SNVS276I April 2004 – February 2019 LM2743
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor
The input capacitors in a Buck converter are subjected to high stress due to the input current trapezoidal waveform. Input capacitors are selected for their ripple current capability and their ability to withstand the heat generated since that ripple current passes through their ESR. Input rms ripple current is approximately:
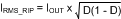
The power dissipated by each input capacitor is:
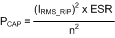
where n is the number of capacitors, and ESR is the equivalent series resistance of each capacitor. The equation above indicates that power loss in each capacitor decreases rapidly as the number of input capacitors increases. The worst-case ripple for a Buck converter occurs during full load and when the duty cycle (D) is 0.5. For this 3.3V to 1.2V design the duty cycle is 0.364. For a 4A maximum load the ripple current is 1.92A.