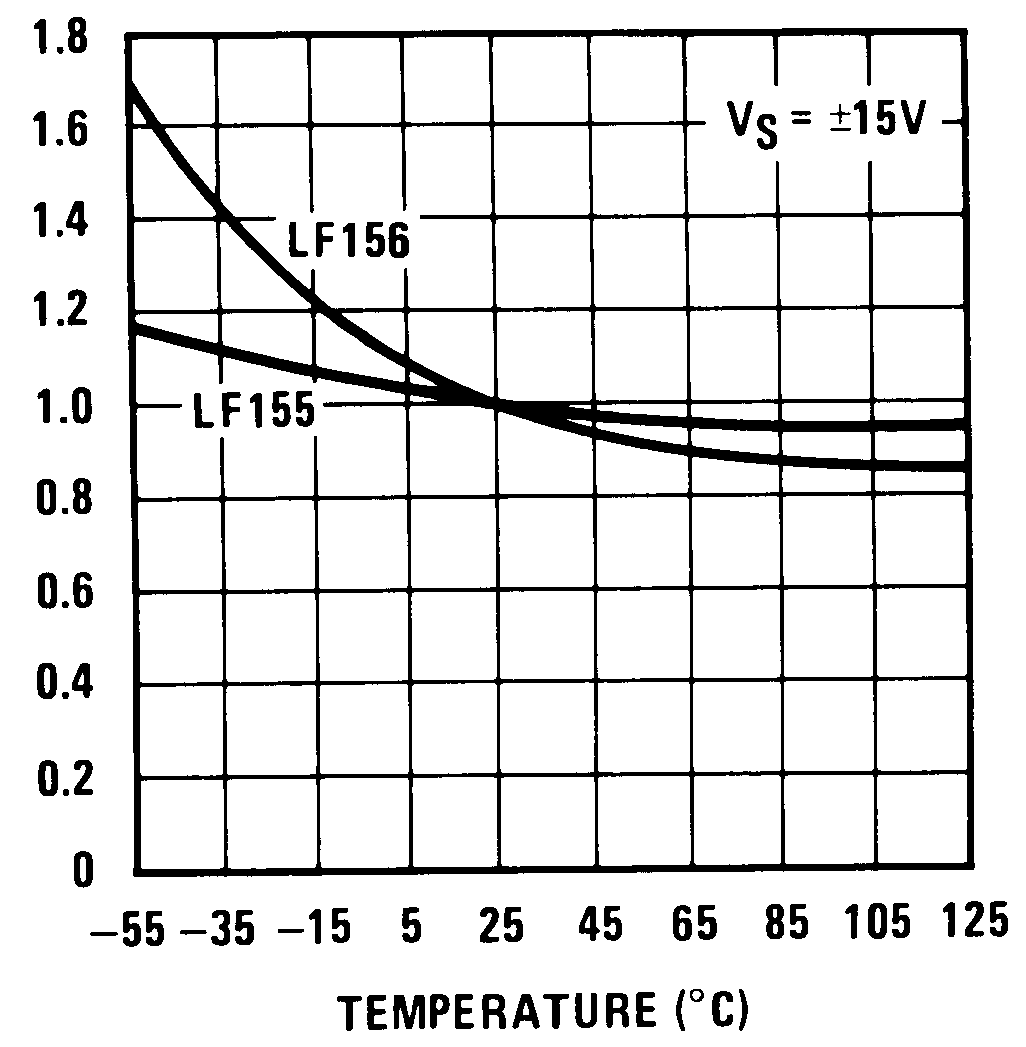 Figure 15. Normalized Slew Rate
Figure 15. Normalized Slew Rate
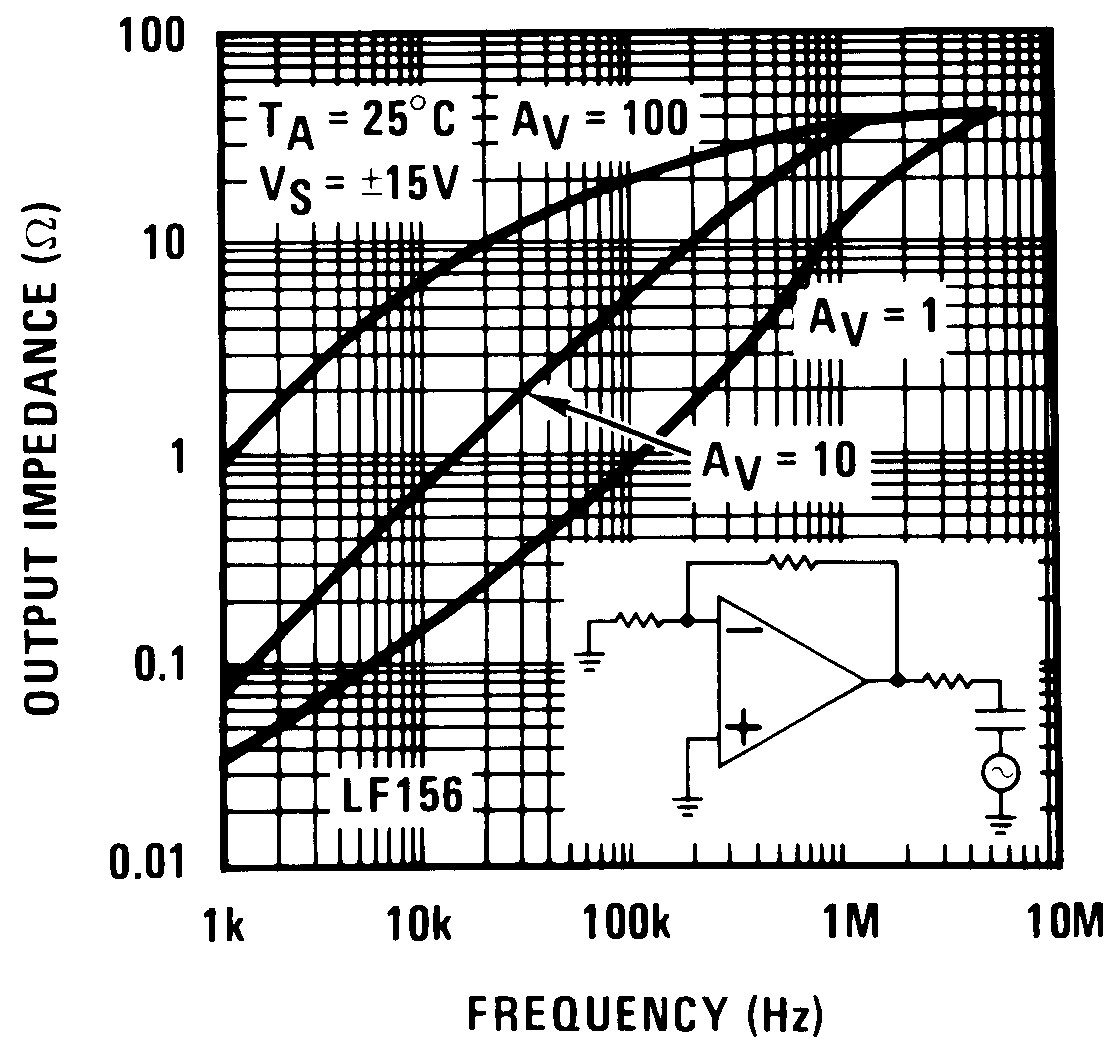 Figure 17. Output Impedance
Figure 17. Output Impedance
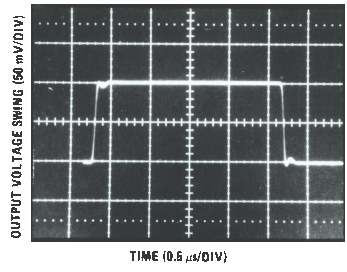 Figure 19. LF156 Small Signal Pulse Response, AV = +1
