SNVS615K January 2010 – February 2018 LM27402
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Wide Input Voltage Range
- 7.3.2 UVLO
- 7.3.3 Precision Enable
- 7.3.4 Soft-Start and Voltage Tracking
- 7.3.5 Output Voltage Setpoint and Accuracy
- 7.3.6 Voltage-Mode Control
- 7.3.7 Power Good
- 7.3.8 Inductor-DCR-Based Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.9 Current Sensing
- 7.3.10 Power MOSFET Gate Drivers
- 7.3.11 Pre-Bias Start-up
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Converter Design
- 8.1.2 Inductor Selection (L)
- 8.1.3 Output Capacitor Selection (COUT)
- 8.1.4 Input Capacitor Selection (CIN)
- 8.1.5 Using Precision Enable
- 8.1.6 Setting the Soft-Start Time
- 8.1.7 Tracking
- 8.1.8 Setting the Switching Frequency
- 8.1.9 Setting the Current Limit Threshold
- 8.1.10 Control Loop Compensation
- 8.1.11 MOSFET Gate Drivers
- 8.1.12 Power Loss and Efficiency Calculations
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.8 Typical Performance Characteristics
Unless otherwise stated, all data sheet curves were recorded using Example Circuit 1. VIN = 12 V.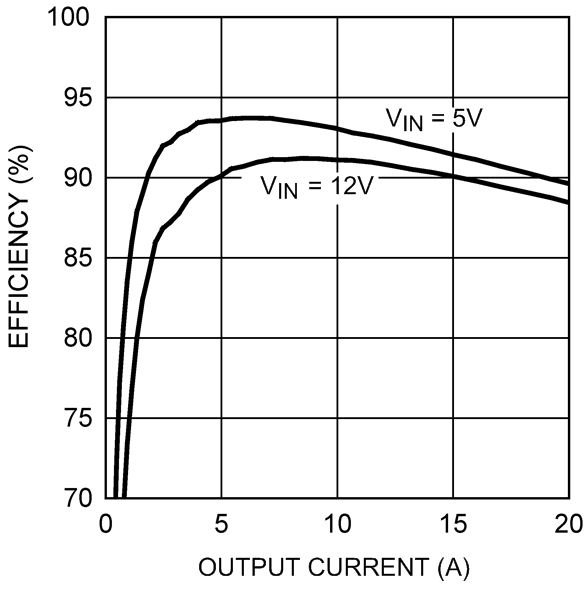 Figure 1. Efficiency (Vout = 1.5 V)
