SNVSC10 March 2022 LM25143
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 9.3.2 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC, VCCX, VDDA)
- 9.3.3 Enable (EN1, EN2)
- 9.3.4 Power-Good Monitor (PG1, PG2)
- 9.3.5 Switching Frequency (RT)
- 9.3.6 Clock Synchronization (DEMB)
- 9.3.7 Synchronization Out (SYNCOUT)
- 9.3.8 Spread Spectrum Frequency Modulation (DITH)
- 9.3.9 Configurable Soft Start (SS1, SS2)
- 9.3.10 Output Voltage Setpoint (FB1, FB2)
- 9.3.11 Minimum Controllable On Time
- 9.3.12 Error Amplifier and PWM Comparator (FB1, FB2, COMP1, COMP2)
- 9.3.13 Slope Compensation
- 9.3.14 Inductor Current Sense (CS1, VOUT1, CS2, VOUT2)
- 9.3.15 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting (RES)
- 9.3.16 High-Side and Low-Side Gate Drivers (HO1/2, LO1/2, HOL1/2, LOL1/2)
- 9.3.17 Output Configurations (MODE, FB2)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Design 1 – 5-V and 3.3-V Dual-Output Buck Regulator for Computing Applications
- 10.2.2 Design 2 – Two-Phase, 15-A, 2.1-MHz Single-Output Buck Regulator for Server Applications
- 10.2.3 Design 3 – Two-Phase, 50-A, 300-kHz Single-Output Buck Regulator for ASIC Power Applications
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Orderable Information
7 Pin Configuration and Functions
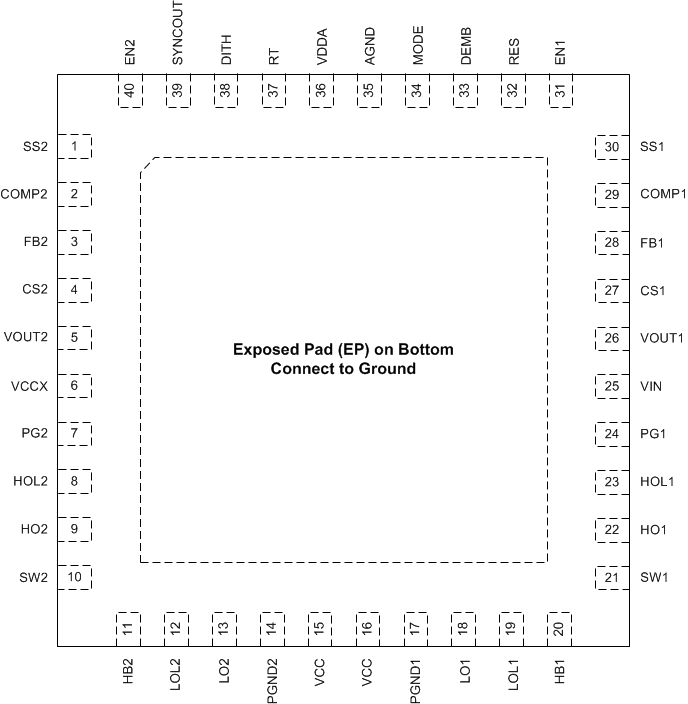
Connect the
exposed pad on the bottom to AGND and PGND on the PCB.
Figure 7-1 40-Pin VQFN RHA Package (Top View)Table 7-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| SS2 | 1 | I | Channel 2 soft-start programming pin. An external ceramic capacitor and an internal 20-μA current source set the ramp rate of the internal error amplifier reference during soft start. Pulling SS2 below 150 mV turns off the channel 2 gate driver outputs, but all the other functions remain active. |
| COMP2 | 2 | O | Output of the channel 2 transconductance error amplifier. COMP2 is high impedance in single-output interleaved or single-output multiphase operation. |
| FB2 | 3 | I | Feedback input of channel 2. Connect FB2 to VDDA for a 3.3-V output or connect FB2 to AGND for a fixed 5-V output. A resistive divider from VOUT2 to FB2 sets the output voltage level between 0.6 V and 55 V. The regulation threshold at FB2 is 0.6 V. |
| CS2 | 4 | I | Channel 2 current sense amplifier input. Connect CS2 to the inductor side of the external current sense resistor (or to the relevant sense capacitor terminal if inductor DCR current sensing is used) using a low-current Kelvin connection. |
| VOUT2 | 5 | I | Output voltage sense and the current sense amplifier input of channel 2. Connect VOUT2 to the output side of the channel 2 current sense resistor (or to the relevant sense capacitor terminal if inductor DCR current sensing is used). |
| VCCX | 6 | P | Optional input for an external bias supply. If VVCCX > 4.3 V, VCCX is internally connected to VCC and the internal VCC regulator is disabled. Connect a ceramic capacitor between VCCX and PGND. |
| PG2 | 7 | O | An open-collector output that goes low if VOUT2 is outside a specified regulation window |
| HOL2 | 8 | O | Channel 2 high-side gate driver turn-off output |
| HO2 | 9 | O | Channel 2 high-side gate driver turn-on output |
| SW2 | 10 | P | Switching node of the channel 2 buck regulator. Connect to the bootstrap capacitor, the source terminal of the high-side MOSFET, and the drain terminal of the low-side MOSFET. |
| HB2 | 11 | P | Channel 2 high-side driver supply for the bootstrap gate drive |
| LOL2 | 12 | O | Channel 2 low-side gate driver turn-off output |
| LO2 | 13 | O | Channel 2 low-side gate driver turn-on output |
| PGND2 | 14 | G | Power-ground connection pin for the low-side NMOS gate driver |
| VCC | 15, 16 | P | VCC bias supply pin. Pins 15 and 16 must to be connected together on the PCB. Connect ceramic capacitors between VCC and PGND1 and between VCC and PGND2. |
| PGND1 | 17 | G | Power-ground connection pin for the low-side NMOS gate driver |
| LO1 | 18 | O | Channel 1 low-side gate driver turn-on output |
| LOL1 | 19 | O | Channel 1 low-side gate driver turn-off output |
| HB1 | 20 | P | Channel 1 high-side driver supply for the bootstrap gate drive |
| SW1 | 21 | P | Switching node of the channel 1 buck regulator. Connect to the channel 1 bootstrap capacitor, the source terminal of the high-side MOSFET, and the drain terminal of the low-side MOSFET. |
