SNOSB87D March 2011 – May 2019 LM21215A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
9 Power Supply Recommendations
The LM21215A converter is designed to operate from an input voltage supply range between 2.95 V and 5.5 V. The characteristics of the input supply must be compatible with the Absolute Maximum Ratings and Recommended Operating Conditions tables. In addition, the input supply must be capable of delivering the required input current to the fully-loaded regulator. Estimate the average input current with Equation 19, where η is the efficiency:
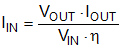
If the converter is connected to an input supply through long wires or PCB traces with large impedance, special care is required to achieve stable performance. The parasitic inductance and resistance of the input cables may have an adverse affect on converter operation. The parasitic inductance in combination with the low ESR ceramic input capacitors form an under-damped resonant circuit. This circuit can cause overvoltage transients at PVIN each time the input supply is cycled on and off. The parasitic resistance causes the PVIN voltage to dip during a load transient. If the regulator is operating close to the minimum input voltage, this dip can cause false UVLO fault triggering and a system reset. The best way to solve such issues is to reduce the distance from the input supply to the regulator and use an aluminum or tantalum input capacitor in parallel with the ceramics. The moderate ESR of the electrolytic capacitors helps to damp the input resonant circuit and reduce any voltage overshoots. A capacitance in the range of 20 µF to 100 µF is usually sufficient to provide input damping and helps to hold the input voltage steady during large load transients.
An EMI input filter is often used in front of the regulator that, unless carefully designed, can lead to instability as well as some of the effects mentioned above. The user guide Simple Success with Conducted EMI for DC-DC Converters, SNVA489, provides helpful suggestions when designing an input filter for any switching regulator.