Figure 1. Efficiency (Vout = 1.5 V)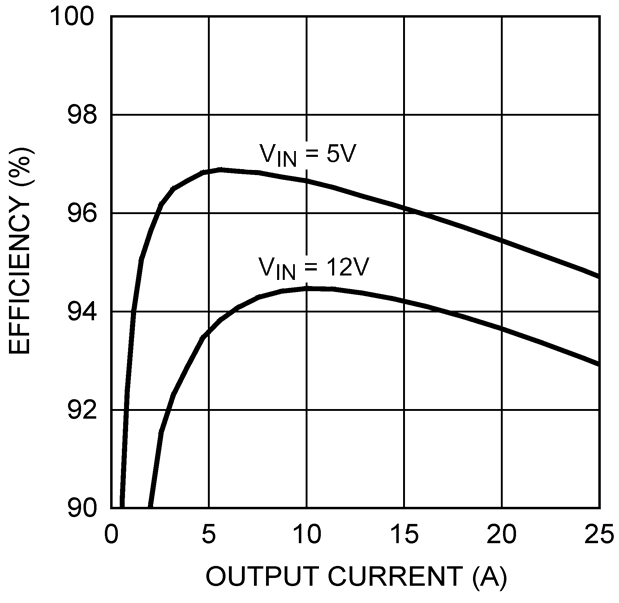 Figure 3. Efficiency (Vout = 3.3 V, Example Circuit 2)
Figure 3. Efficiency (Vout = 3.3 V, Example Circuit 2) 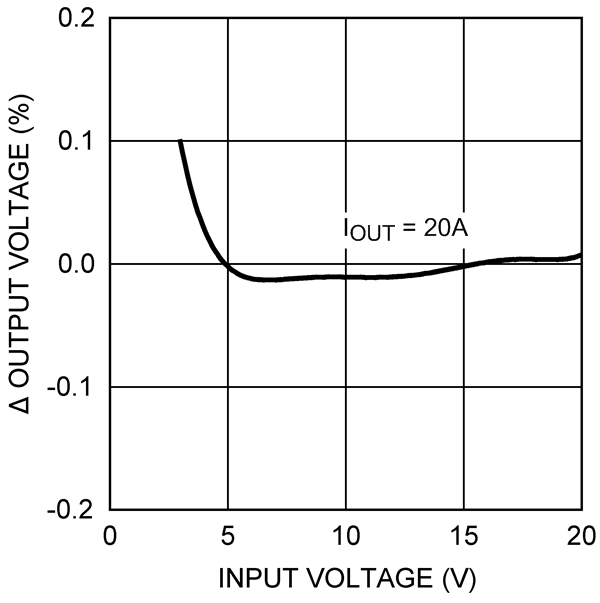 Figure 5. Line Regulation (Vout = 1.5 V)
Figure 5. Line Regulation (Vout = 1.5 V)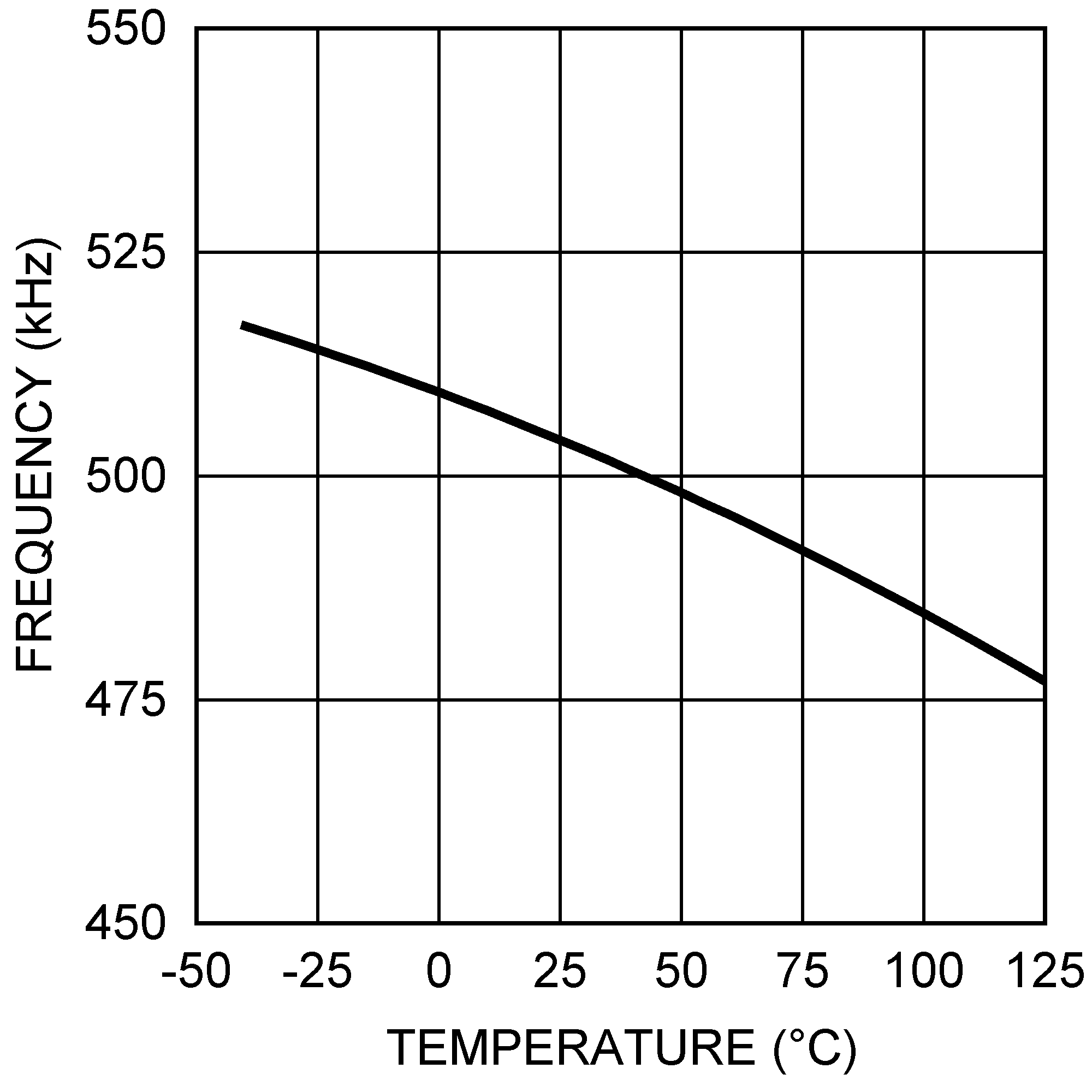 Figure 7. Frequency vs Temperature (RFADJ = 20 kΩ)
Figure 7. Frequency vs Temperature (RFADJ = 20 kΩ) 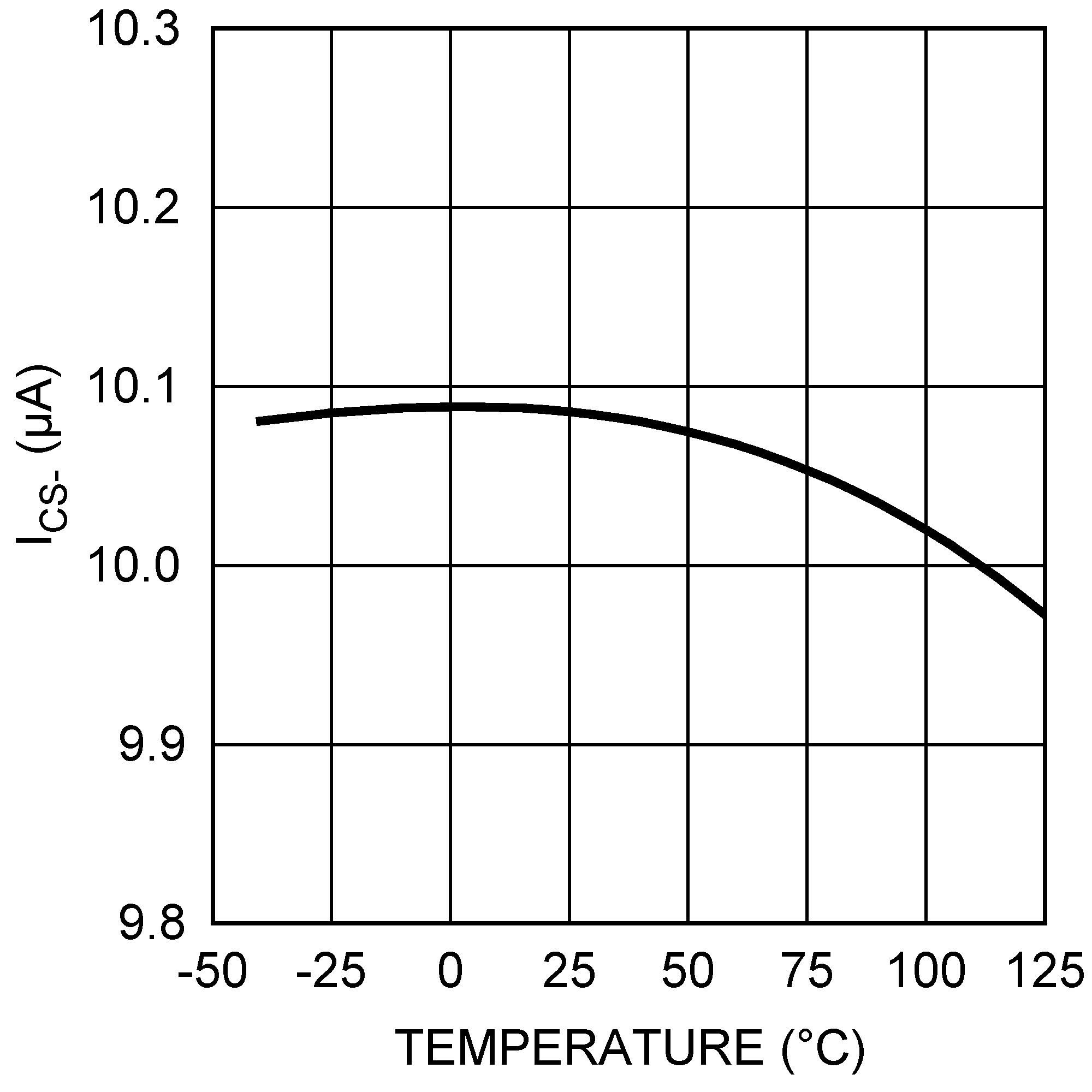 