Figure 19. LF156 Small Signal Pulse Response, AV = +1
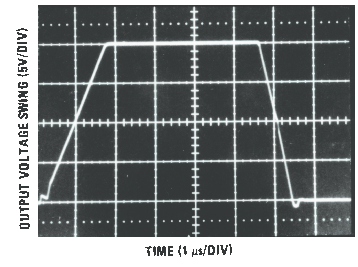
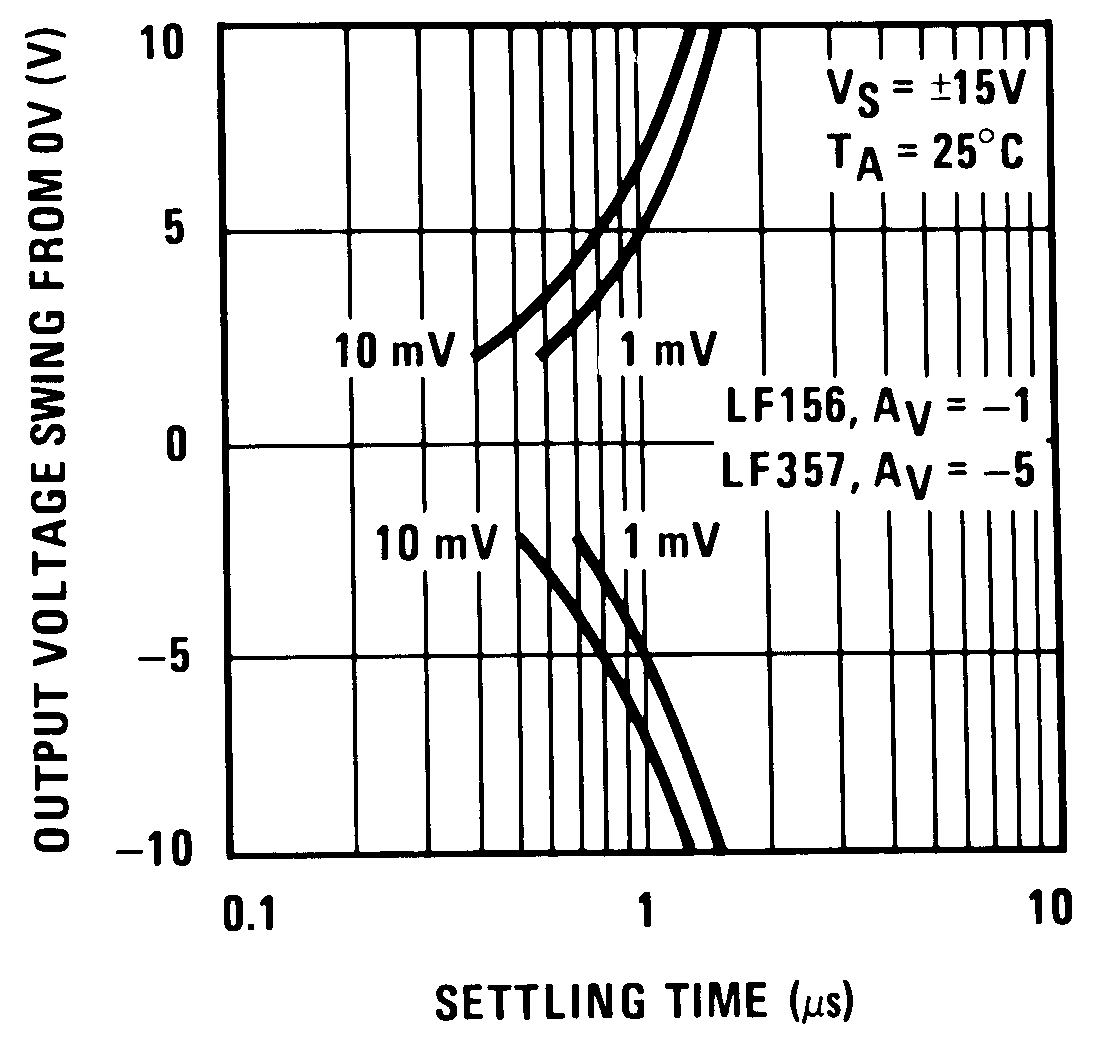 Figure 23. Inverter Settling Time
Figure 23. Inverter Settling Time
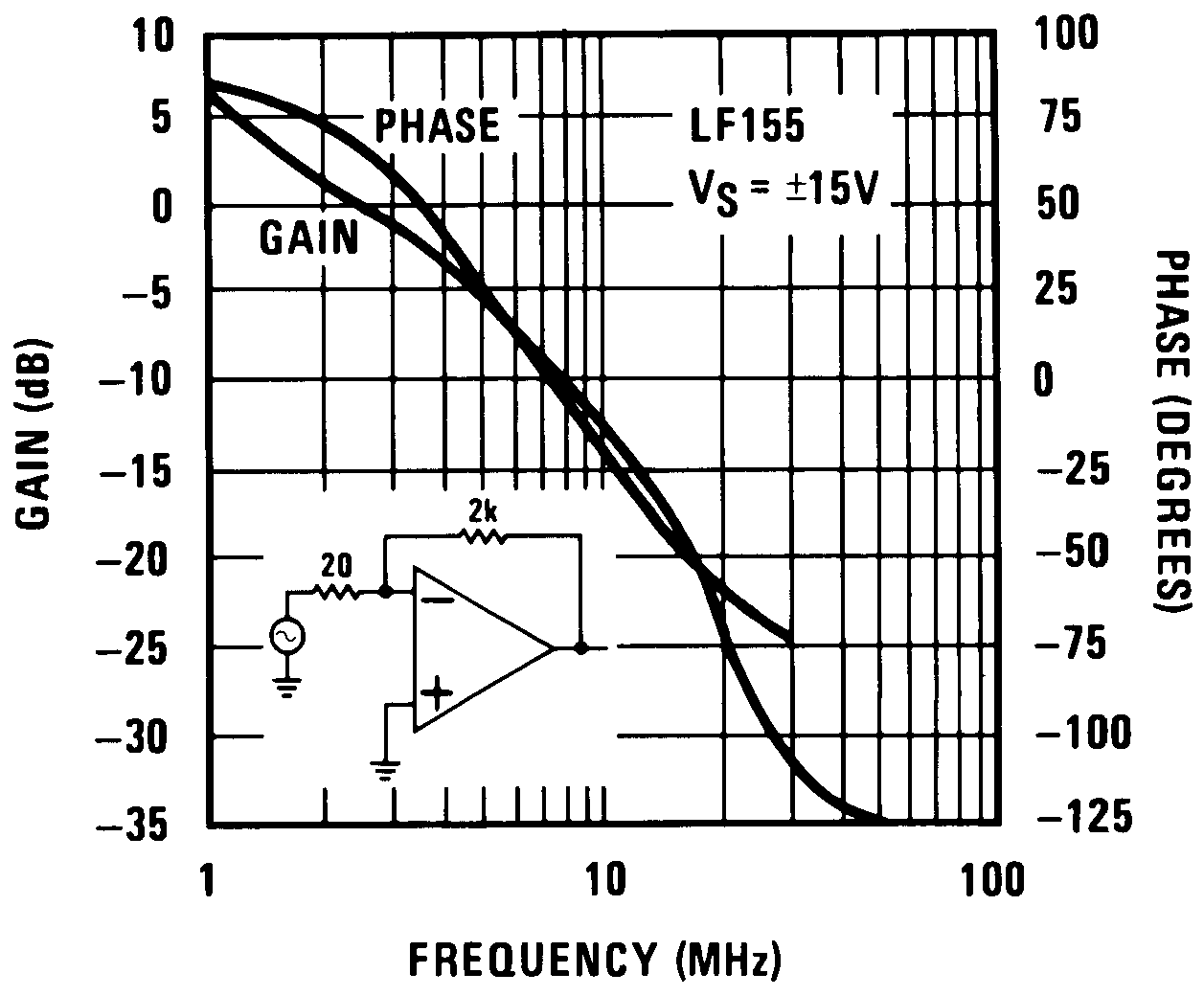 Figure 25. Bode Plot
