SNVSC05 December 2021 LM25148
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 8.3.2 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC, VCCX, VDDA)
- 8.3.3 Precision Enable (EN)
- 8.3.4 Power-Good Monitor (PG)
- 8.3.5 Switching Frequency (RT)
- 8.3.6 Dual Random Spread Spectrum (DRSS)
- 8.3.7 Soft Start
- 8.3.8 Output Voltage Setpoint (FB)
- 8.3.9 Minimum Controllable On Time
- 8.3.10 Error Amplifier and PWM Comparator (FB, EXTCOMP)
- 8.3.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.12 Inductor Current Sense (ISNS+, VOUT)
- 8.3.13 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting
- 8.3.14 High-Side and Low-Side Gate Drivers (HO, LO)
- 8.3.15 Output Configurations (CNFG)
- 8.3.16 Single-Output Dual-Phase Operation
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Design 1 – High Efficiency 2.1-MHz Synchronous
Buck Regulator
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.1.2.2 Custom Design With Excel Quickstart Tool
- 9.2.1.2.3 Buck Inductor
- 9.2.1.2.4 Current-Sense Resistance
- 9.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitors
- 9.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitors
- 9.2.1.2.7 Frequency Set Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.8 Feedback Resistors
- 9.2.1.2.9 Compensation Components
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2 Design 2 – High Efficiency 440-kHz Synchronous Buck Regulator
- 9.2.3 Design 3 – Dual-Phase 400-kHz 20-A Synchronous Buck Regulator
- 9.2.1
Design 1 – High Efficiency 2.1-MHz Synchronous
Buck Regulator
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGY|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGY|24
Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.9 Compensation Components
Choose compensation components for a stable control loop using the procedure outlined as follows:
- Based on a specified loop gain crossover
frequency, fC, of 60 kHz, use Equation 42 to calculate RCOMP, assuming an effective output capacitance of
100 µF. Choose a standard value for RCOMP of 10 kΩ. Equation 42.

- To provide adequate phase boost at crossover
while also allowing a fast settling time during a load or line transient, select
CCOMP to place a zero at the higher of (1) one tenth of the
crossover frequency, or (2) the load pole. Choose a standard value for
CCOMP of 2.7 nF. Equation 43.

Such a low capacitance value also helps to avoid output voltage overshoot when recovering from dropout (when the input voltage is less than the output voltage setpoint and VCOMP is railed high).
- Calculate CHF to create a pole at the
ESR zero and to attenuate high-frequency noise at COMP. CBW is the
bandwidth-limiting capacitance of the error amplifier. CHF may not be
significant enough to be necessary in some designs, like this one.
CHF can be unpopulated, or used with a small 22 pF for more noise
filtering.Equation 44.
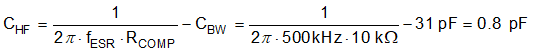
Set a fast loop with high RCOMP and low CCOMP values to improve the response when recovering from operation in dropout.
For technical solutions, industry trends, and insights for designing and managing power supplies, please refer to TI's technical articles.