SNVS678F June 2010 – November 2015 LM3414 , LM3414HV
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
Discontinuous currents are the most likely to generate EMI; therefore, take care when routing these paths. The main path for discontinuous current in the LM3414/HV buck converter contains the input capacitor (CIN), the recirculating diode (D1), and the switch node (LX). This loop should be kept as small as possible and the connections between all three components should be short and thick to minimize parasitic inductance. In particular, the switch node (where L1, D1 and LX connect) should be just large enough to connect the components without excessive heating from the current it carries.
The IADJ, FS, and DIM pins are all high-impedance control inputs which couple external noise easily, therefore the loops containing these high impedance nodes should be minimized. The frequency setting resistor (RFS) and current setting resistor (RIADJ) should be placed close to the FS and IADJ pins as possible.
10.2 Layout Example
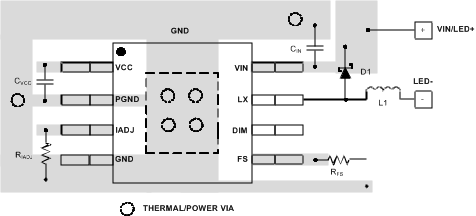 Figure 25. Layout Recommendation
Figure 25. Layout Recommendation