| HO1 | 22 | O | Channel 1 high-side gate driver turn-on output |
| HOL1 | 23 | O | Channel 1 high-side gate driver turn-off output |
| PG1 | 24 | O | An open-collector output that goes low if VOUT1 is outside a specified regulation window |
| VIN | 25 | P | Supply voltage input source for the VCC regulators |
| VOUT1 | 26 | I | Output voltage sense and the current sense amplifier input of channel 1. Connect VOUT1 to the output side of the channel 1 current sense resistor (or to the relevant sense capacitor terminal if inductor DCR current sensing is used). |
| CS1 | 27 | I | Channel 1 current sense amplifier input. Connect CS1 to the inductor side of the external current sense resistor (or to the relevant sense capacitor terminal if inductor DCR current sensing is used) using a low-current Kelvin connection. |
| FB1 | 28 | I | Feedback input of channel 1. Connect the FB1 pin to VDDA for a 3.3-V output or connect FB1 to AGND for a 5-V output. A resistive divider from VOUT1 to FB1 sets the output voltage level between 0.6 V and 55 V. The regulation threshold at FB1 is 0.6 V. |
| COMP1 | 29 | O | Output of the channel 1 transconductance error amplifier (EA) |
| SS1 | 30 | I | Channel 1 soft-start programming pin. An external capacitor and an internal 20-μA current source set the ramp rate of the internal error amplifier reference during soft start. Pulling the SS1 voltage below 150 mV turns off the channel 1 gate driver outputs, but all the other functions remain active. |
| EN1 | 31 | I | An active high input (VEN1 > 2 V) enables output 1. If outputs 1 and 2 are disabled, the LM25143 is in shutdown mode unless a SYNC signal is present at DEMB. EN1 must never be floating. |
| RES | 32 | O | Restart timer pin. An external capacitor configures the hiccup-mode current limiting. A capacitor at the RES pin determines the time the controller remains off before automatically restarting in hiccup mode. The two regulator channels operate independently. One channel can operate in normal mode while the other is in hiccup-mode overload protection. Hiccup mode commences when either channel experiences 512 consecutive PWM cycles with cycle-by-cycle current limiting. Connect RES to VDDA during power up to disable hiccup-mode protection. |
| DEMB | 33 | I | Diode emulation pin. Connect DEMB to AGND to enable diode emulation mode. Connect DEMB to VDDA to operate the LM25143 in forced PWM (FPWM) mode with continuous conduction at light loads. DEMB can also be used as a synchronization input to synchronize the internal oscillator to an external clock. |
| MODE | 34 | I | Connect MODE to AGND or VDDA for dual-output or interleaved single-output operation, respectively. This also configures the LM25143 with an EA transconductance of 1200 µS. Connecting a 10-kΩ resistor between MODE and AGND sets the LM25143 for dual-output operation with an ultra-low IQ mode and an EA transconductance of 60 µS. |
| AGND | 35 | G | Analog ground connection. Ground return for the internal voltage reference and analog circuits |
| VDDA | 36 | O | Internal analog bias regulator output. Connect a ceramic decoupling capacitor from VDDA to AGND. |
| RT | 37 | I | Frequency programming pin. A resistor from RT to AGND sets the oscillator frequency between 100 kHz and 2.2 MHz. |
| DITH | 38 | I | A capacitor connected between the DITH pin and AGND is charged and discharged with a 20-µA current source. If dithering is enabled, the voltage on the DITH pin ramps up and down modulating the oscillator frequency between –5% and +5% of the internal oscillator. Connecting DITH to VDDA during power up disables the dither feature. DITH is ignored if an external synchronization clock is used. |
| SYNCOUT | 39 | O | SYNCOUT is a logic level signal with a rising edge approximately 90° lagging HO2 (or 90° leading HO1). When the SYNCOUT signal is used to synchronize a second LM25143 controller, all phases are 90° out of phase. |
| EN2 | 40 | I | An active high input (VEN2 > 2 V) enables output 2. If outputs 1 and 2 are disabled, the LM25143 is in shutdown mode unless a SYNC signal is present on DEMB. EN2 must never be floating. |
(1) P = Power, G = Ground, I = Input, O = Output