Figure 25. Bode Plot
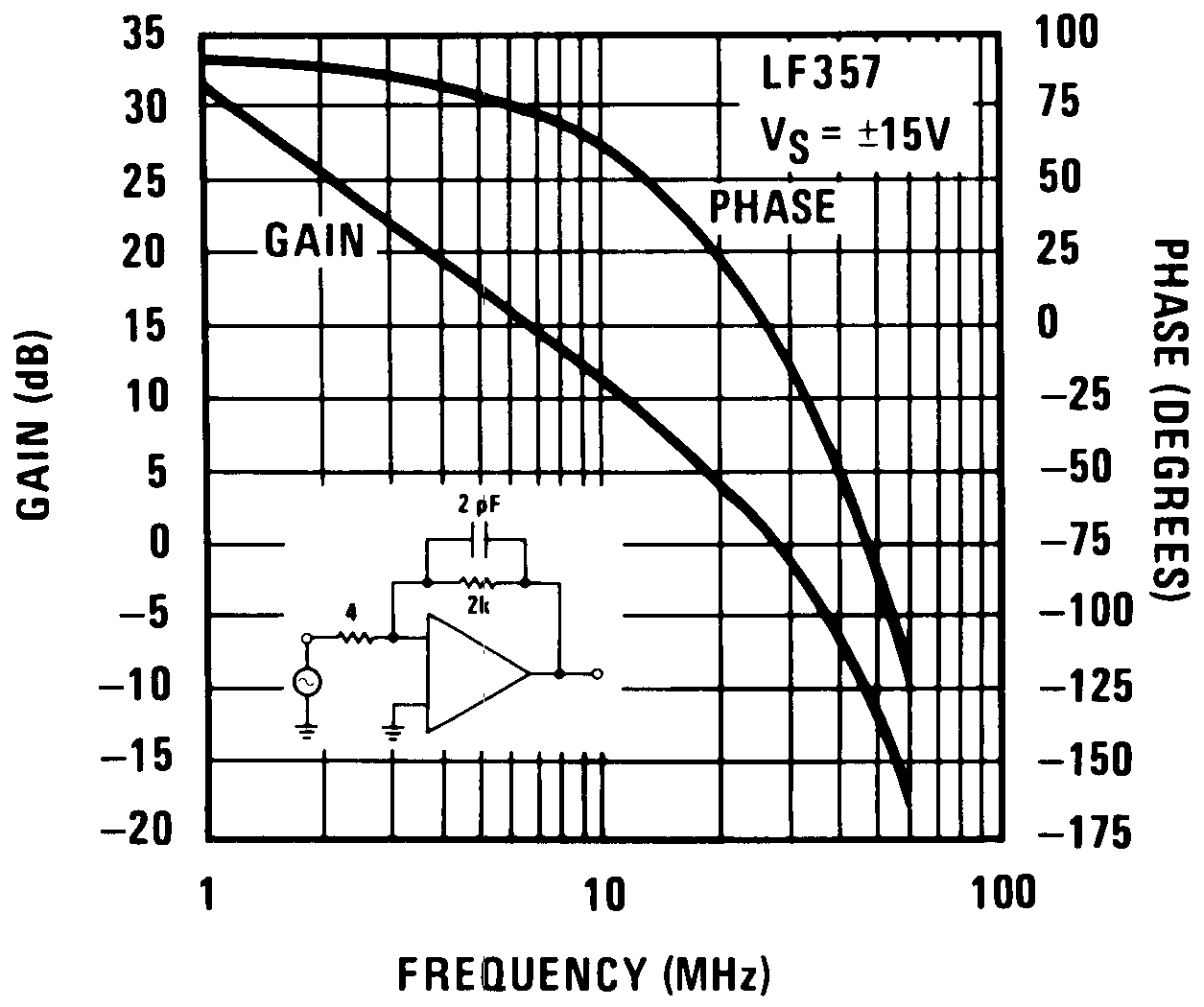 Figure 27. Bode Plot
Figure 27. Bode Plot
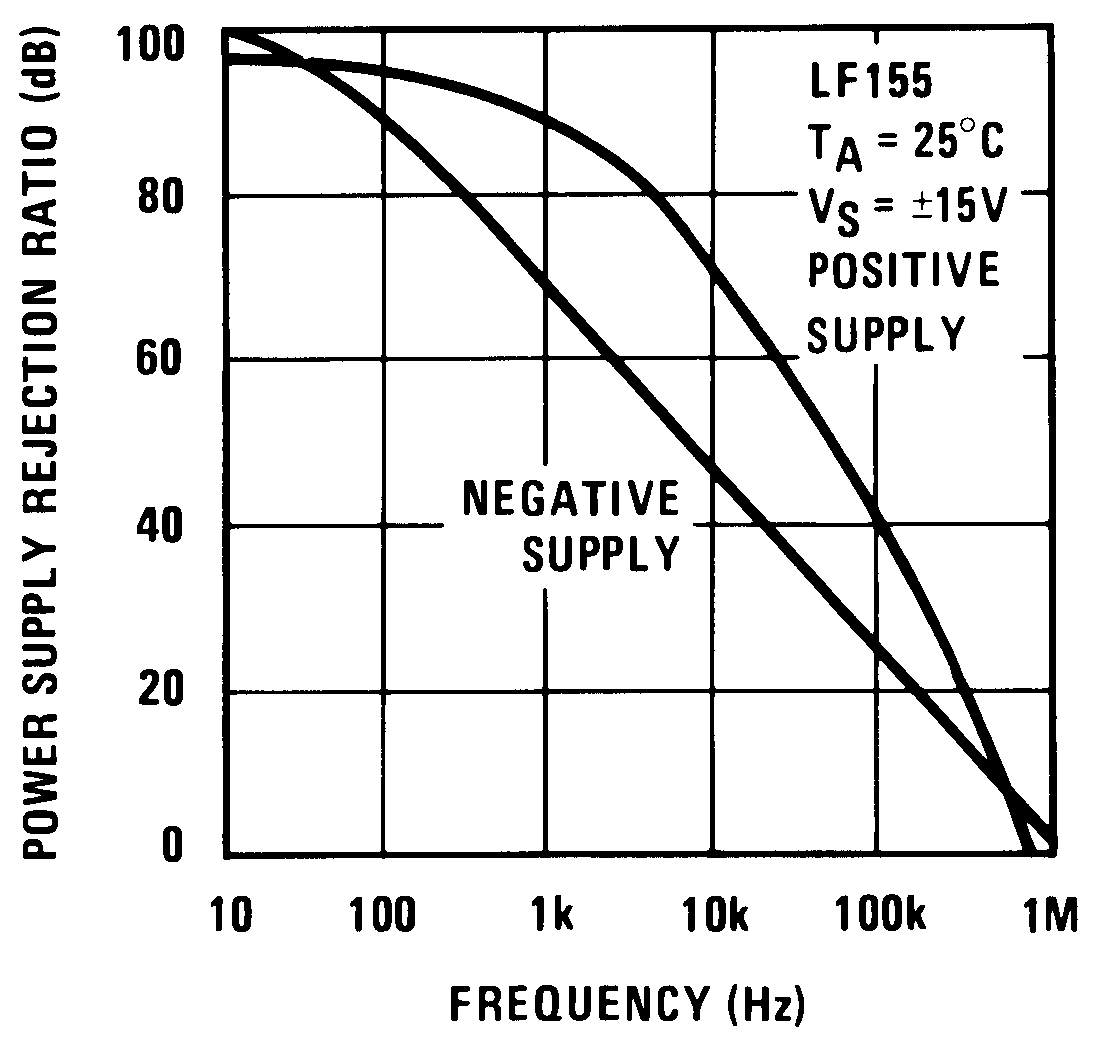 Figure 29. Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Figure 29. Power Supply Rejection Ratio