Figure 9. CS– Current Source vs Temperature
Figure 9. CS– Current Source vs Temperature Figure 11. CS– Current Source Compliance Voltage
Figure 11. CS– Current Source Compliance Voltage
Horizontal Scale: 2 ms/DIV
Figure 13. Start-up Waveforms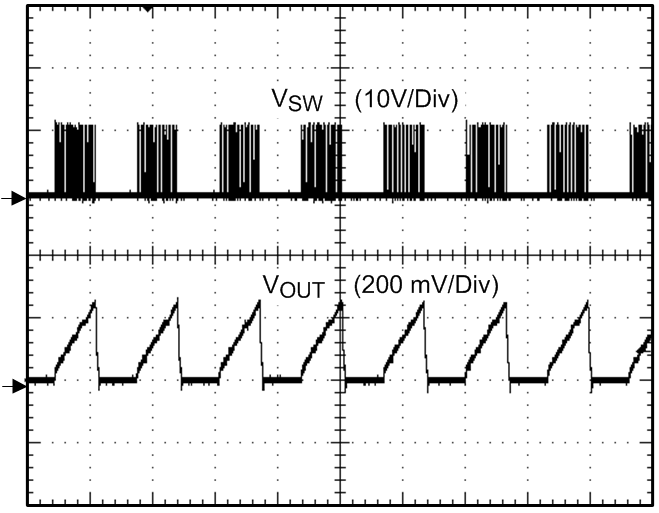
Horizontal Scale: 2 ms/DIV
Figure 15. OCP Hiccup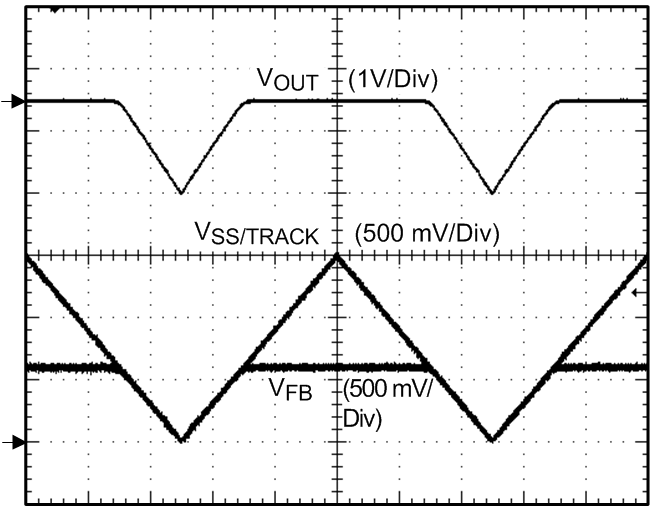
Horizontal Scale: 2 ms/DIV
