This typical
characteristics section is applicable for LM358B and LM2904B. Typical
characteristics data in this section was taken with TA = 25°C,
VS = 36 V (±18 V), VCM = VS / 2,
RLOAD = 10 kΩ connected to VS / 2 (unless otherwise
noted).
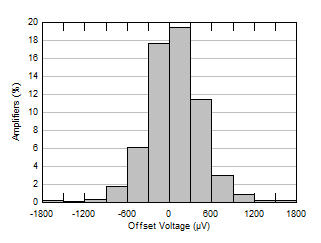 Figure 5-1 Offset Voltage Production Distribution
Figure 5-1 Offset Voltage Production Distribution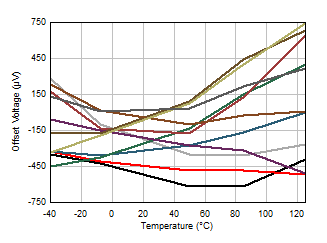 Figure 5-3 Offset Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 5-3 Offset Voltage vs Temperature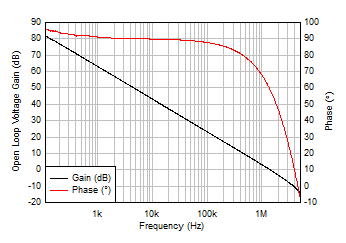 Figure 5-5 Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 5-5 Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency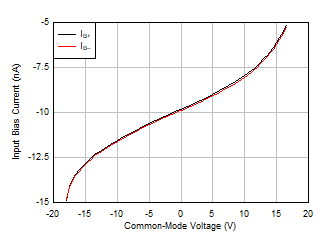 Figure 5-7 Input Bias Current vs Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 5-7 Input Bias Current vs Common-Mode Voltage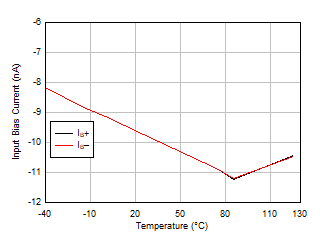 Figure 5-9 Input Bias Current vs Temperature
Figure 5-9 Input Bias Current vs Temperature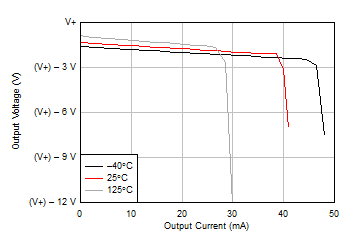 Figure 5-11 Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Sourcing)
Figure 5-11 Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Sourcing)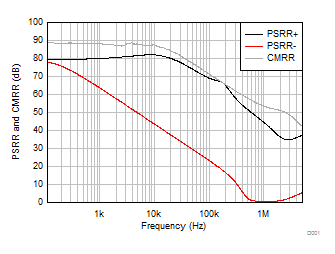 Figure 5-13 CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 5-13 CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency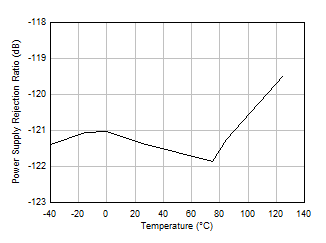 Figure 5-15 Power
Supply Rejection Ratio vs Temperature (dB)
Figure 5-15 Power
Supply Rejection Ratio vs Temperature (dB)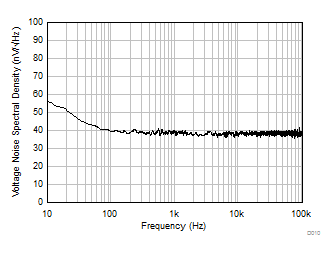 Figure 5-17 Input Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency
Figure 5-17 Input Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency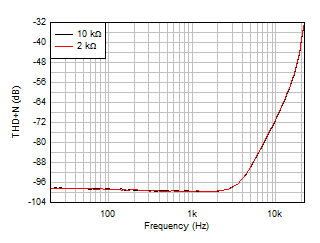
| G = –1, f = 1 kHz, BW = 80
kHz, |
| VOUT = 10
VPP, RL connected to
V– |
| See Figure 6-3 |
Figure 5-19 THD+N
Ratio vs Frequency, G = –1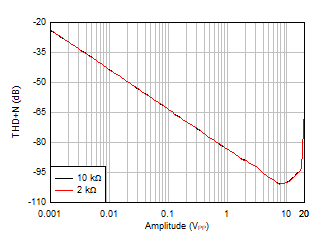
| G = –1, f = 1 kHz, BW = 80
kHz, |
| RL connected to
V– |
| See Figure 6-3 |
Figure 5-21 THD+N
vs Output Amplitude, G = –1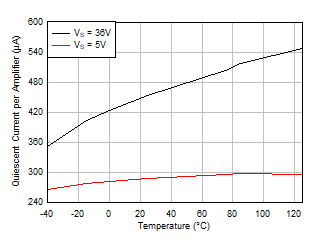 Figure 5-23 Quiescent Current vs Temperature