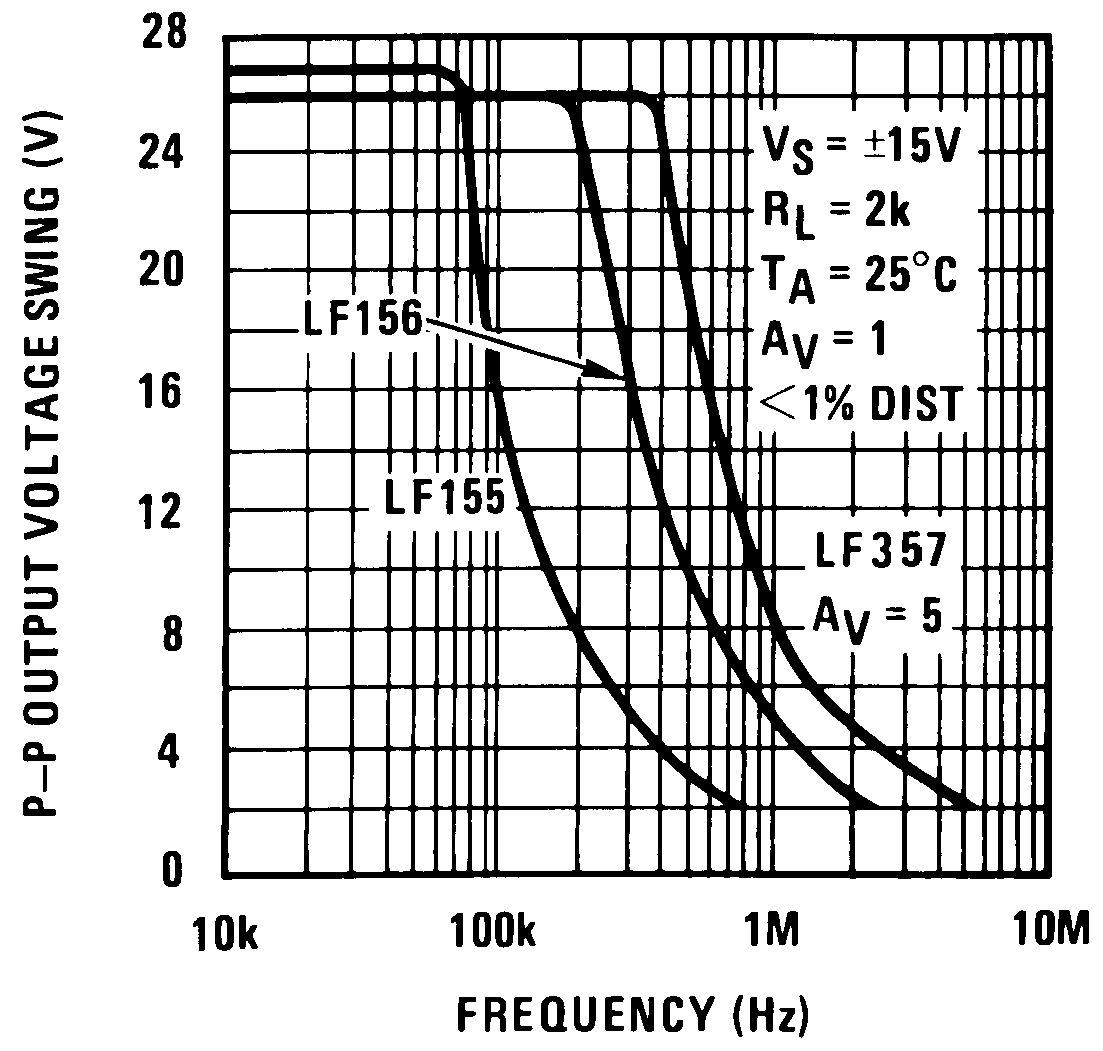 Figure 31. Undistorted Output Voltage Swing
Figure 31. Undistorted Output Voltage Swing
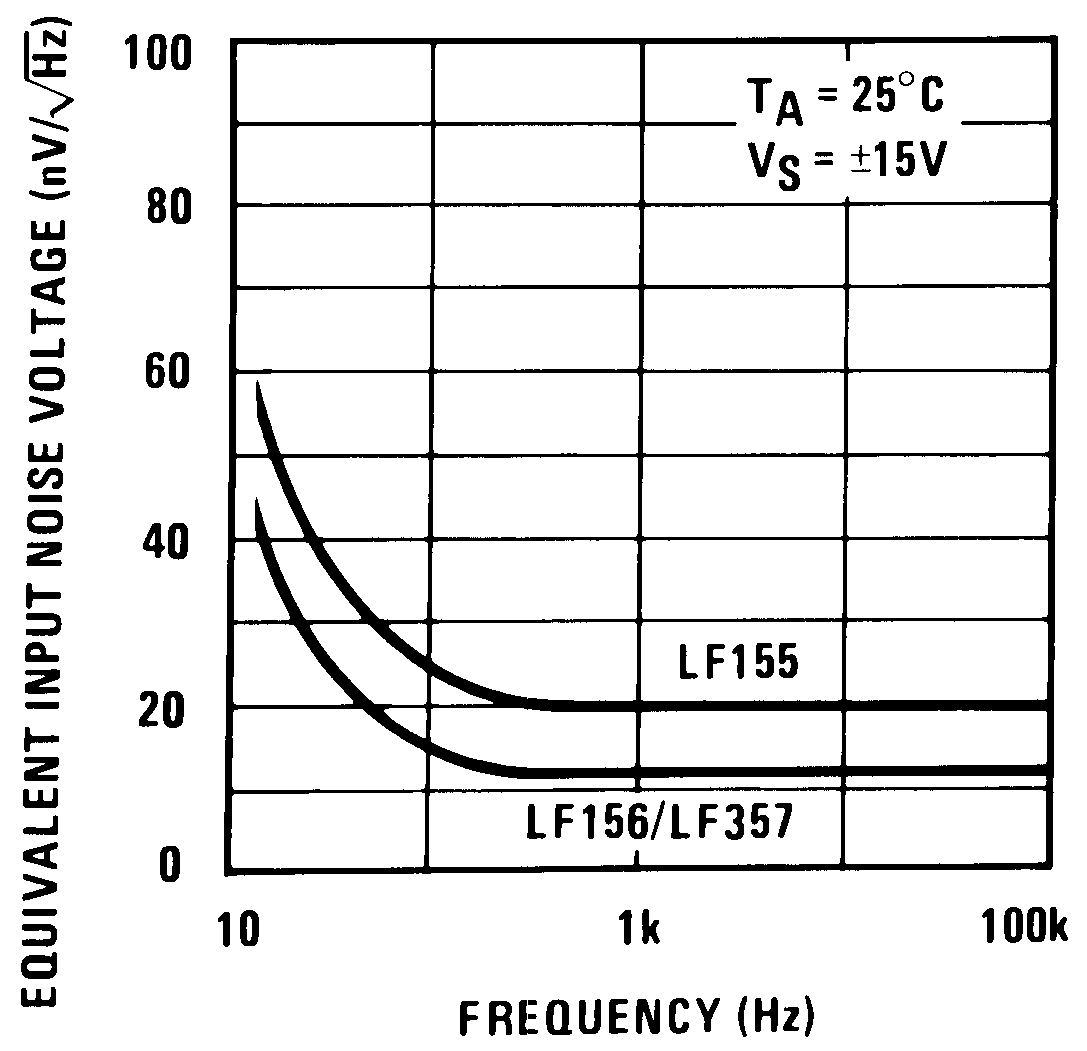 Figure 33. Equivalent Input Noise Voltage (Expanded Scale)
Figure 33. Equivalent Input Noise Voltage (Expanded Scale)