Figure 17. Tracking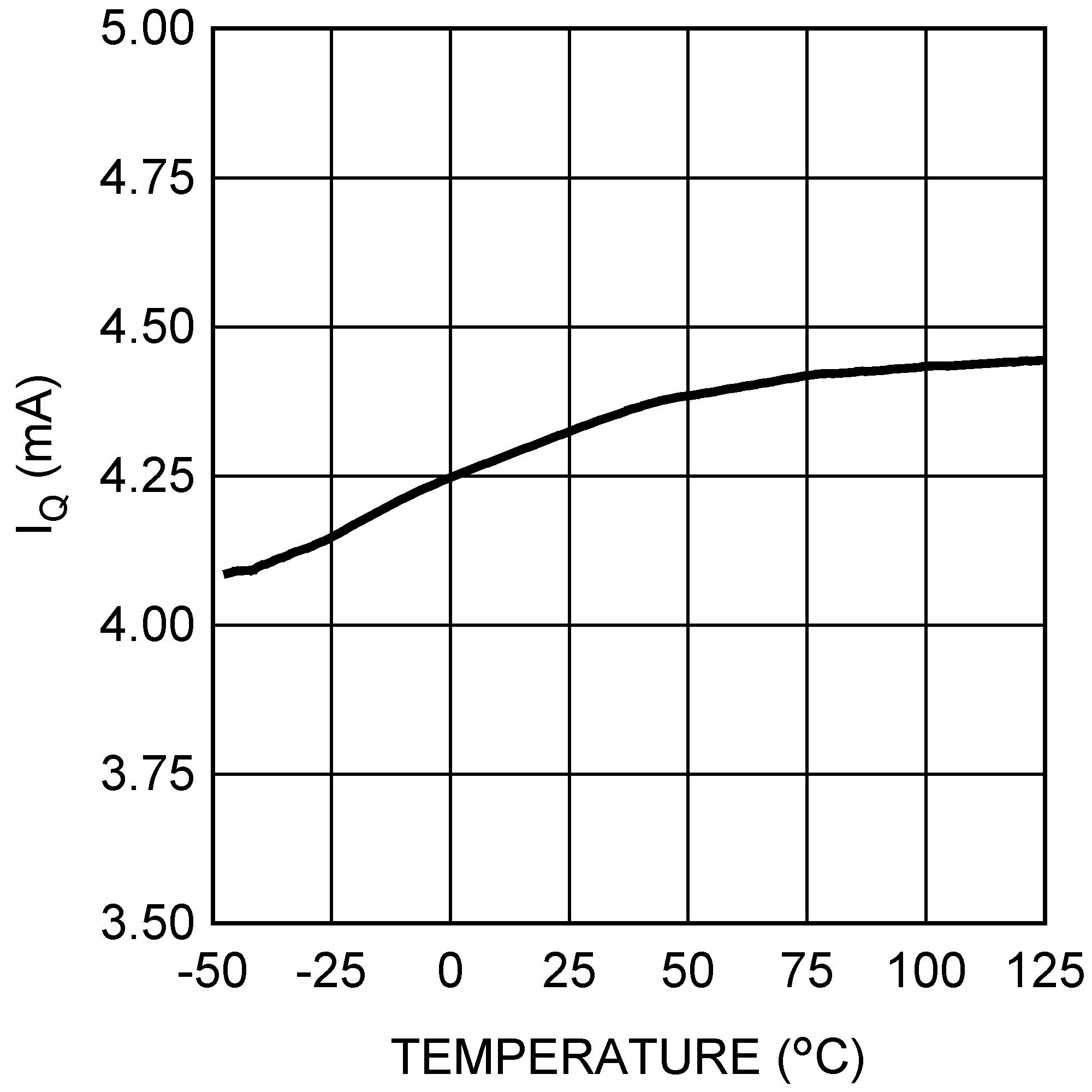 Figure 19. Quiescent Current vs Temperature
Figure 19. Quiescent Current vs Temperature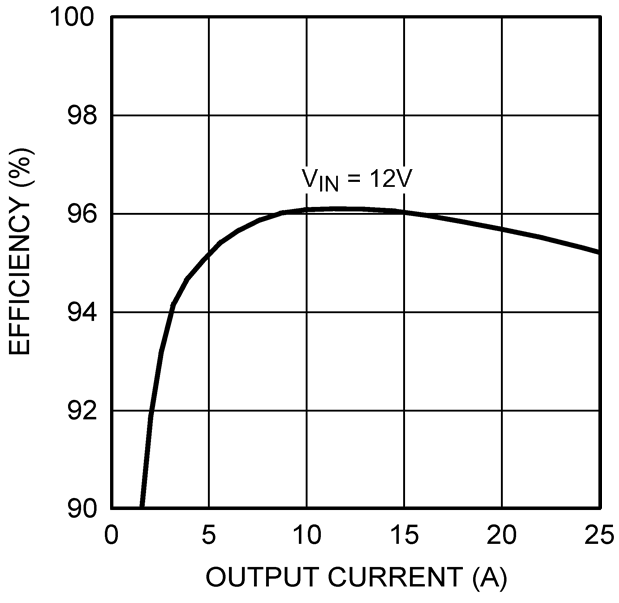 Figure 2. Efficiency (Vout = 5 V, Example Circuit 2)
Figure 2. Efficiency (Vout = 5 V, Example Circuit 2)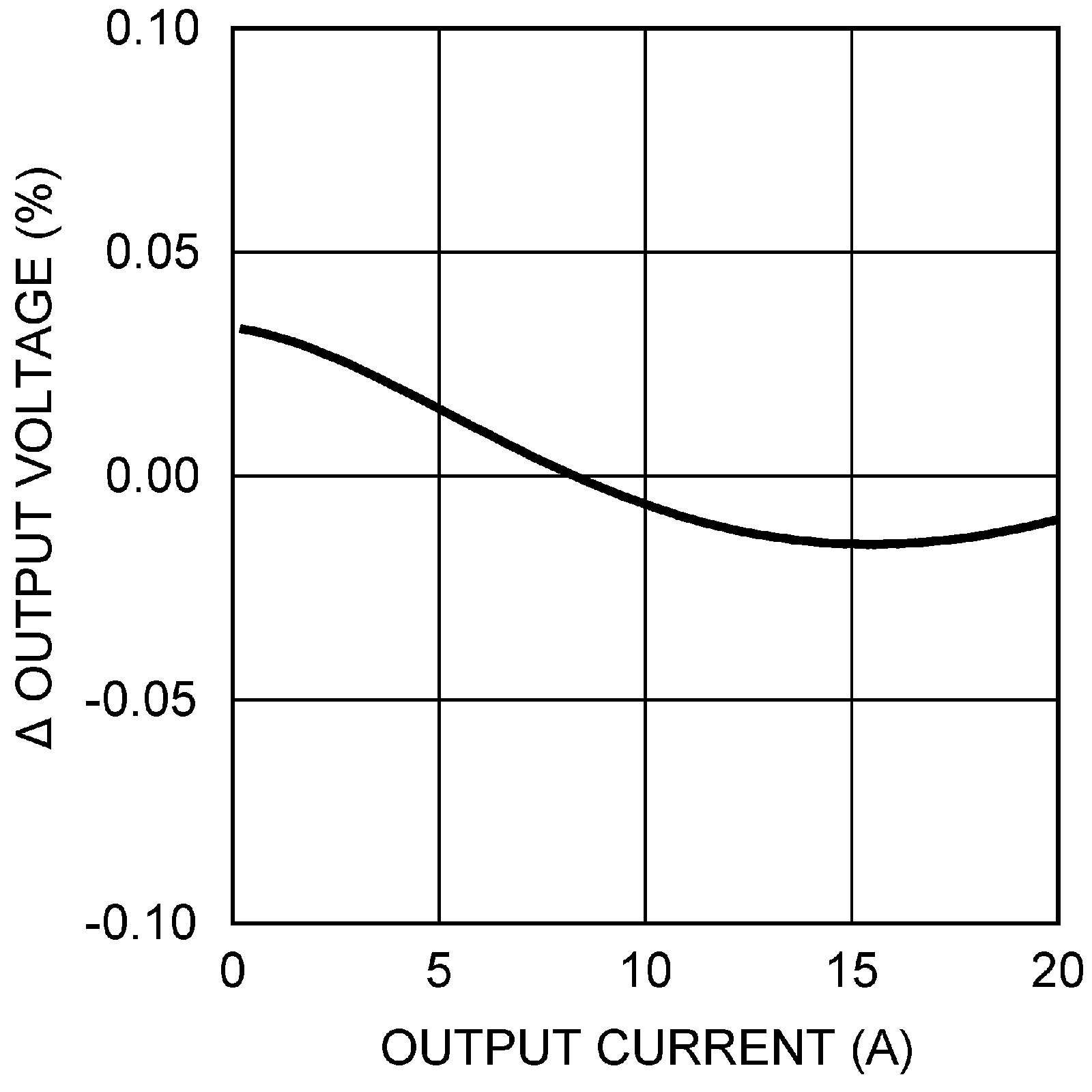 Figure 4. Load Regulation (Vout = 1.5 V)