Figure 5-23 Quiescent Current vs Temperature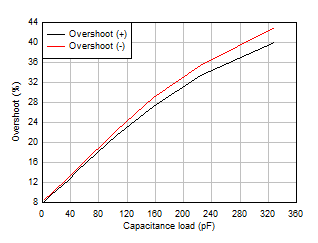
| G = 1, 100-mV output step,
RL = open |
Figure 5-25 Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load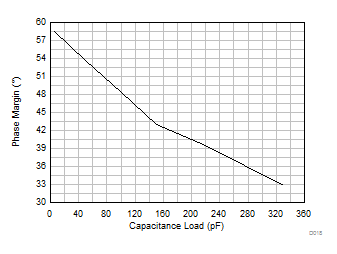 Figure 5-27 Phase
Margin vs Capacitive Load
Figure 5-27 Phase
Margin vs Capacitive Load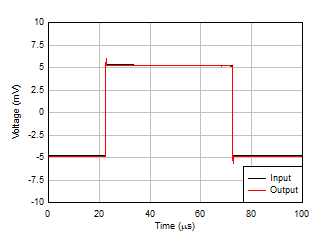 Figure 5-29 Small-Signal Step Response, G = 1
Figure 5-29 Small-Signal Step Response, G = 1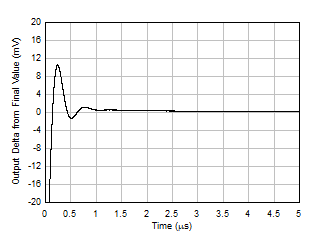 Figure 5-31 Large-Signal Step Response (Rising)
Figure 5-31 Large-Signal Step Response (Rising)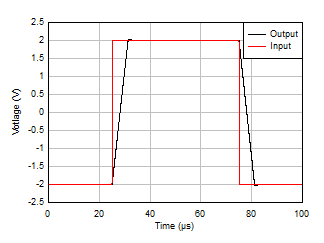 Figure 5-33 Large-Signal Step Response
Figure 5-33 Large-Signal Step Response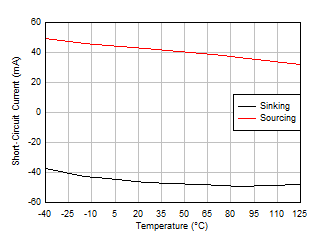 Figure 5-35 Short-Circuit Current vs Temperature
Figure 5-35 Short-Circuit Current vs Temperature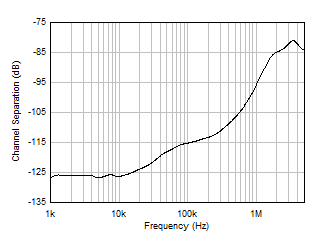 Figure 5-37 Channel Separation vs Frequency
Figure 5-37 Channel Separation vs Frequency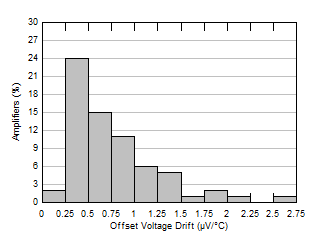 Figure 5-2 Offset Voltage Drift Distribution
Figure 5-2 Offset Voltage Drift Distribution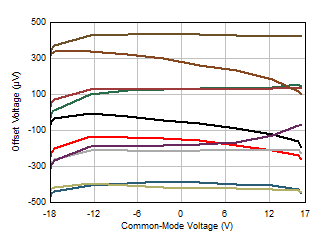 Figure 5-4 Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 5-4 Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage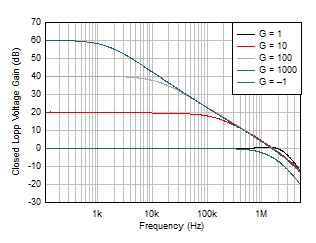 Figure 5-6 Closed-Loop Gain vs Frequency
Figure 5-6 Closed-Loop Gain vs Frequency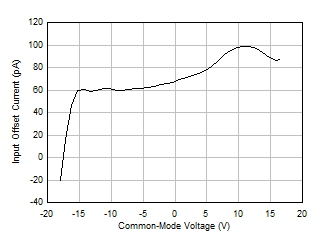 Figure 5-8 Input Offset Current vs Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 5-8 Input Offset Current vs Common-Mode Voltage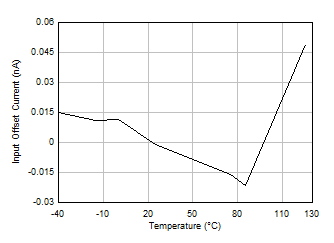 Figure 5-10 Input Offset Current vs Temperature
Figure 5-10 Input Offset Current vs Temperature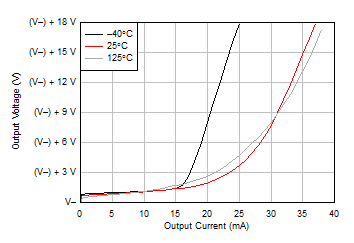 Figure 5-12 Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Sinking)
Figure 5-12 Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Sinking)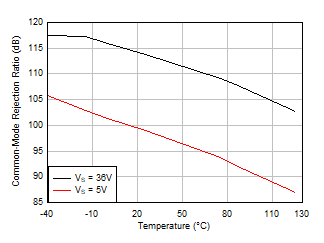 Figure 5-14 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs
Figure 5-14 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs
Temperature