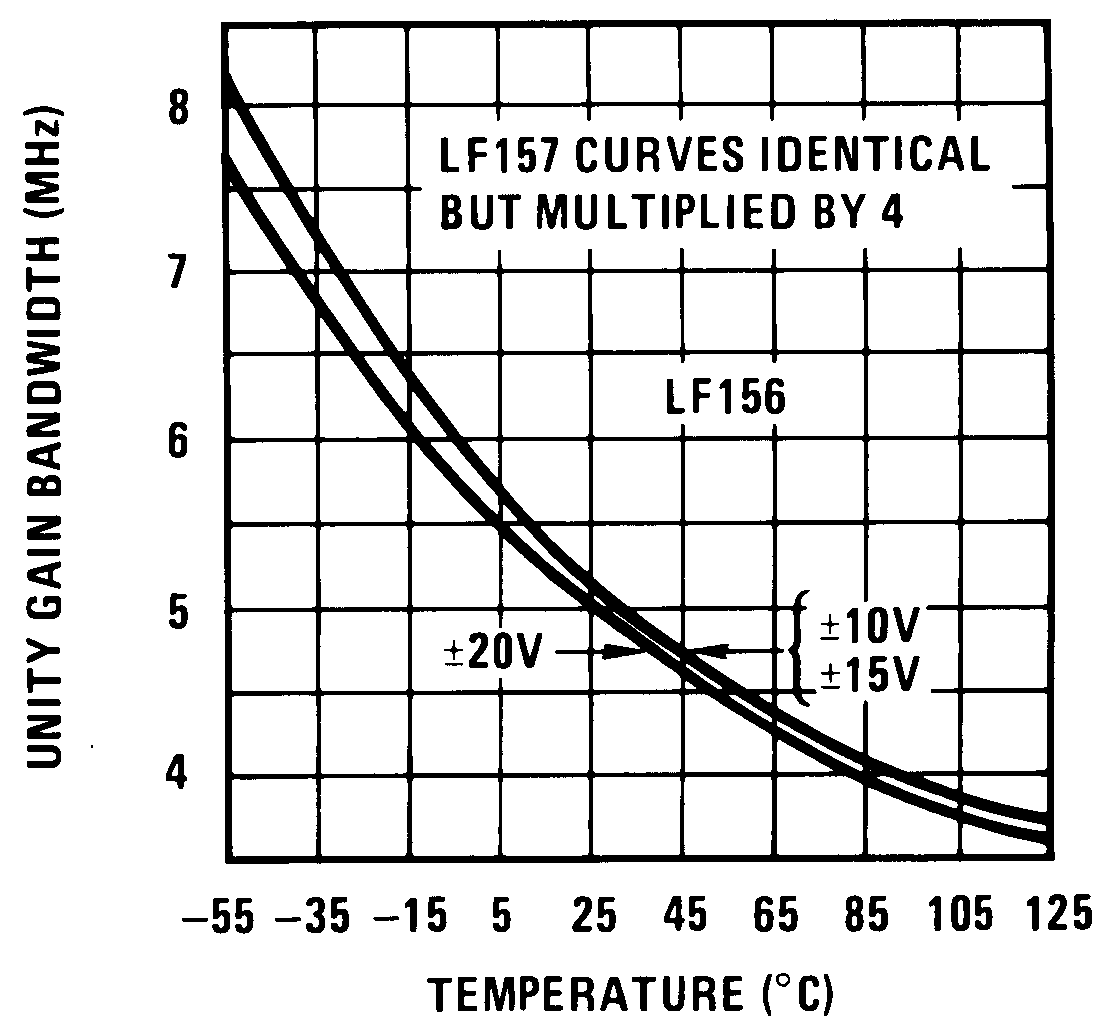 Figure 14. Gain Bandwidth
Figure 14. Gain Bandwidth
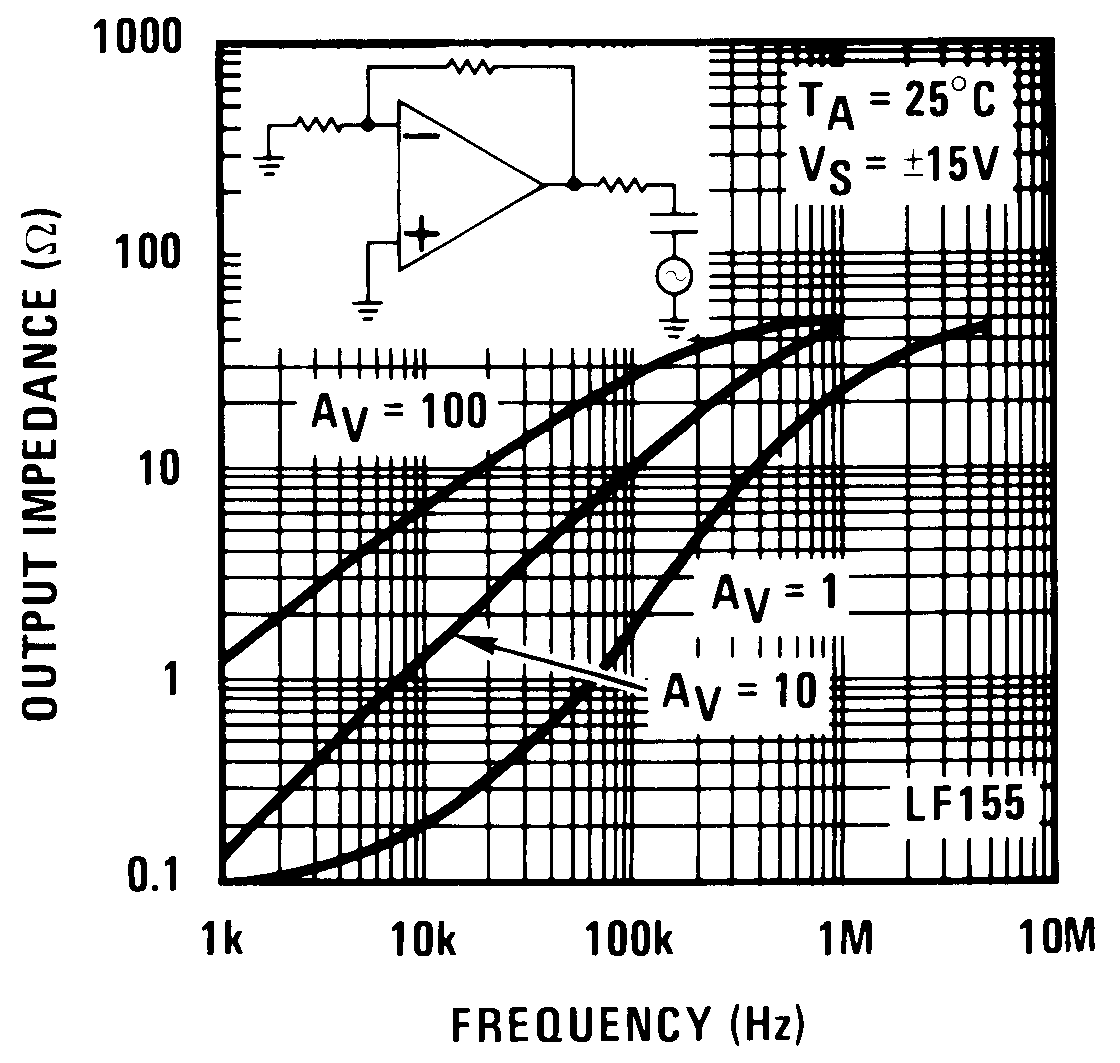 Figure 16. Output Impedance
Figure 16. Output Impedance
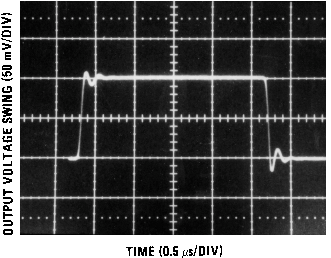
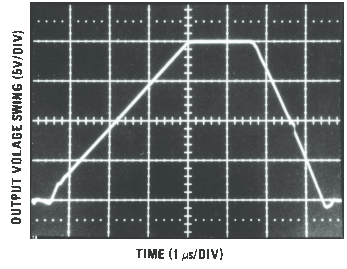 Figure 20. LF155 Large Signal Pulse Response, AV = +1