Figure 4. Load Regulation (Vout = 1.5 V) Figure 6. VDD Voltage vs Temperature (IVDD = 25 mA)
Figure 6. VDD Voltage vs Temperature (IVDD = 25 mA)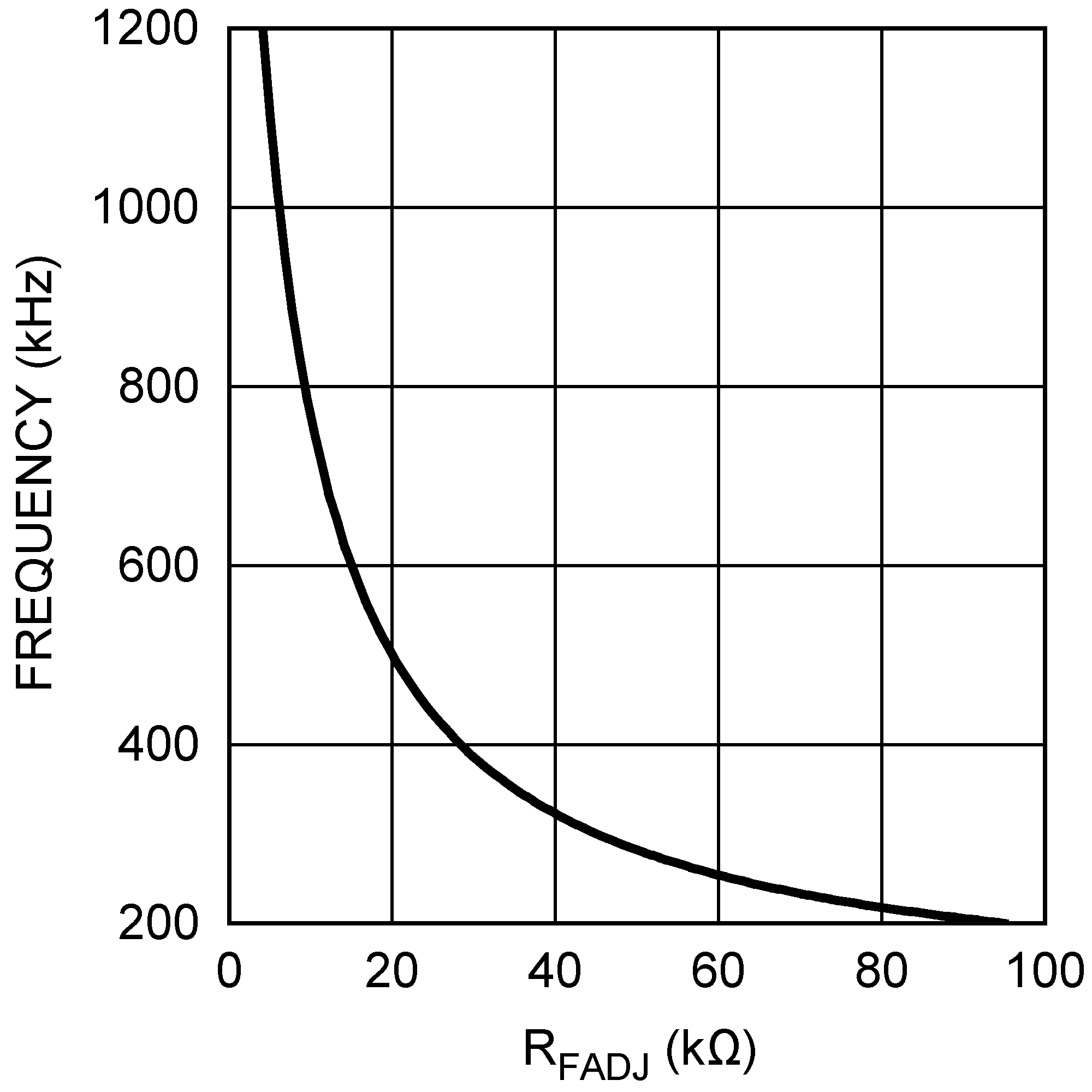 Figure 8. Frequency vs RFADJ
Figure 8. Frequency vs RFADJ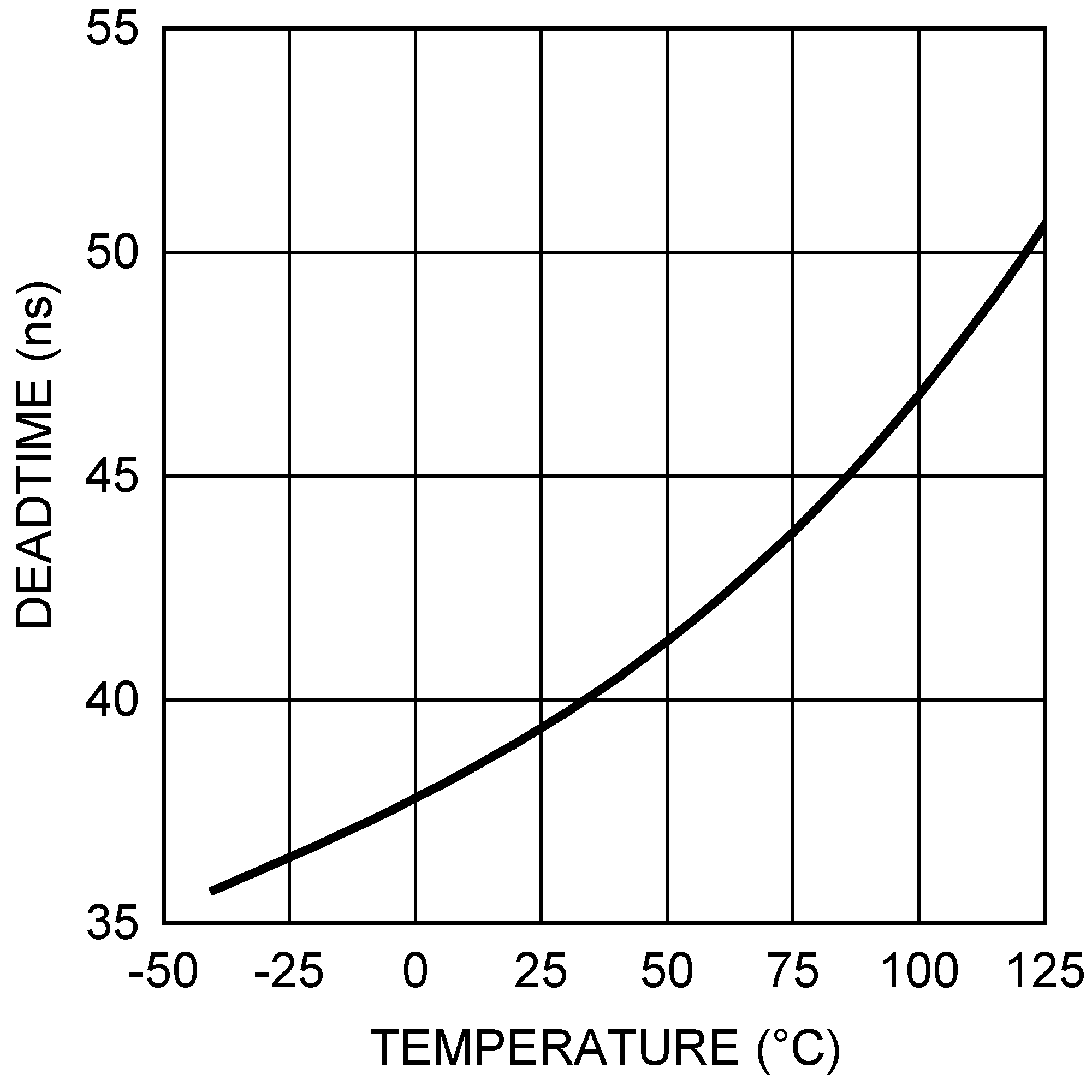 Figure 10. Deadtime vs Temperature
Figure 10. Deadtime vs Temperature
Horizontal Scale: 100 µs/DIV
Figure 12. Load Transient
Horizontal Scale: 2 ms/DIV
