SNVS617H April 2009 – November 2014 LM25011 , LM25011-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGQ|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGQ|10
Orderable Information
7.3.2 On-Time Timer
The on-time for the LM25011/LM25011A is determined by the RT resistor and the input voltage (VIN), calculated from:
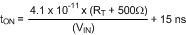
The inverse relationship with VIN results in a nearly constant frequency as VIN is varied. To set a specific continuous conduction mode switching frequency (FS), the RT resistor is determined from the following:

The on-time must be chosen greater than 90 ns for proper operation. Equation 1, Equation 5, and Equation 6 are valid only during normal operation; that is, the circuit is not in current limit. When the LM25011 operates in current limit, the on-time is reduced by approximately 40% (this feature is not present in LM25011A). This feature reduces the peak inductor current which may be excessively high if the load current and the input voltage are simultaneously high. This feature operates on a cycle-by-cycle basis until the load current is reduced and the output voltage resumes its normal regulated value. The maximum continuous current into the RT pin must be less than 2 mA. For high-frequency applications, the maximum switching frequency is limited at the maximum input voltage by the minimum on-time one-shot period (90 ns). At minimum input voltage the maximum switching frequency is limited by the minimum off-time one-shot period which, if reached, prevents achievement of the proper duty cycle.