SNVSB73 September 2018 LM2735-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 1
- 8.2.2 LM2735Y-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 2
- 8.2.3 LM2735X-Q1 WSON Design Example 3
- 8.2.4 LM2735Y-Q1 WSON Design Example 4
- 8.2.5 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 6
- 8.2.6 LM2735Y-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 7
- 8.2.7 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 8
- 8.2.8 LM2735Y-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 9
- 8.2.9 LM2735X-Q1 WSON Design Example 10
- 8.2.10 LM2735Y-Q1 WSON Design Example 11
- 8.2.11 LM2735X-Q1 WSON SEPIC Design Example 12
- 8.2.12 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 LED Design Example 14
- 8.2.13 LM2735Y-Q1 WSON FlyBack Design Example 15
- 8.2.14 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 LED Design Example 16 VRAIL > 5.5 V Application
- 8.2.15 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 LED Design Example 17 Two-Input Voltage Rail Application
- 8.2.16 SEPIC Converter
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.6 Typical Characteristics
 Figure 1. Current Limit vs Temperature
Figure 1. Current Limit vs Temperature  Figure 3. Oscillator Frequency vs Temperature - "X"
Figure 3. Oscillator Frequency vs Temperature - "X"  Figure 5. Typical Maximum Output Current vs VIN
Figure 5. Typical Maximum Output Current vs VIN 
VO = 20 V
Figure 7. LM2735-Q1X Efficiency vs Load Current 
VO = 12 V
Figure 9. LM2735-Q1X Efficiency vs Load Current  Figure 11. Output Voltage Load Regulation
Figure 11. Output Voltage Load Regulation 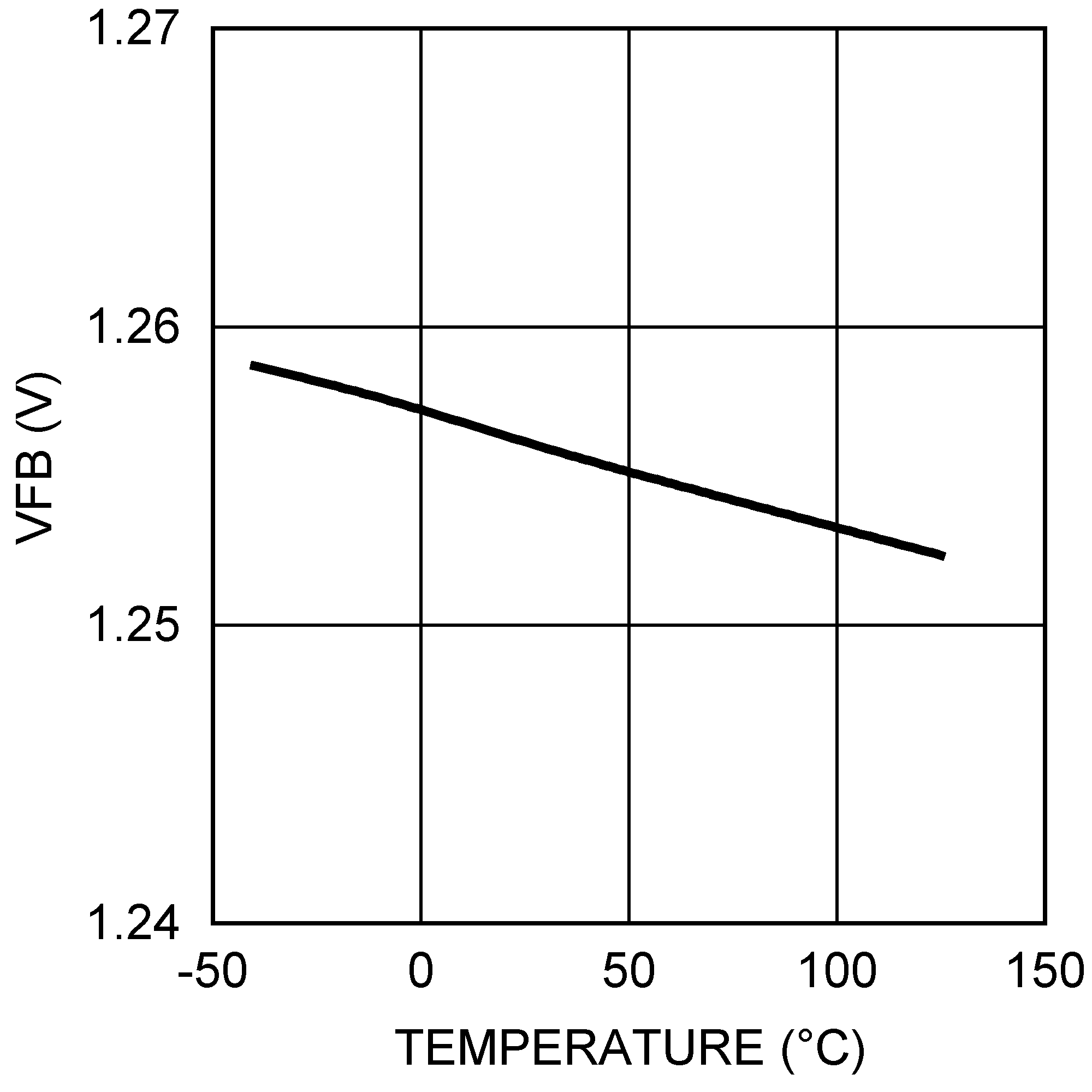 Figure 2. FB Pin Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 2. FB Pin Voltage vs Temperature  Figure 4. Oscillator Frequency vs Temperature - "Y"
Figure 4. Oscillator Frequency vs Temperature - "Y"  Figure 6. RDSON vs Temperature
Figure 6. RDSON vs Temperature 
VO = 20 V
Figure 8. LM2735-Q1Y Efficiency vs Load Current 
VO = 12 V
Figure 10. LM2735-Q1Y Efficiency vs Load Current  Figure 12. Output Voltage Line Regulation
Figure 12. Output Voltage Line Regulation