SNVS509F April 2007 – November 2023 LM25116
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Application
- 7.2.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.2.1 Timing Resistor
- 7.2.2.2 Output Inductor
- 7.2.2.3 Current Sense Resistor
- 7.2.2.4 Ramp Capacitor
- 7.2.2.5 Output Capacitors
- 7.2.2.6 Input Capacitors
- 7.2.2.7 VCC Capacitor
- 7.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor
- 7.2.2.9 Soft Start Capacitor
- 7.2.2.10 Output Voltage Divider
- 7.2.2.11 UVLO Divider
- 7.2.2.12 MOSFETs
- 7.2.2.13 MOSFET Snubber
- 7.2.2.14 Error Amplifier Compensation
- 7.2.2.15 Comprehensive Equations
- 7.2.3 Application Curves
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
7.2.2.15.2 Modulator Transfer Function
Equation 43 through Equation 47 can be used to calculate the control-to-output transfer function.
Equation 43. 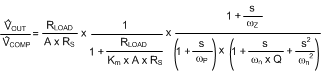
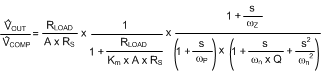
Equation 44. 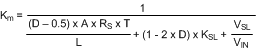
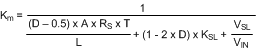
Equation 45. 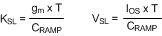
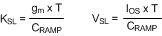
Equation 46. 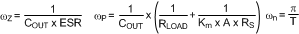
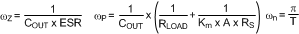
Equation 47. 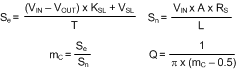
Km is the effective DC gain of the modulating comparator. The duty cycle D = VOUT / VIN. KSL is the proportional slope compensation term. VSL is the fixed slope compensation term. Slope compensation is set by mc, which is the ratio of the external ramp to the natural ramp. The switching frequency sampling gain is characterized by ωn and Q, which accounts for the high frequency inductor pole.
For VSL without RRAMP, use IOS = 25 µA.
For VSL with RRAMP to VCC, use IOS = 25 µA + VCC/RRAMP.
For VSL with RRAMP to -VCC, use IOS = 25 µA - VCC/RRAMP.