SNVS726F July 2011 – March 2018 LM25118
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 R7 = RT
- 8.2.2.3 Inductor Selection – L1
- 8.2.2.4 R13 = RSENSE
- 8.2.2.5 C15 = CRAMP
- 8.2.2.6 Inductor Current Limit Calculation
- 8.2.2.7 C9 - C12 = Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.8 D1
- 8.2.2.9 D4
- 8.2.2.10 C1 – C5 = Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.11 C20
- 8.2.2.12 C8
- 8.2.2.13 C16 = CSS
- 8.2.2.14 R8, R9
- 8.2.2.15 R1, R3, C21
- 8.2.2.16 R2
- 8.2.2.17 Snubber
- 8.2.2.18 Error Amplifier Configuration
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
8.2.2.10 C1 – C5 = Input Capacitors
A typical regulator supply voltage has a large source impedance at the switching frequency. Good-quality input capacitors are necessary to limit the ripple voltage at the VIN pin while supplying most of the switch current during the buck switch on-time. When the buck switch turns on, the current into the buck switch steps from zero to the lower peak of the inductor current waveform, then ramps up to the peak value, and then drops to the zero at turnoff. The RMS current rating of the input capacitors depends on which mode of operation is most critical.
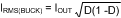
The RMS current demand on the input capacitor(s) is at the maximum value when the duty cycle is at 50%.
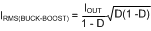
Checking both modes of operation we find:
Therefore C1 — C5 should be sized to handle 4.7 A of ripple current. Quality ceramic capacitors with a low ESR should be selected. To allow for capacitor tolerances, five 2.2-µF, 100-V ceramic capacitors will be used. If step input voltage transients are expected near the maximum rating of the LM25118, a careful evaluation of the ringing and possible spikes at the device VIN pin should be completed. An additional damping network or input voltage clamp may be required in these cases.