Figure 20. LF155 Large Signal Pulse Response, AV = +1
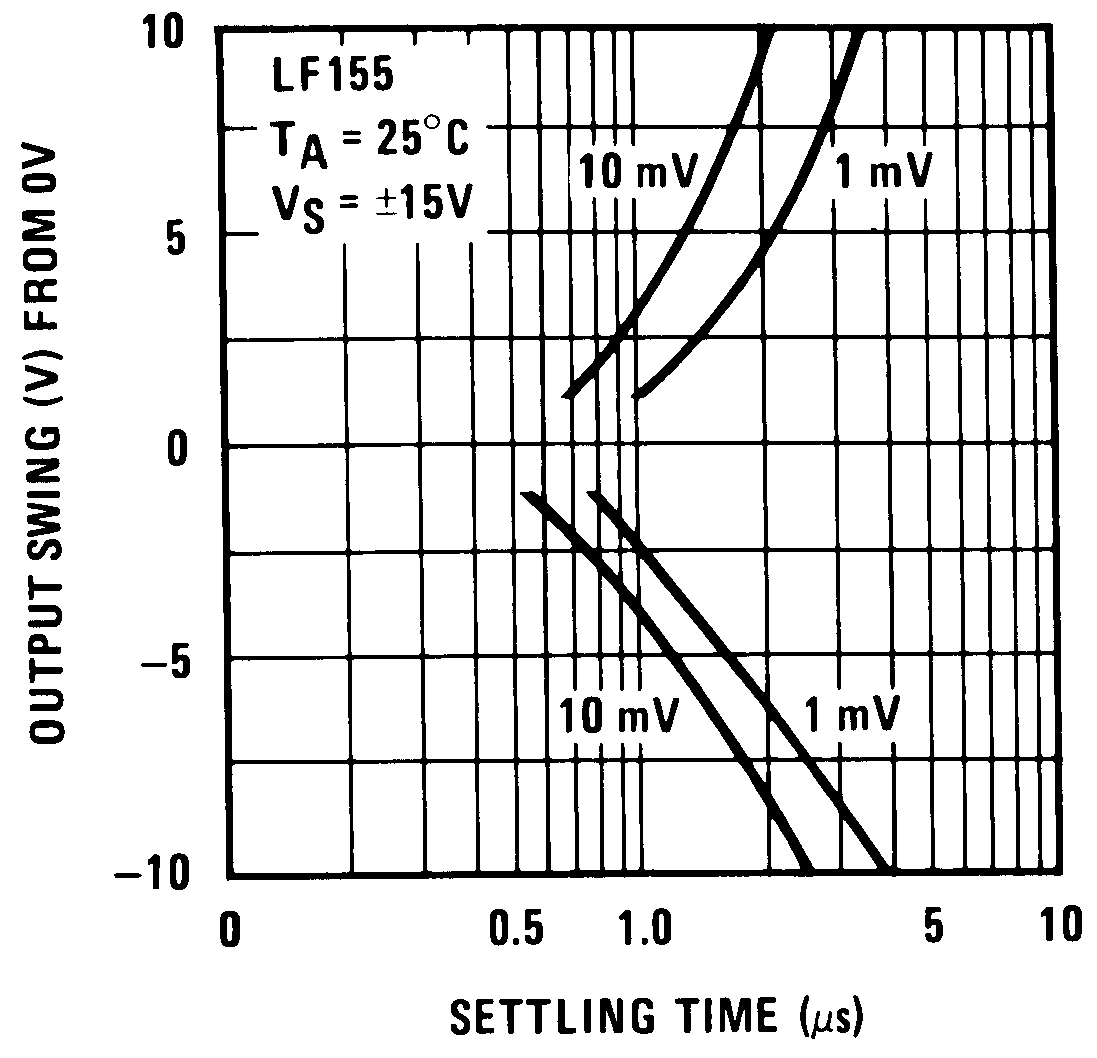 Figure 22. Inverter Settling Time
Figure 22. Inverter Settling Time
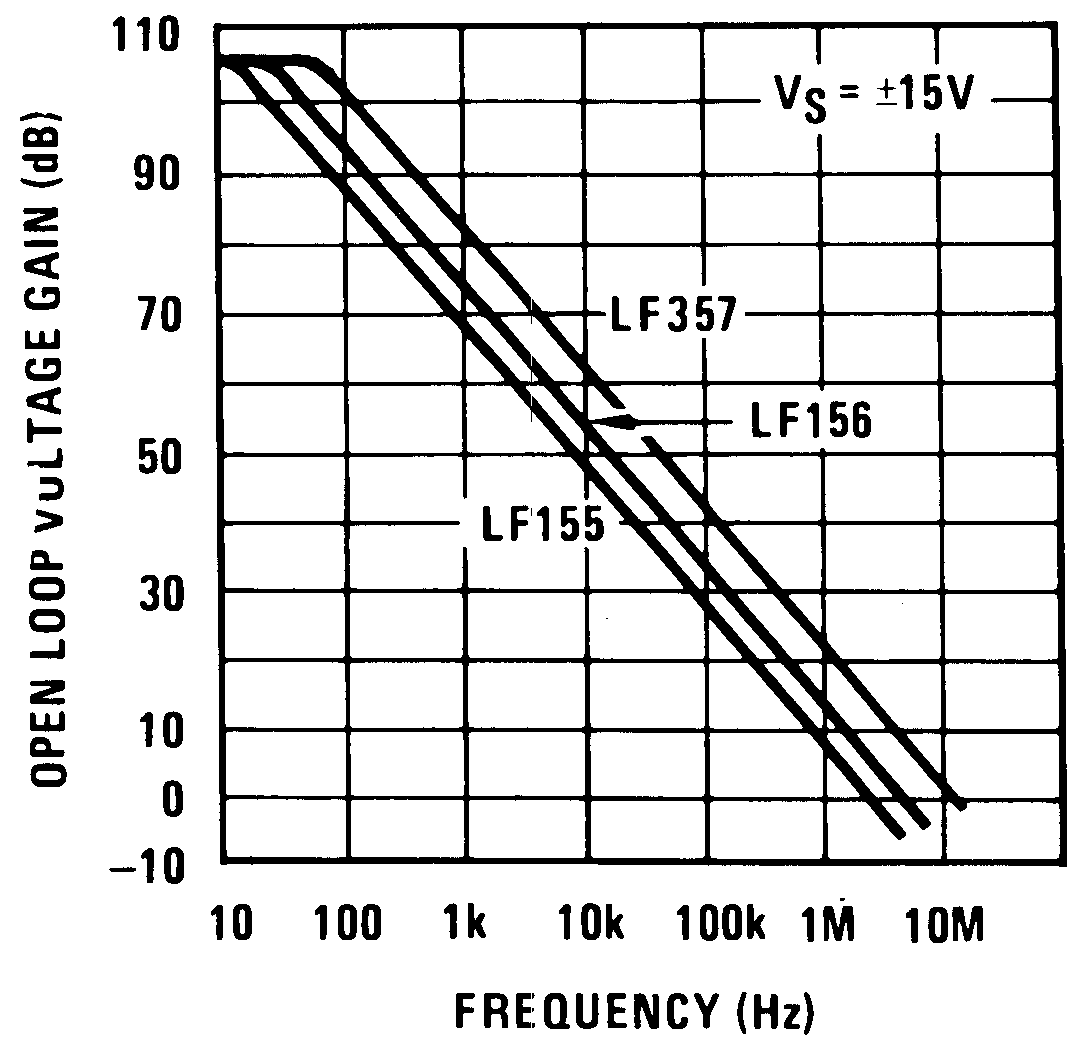 Figure 24. Open-Loop Frequency Response
