SNVSC25 October 2021 LM117HVQML-SP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Related Products
- 6 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.1 Setting Output Voltage
In operation, the LM117HVQML-SP develops a nominal 1.25-V reference voltage, VREF, between the output and adjustment terminal. The reference voltage is expressed across R1 and, since the voltage is constant, a constant current I1 then flows through R2, giving an output voltage of:
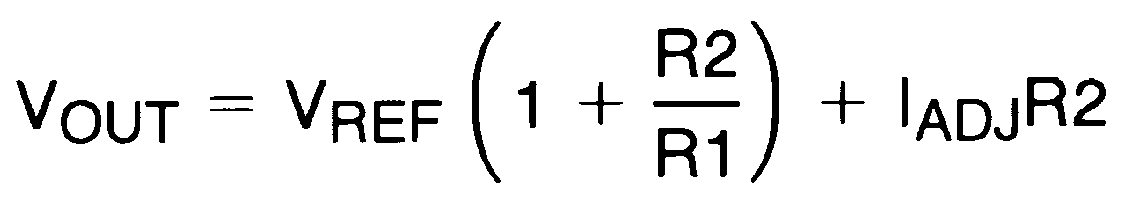
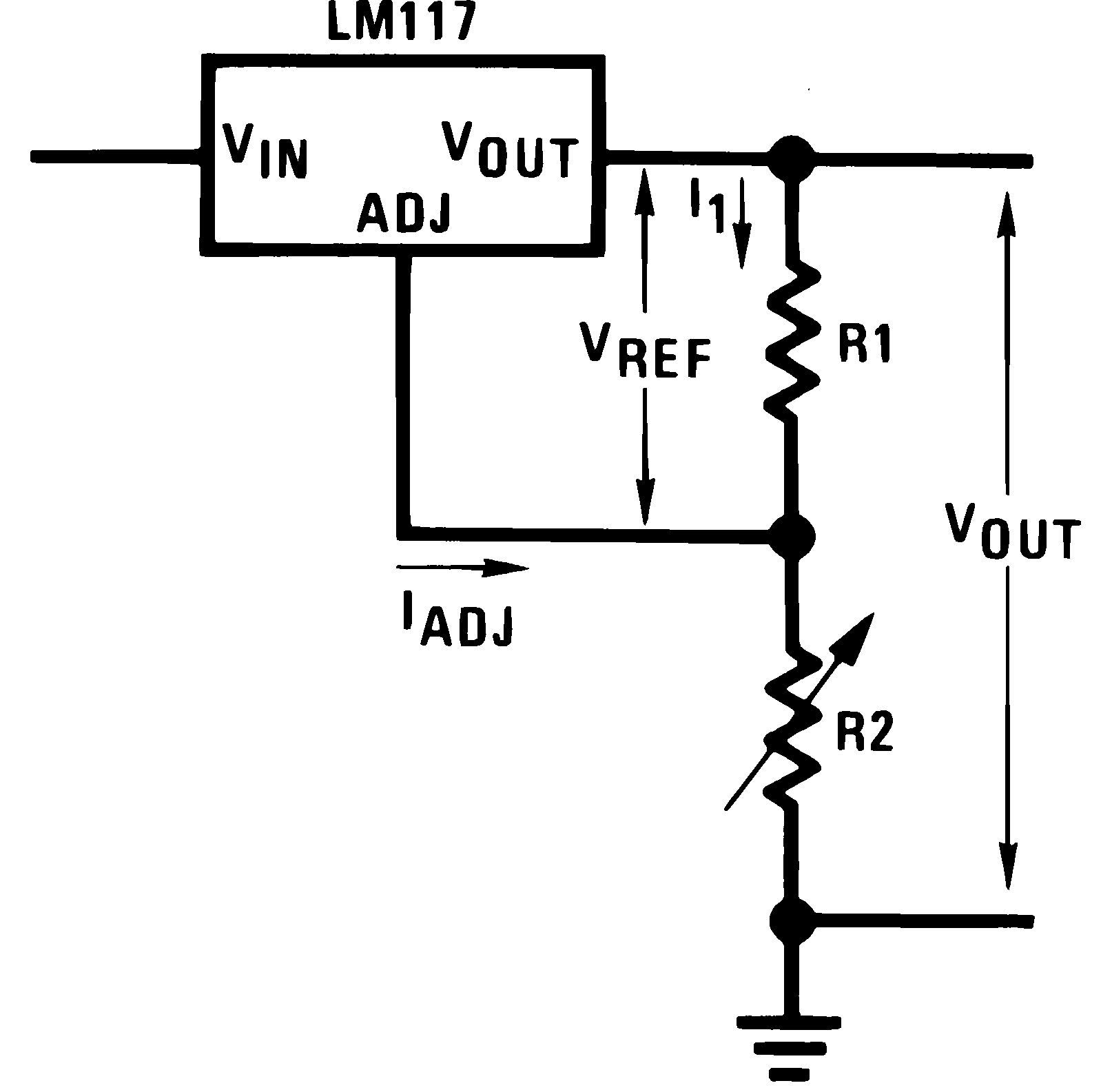
Since the 100-μA current from the adjustment terminal represents an error term, the LM117HVQML-SP was designed to minimize IADJ and make it very constant with line and load changes. To do this, all quiescent operating current is returned to the output establishing a minimum load current requirement. If there is insufficient load on the output, the output will rise.
To mitigate the requirement for an added load to sink the required output current, the resistor divider may be selected so that it alone can sink the largest specified output load current of 5 mA (nominal). This has the additional benefit of minimizing the IADJ error term (which varies over temperature).