Figure 14. Pre-Bias Start-up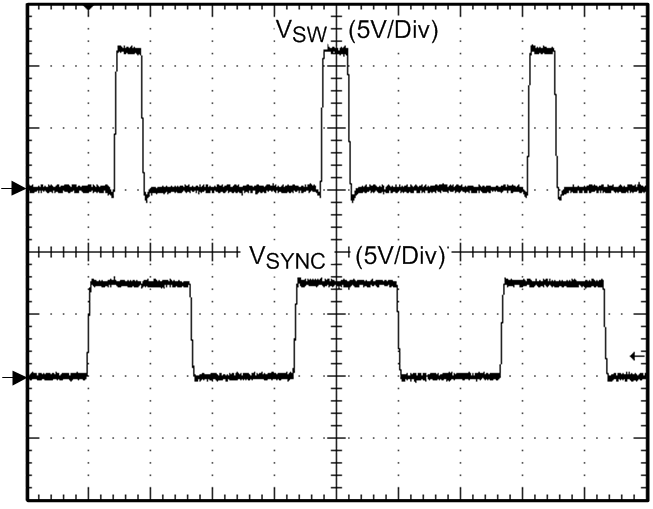
Horizontal Scale: 400 ns/DIV
Figure 16. Frequency Synchronization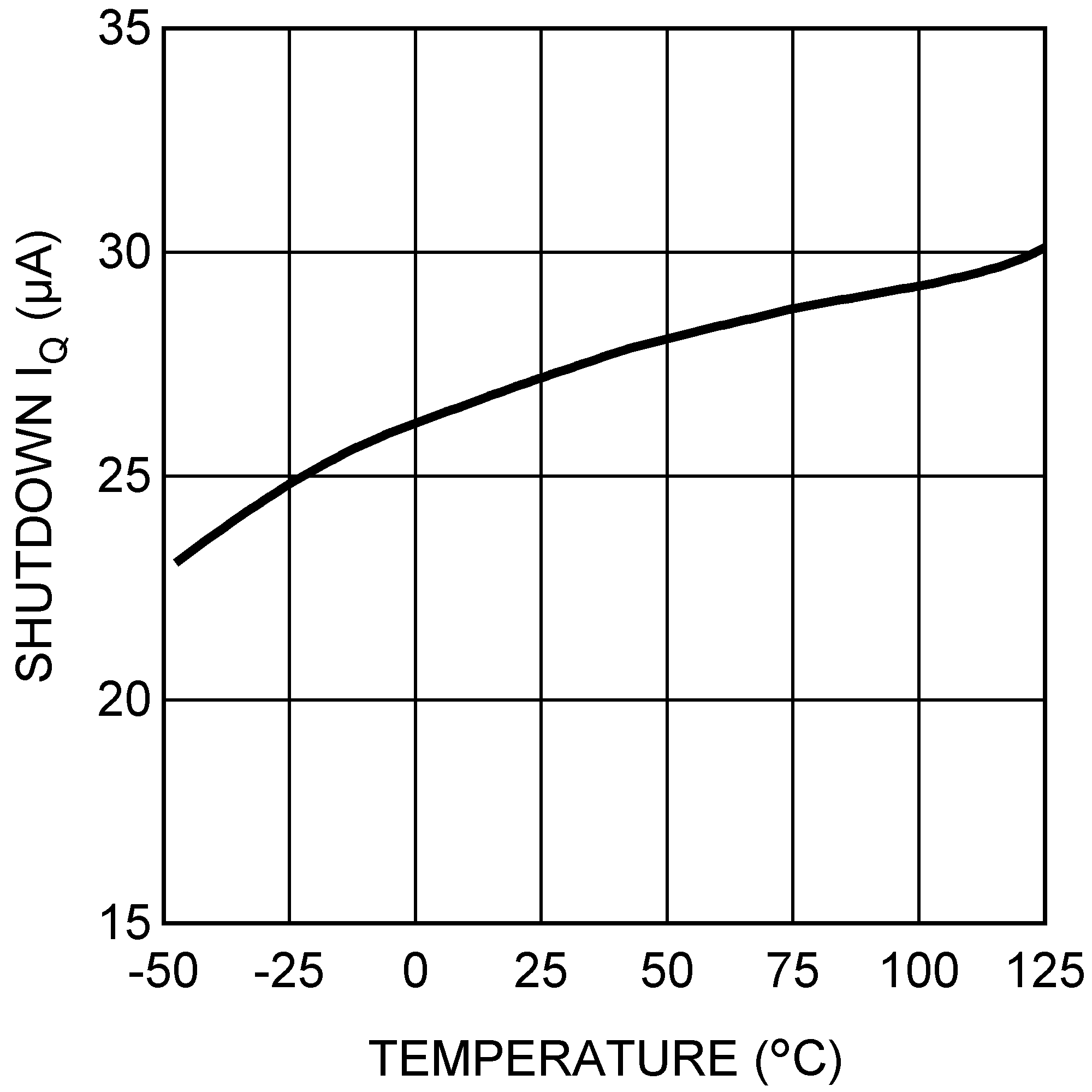 Figure 18. Shutdown Quiescent Current vs Temperature
Figure 18. Shutdown Quiescent Current vs Temperature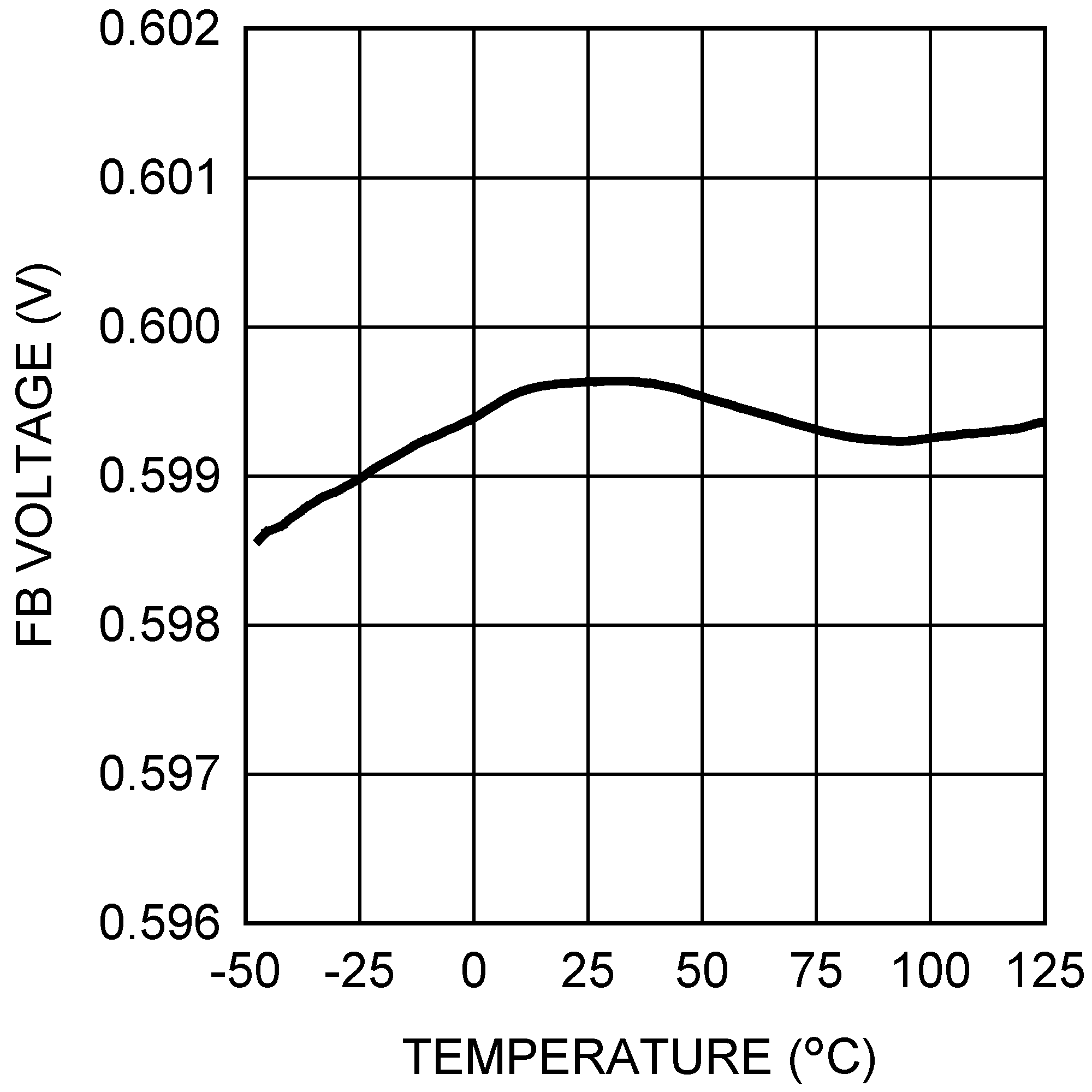 Figure 20. Feedback Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 20. Feedback Voltage vs Temperature