Figure 24. Open-Loop Frequency Response
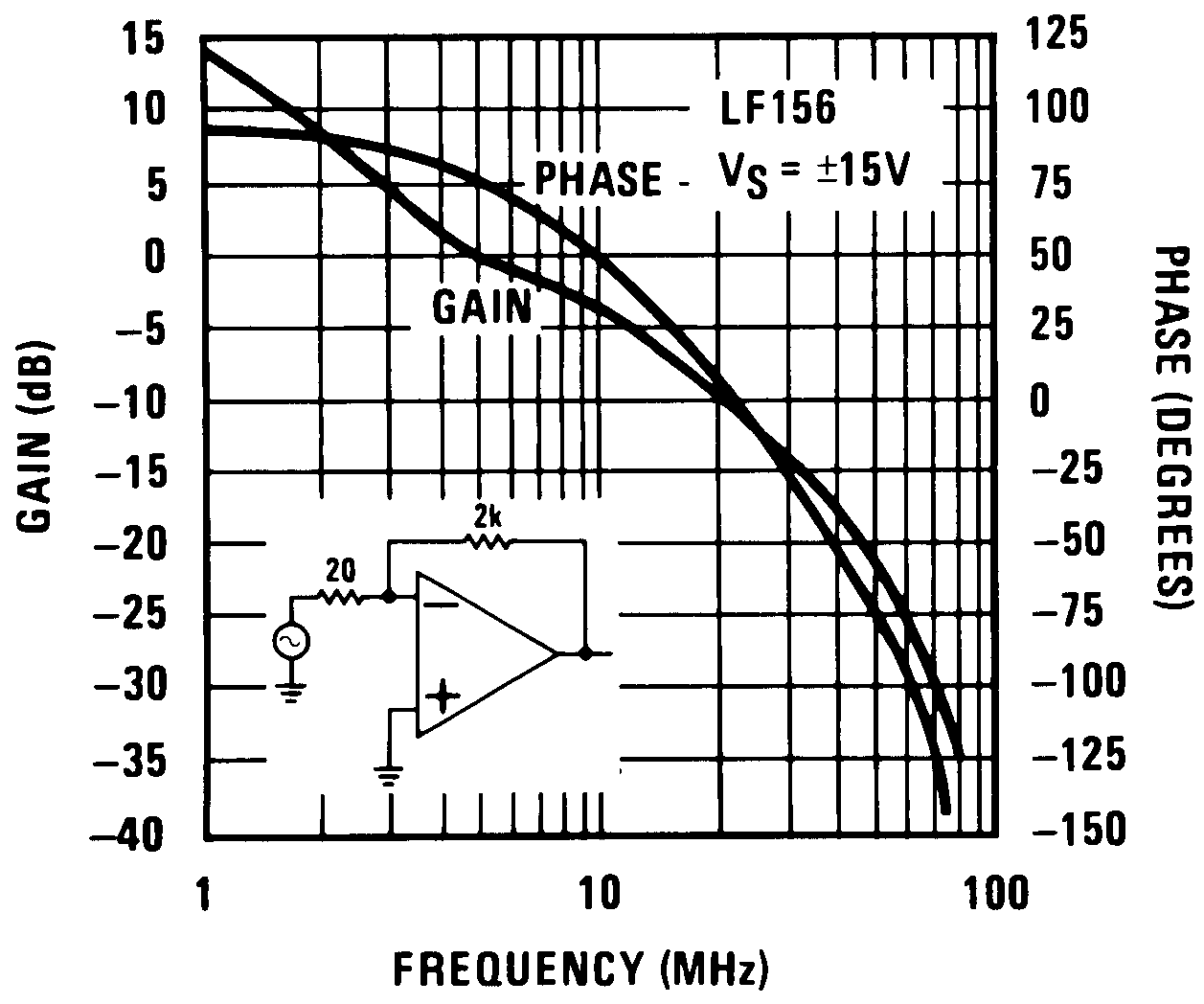 Figure 26. Bode Plot
Figure 26. Bode Plot
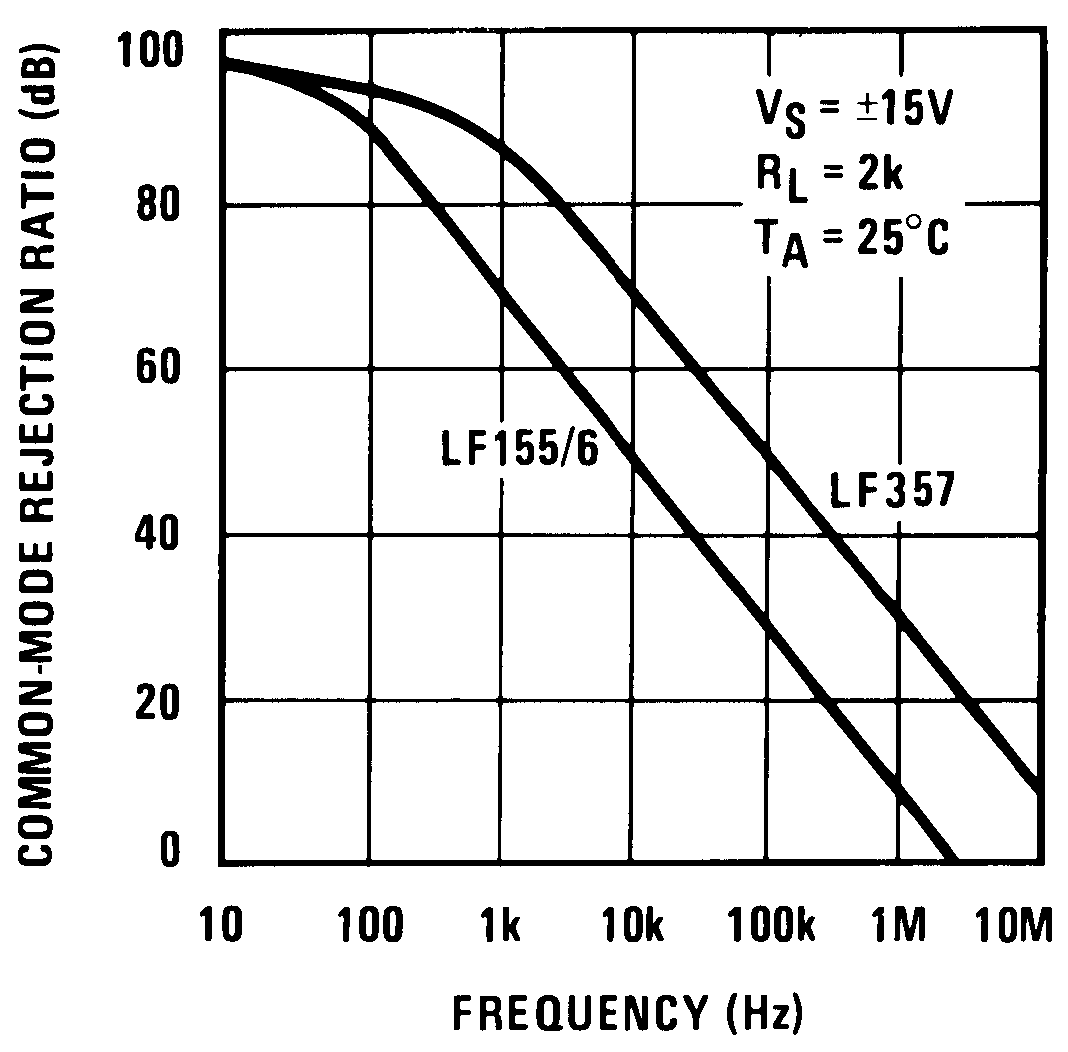 Figure 28. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
Figure 28. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
