SNOSB87D March 2011 – May 2019 LM21215A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
10.1.2 Thermal Design
As with any power conversion device, the LM21215A dissipates internal power while operating. The effect of this power dissipation is to raise the internal junction temperature of the LM21215A above ambient. The junction temperature (TJ) is a function of the ambient temperature (TA), the power dissipation and the effective thermal resistance of the device and PCB combination (RθJA). The maximum operating junction temperature for the LM21215A is 125°C, thus establishing a limit on the maximum device power dissipation and therefore the load current at high ambient temperatures. Equation 20 shows the relationships between these parameters.
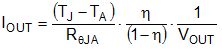
High ambient temperatures and large values of RθJA reduce the maximum available output current. If the junction temperature exceeds 165°C, the LM21215A cycles in and out of thermal shutdown. Thermal shutdown may be a sign of inadequate heat-sinking or excessive power dissipation. Improve PCB heat-sinking by using more thermal vias, a larger board, or more heat-spreading layers within that board.
As stated in application note Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics, SPRA953, the values given in the Thermal Information table are not always valid for design purposes to estimate the thermal performance of the application. The values reported in the Thermal Information table are measured under a specific set of conditions that are seldom obtained in an actual application. The effective RθJA is a critical parameter and depends on many factors (such as power dissipation, air temperature, PCB area, copper heat-sink area, number of thermal vias under the package, air flow, and adjacent component placement). The LM21215A uses an advanced flip-chip-on-lead (FCOL) package and its exposed pad has a direct electrical and thermal connection to PGND. This pad must be soldered directly to the PCB copper ground plane to provide an effective heat-sink and proper electrical connection. Use the documents listed in Related Documentation as a guide for optimized thermal PCB design and estimating RθJA for a given application environment.