(dB)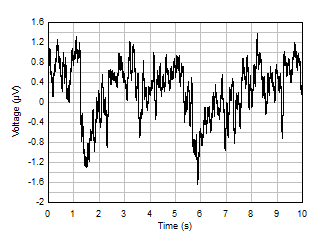 Figure 5-16 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise
Figure 5-16 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise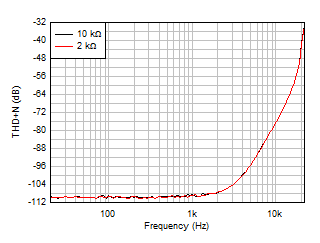
| G = 1, f = 1 kHz, BW = 80
kHz, |
| VOUT = 10
VPP, RL connected to
V– |
Figure 5-18 THD+N
Ratio vs Frequency, G = 1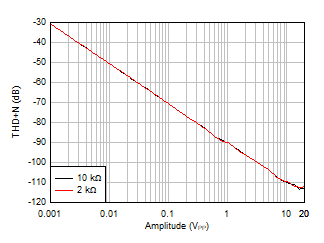
| G = 1, f = 1 kHz, BW = 80
kHz, |
| RL connected to
V– |
| |
Figure 5-20 THD+N
vs Output Amplitude, G = 1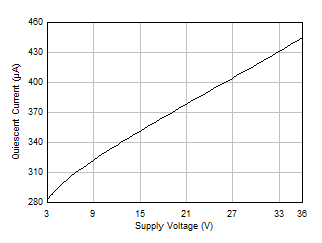 Figure 5-22 Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 5-22 Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage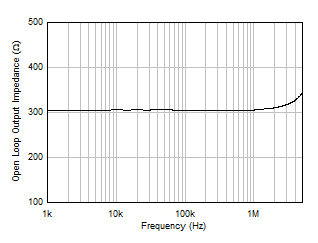 Figure 5-24 Open-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency
Figure 5-24 Open-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency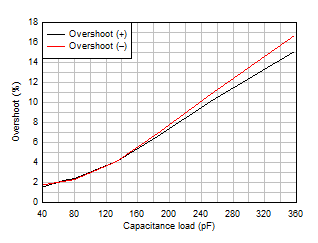
| G = –1, 100-mV output step,
RL = open |
Figure 5-26 Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load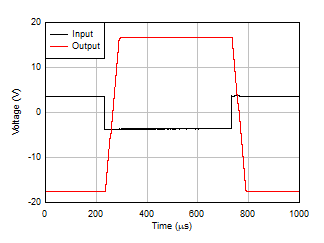 Figure 5-28 Overload Recovery
Figure 5-28 Overload Recovery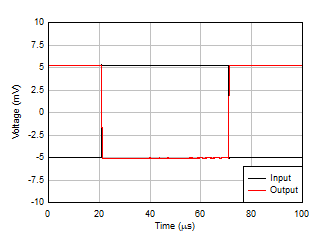 Figure 5-30 Small-Signal Step Response, G = –1
Figure 5-30 Small-Signal Step Response, G = –1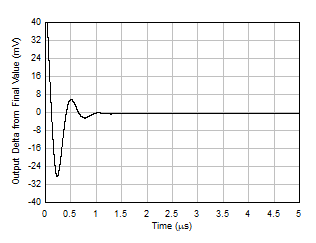 Figure 5-32 Large-Signal Step Response (Falling)
Figure 5-32 Large-Signal Step Response (Falling)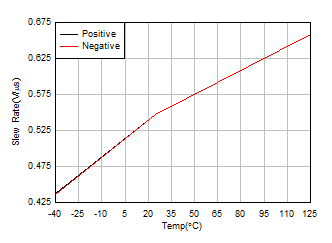 Figure 5-34 Slew
Rate vs Temperature
Figure 5-34 Slew
Rate vs Temperature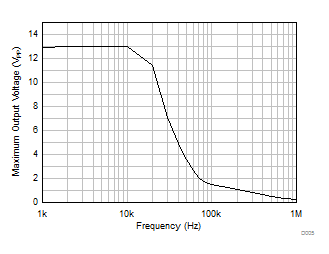 Figure 5-36 Maximum Output Voltage vs Frequency
Figure 5-36 Maximum Output Voltage vs Frequency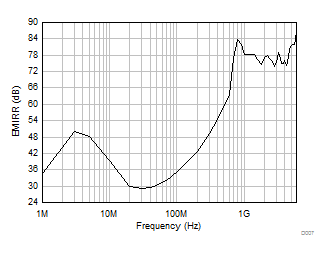 Figure 5-38 EMIRR (Electromagnetic Interference Rejection Ratio) vs Frequency
Figure 5-38 EMIRR (Electromagnetic Interference Rejection Ratio) vs Frequency





 Figure 5-13 CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency
Figure 5-13 CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency

















 Figure 5-14 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs
Figure 5-14 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs 