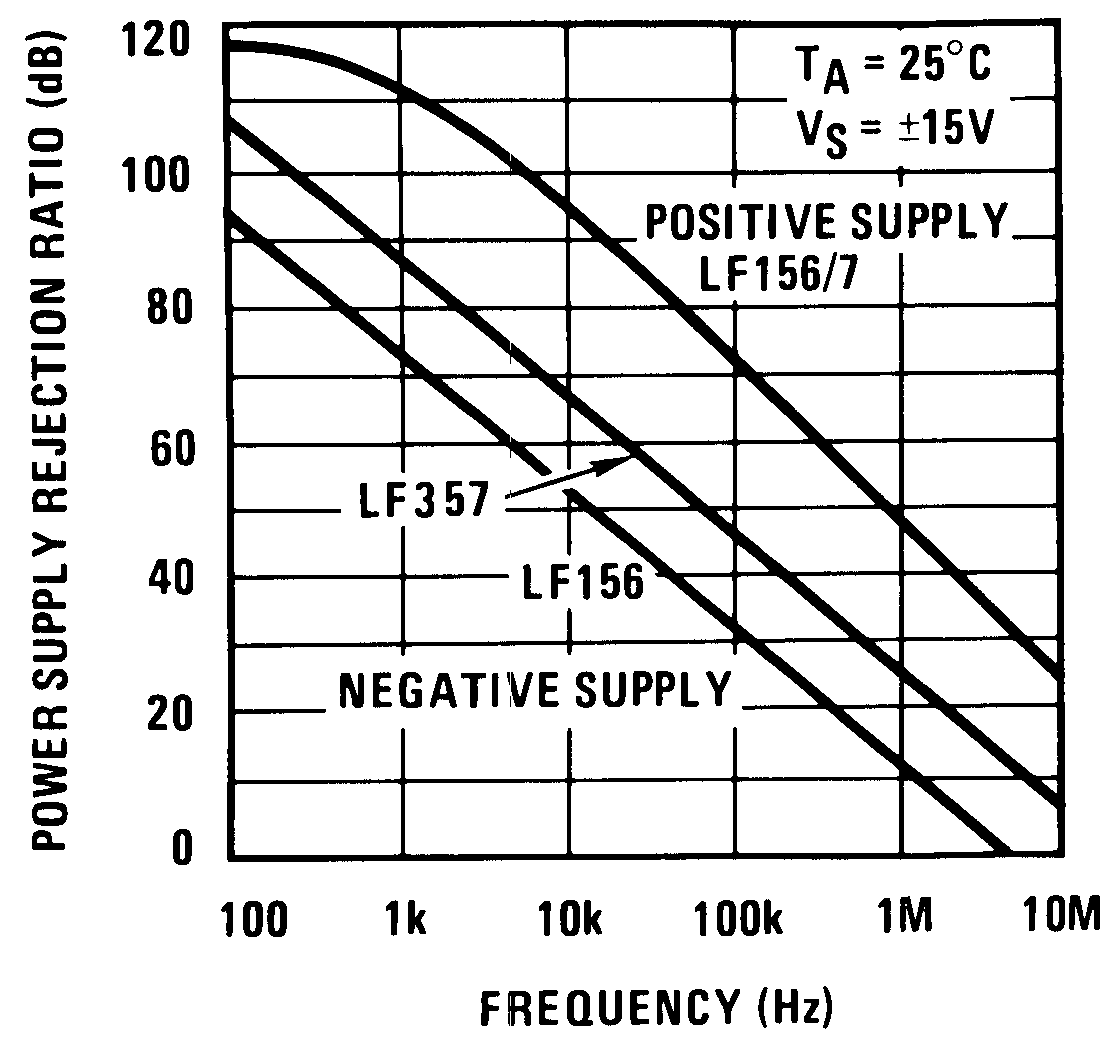 Figure 30. Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Figure 30. Power Supply Rejection Ratio
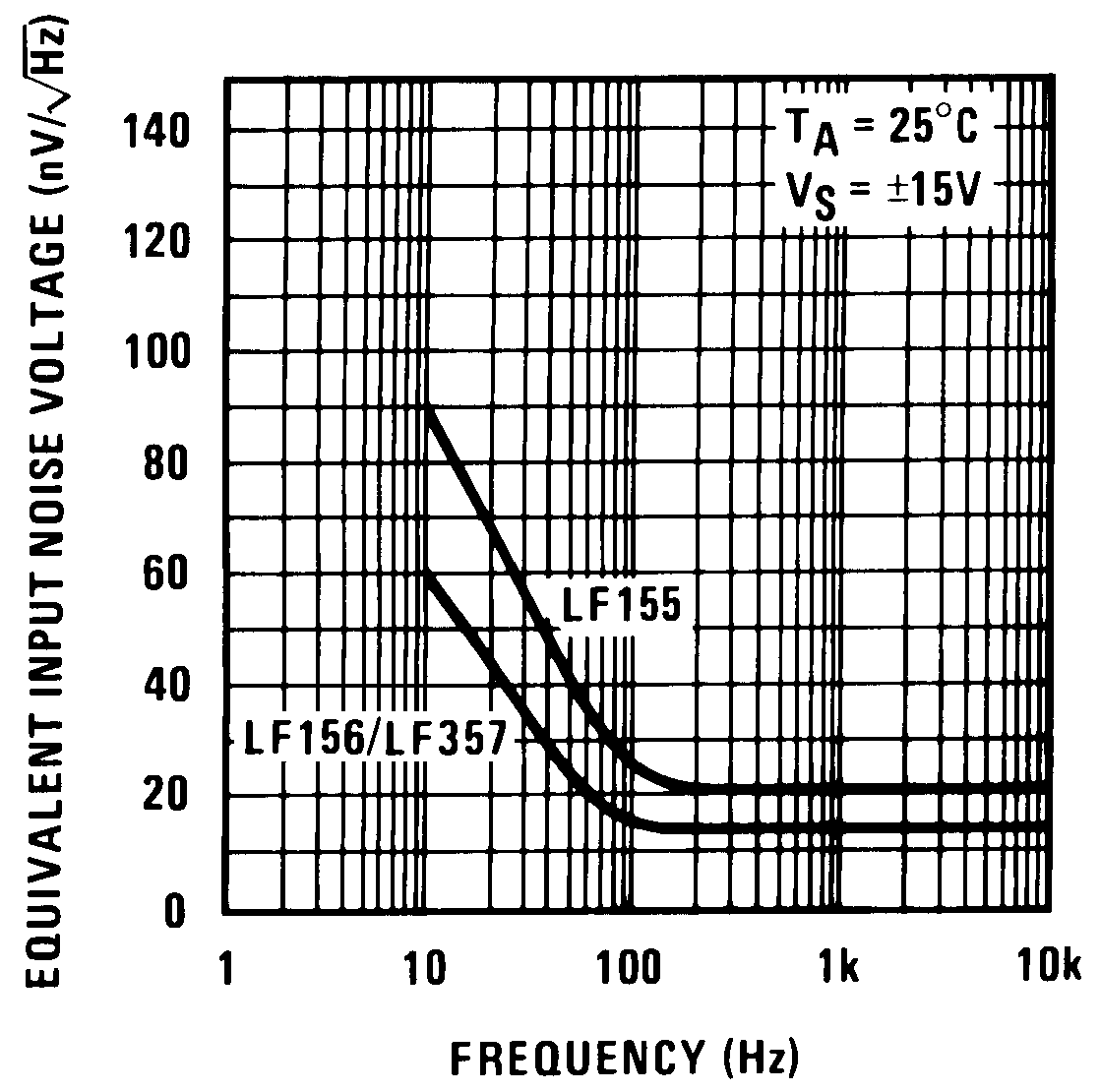 Figure 32. Equivalent Input Noise Voltage
Figure 32. Equivalent Input Noise Voltage