SNVS574G July 2008 – July 2019 LM3421 , LM3423
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Current Regulators
- 8.3.2 Predictive Off-Time (PRO) Control
- 8.3.3 Average LED Current
- 8.3.4 Analog Dimming
- 8.3.5 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.3.6 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.7 Zero Current Shutdown
- 8.3.8 Control Loop Compensation
- 8.3.9 Start-Up Regulator
- 8.3.10 Overvoltage Lockout (OVLO)
- 8.3.11 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.12 PWM Dimming
- 8.3.13 LM3423 Only: DPOL, FLT, TIMR, and LRDY
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Basic Topology Schematics
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Operating Point
- 9.2.1.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 9.2.1.2.3 Average LED Current
- 9.2.1.2.4 Inductor Ripple Current
- 9.2.1.2.5 LED Ripple Current
- 9.2.1.2.6 Peak Current Limit
- 9.2.1.2.7 Loop Compensation
- 9.2.1.2.8 Input Capacitance
- 9.2.1.2.9 N-channel FET
- 9.2.1.2.10 Diode
- 9.2.1.2.11 Output OVLO
- 9.2.1.2.12 Input UVLO
- 9.2.1.2.13 PWM Dimming Method
- 9.2.1.2.14 Analog Dimming Method
- 9.2.2
LM3421 Buck-Boost Application
- 9.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.2.1 Operating Point
- 9.2.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 9.2.2.2.3 Average LED Current
- 9.2.2.2.4 Inductor Ripple Current
- 9.2.2.2.5 Output Capacitance
- 9.2.2.2.6 Peak Current Limit
- 9.2.2.2.7 Loop Compensation
- 9.2.2.2.8 Input Capacitance
- 9.2.2.2.9 N-channel FET
- 9.2.2.2.10 Diode
- 9.2.2.2.11 Input UVLO
- 9.2.2.2.12 Output OVLO
- 9.2.2.3 Application Curve
- 9.2.3 LM3421 BOOST Application
- 9.2.4 LM3421 Buck-Boost Application
- 9.2.5 LM3423 Boost Application
- 9.2.6 LM3421 Buck-Boost Application
- 9.2.7 LM3423 Buck Application
- 9.2.8 LM3423 Buck-Boost Application
- 9.2.9 LM3421 SEPIC Application
- 9.2.1
Basic Topology Schematics
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.1 Operating Point
Given the number of series LEDs (N), the forward voltage (VLED) and dynamic resistance (rLED) for a single LED, solve for the nominal output voltage (VO) and the nominal LED string dynamic resistance (rD):
Equation 34. 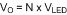
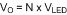
Equation 35. 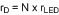
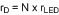
Solve for the ideal nominal duty cycle (D):
Buck:
Equation 36. 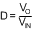
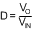
Boost:
Equation 37. 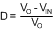
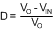
Buck-Boost:
Equation 38. 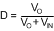
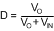
Using the same equations, find the minimum duty cycle (DMIN) using maximum input voltage (VIN-MAX) and the maximum duty cycle (DMAX) using the minimum input voltage (VIN-MIN). Also, remember that D' = 1 - D.