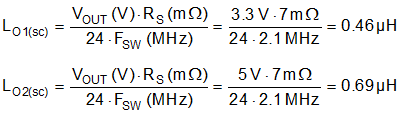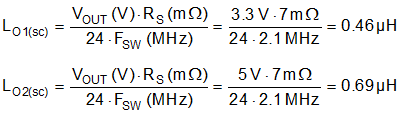SNVSC10 March 2022 LM25143
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 9.3.2 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC, VCCX, VDDA)
- 9.3.3 Enable (EN1, EN2)
- 9.3.4 Power-Good Monitor (PG1, PG2)
- 9.3.5 Switching Frequency (RT)
- 9.3.6 Clock Synchronization (DEMB)
- 9.3.7 Synchronization Out (SYNCOUT)
- 9.3.8 Spread Spectrum Frequency Modulation (DITH)
- 9.3.9 Configurable Soft Start (SS1, SS2)
- 9.3.10 Output Voltage Setpoint (FB1, FB2)
- 9.3.11 Minimum Controllable On Time
- 9.3.12 Error Amplifier and PWM Comparator (FB1, FB2, COMP1, COMP2)
- 9.3.13 Slope Compensation
- 9.3.14 Inductor Current Sense (CS1, VOUT1, CS2, VOUT2)
- 9.3.15 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting (RES)
- 9.3.16 High-Side and Low-Side Gate Drivers (HO1/2, LO1/2, HOL1/2, LOL1/2)
- 9.3.17 Output Configurations (MODE, FB2)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Design 1 – 5-V and 3.3-V Dual-Output Buck Regulator for Computing Applications
- 10.2.2 Design 2 – Two-Phase, 15-A, 2.1-MHz Single-Output Buck Regulator for Server Applications
- 10.2.3 Design 3 – Two-Phase, 50-A, 300-kHz Single-Output Buck Regulator for ASIC Power Applications
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Orderable Information
10.2.1.2.3 Inductor Calculation
- Use Equation 33 to calculate the required buck inductance for each channel based on a 30% inductor ripple current at nominal input voltages.
Equation 33.
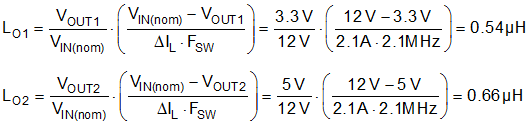
- Select a standard inductor value of 0.68 µH for
both channels. Use Equation 34 to calculate the peak inductor currents at maximum steady-state input
voltage. Subharmonic oscillation occurs with a duty cycle greater than 50% for
peak current-mode control. For design simplification, the LM25143 has an internal slope compensation ramp
proportional to the switching frequency that is added to the current sense
signal to damp any tendency toward subharmonic oscillation. Equation 34.
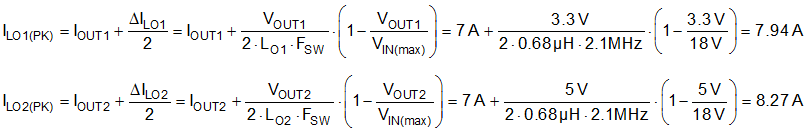
- Based on Equation 10, use Equation 35 to cross-check the inductance to set a slope compensation equal to the ideal one times the inductor current downslope.
Equation 35.