SNVS085X July 2000 – December 2017 LM3478
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Typical High Efficiency Step-Up (Boost) Converter
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Power Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.3 Programming the Output Voltage
- 8.2.1.2.4 Setting the Current Limit
- 8.2.1.2.5 Current Limit with External Slope Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.6 Power Diode Selection
- 8.2.1.2.7 Power MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.1.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.10 Compensation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Typical SEPIC Converter
- 8.2.1
Typical High Efficiency Step-Up (Boost) Converter
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.9 Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor in a boost converter provides all the output current when the inductor is charging. As a result it sees very large ripple currents. The output capacitor should be capable of handling the maximum RMS current. Equation 32 shows the RMS current in the output capacitor.
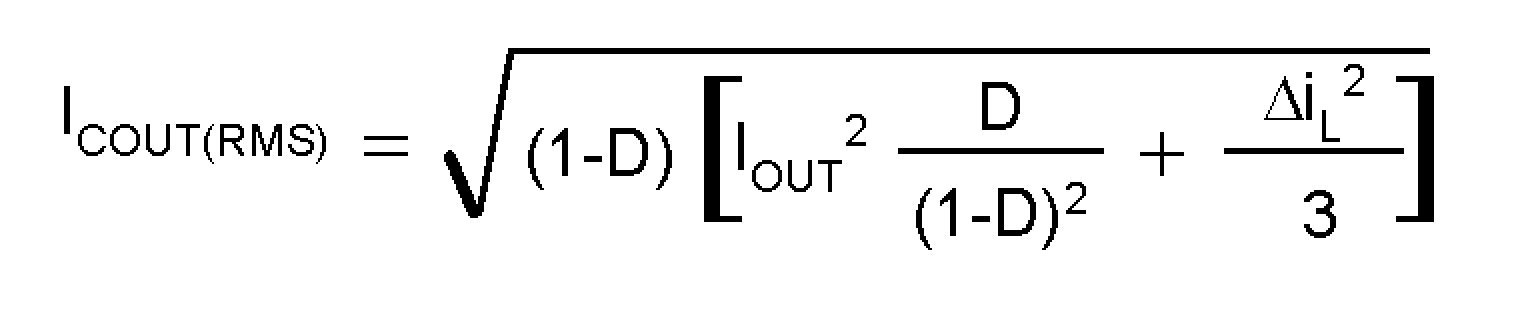
Where
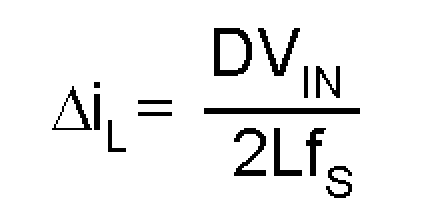
The ESR and ESL of the capacitor directly control the output ripple. Use capacitors with low ESR and ESL at the output for high efficiency and low ripple voltage. Surface mount tantalums, surface mount polymer electrolytic, polymer tantalum, or multi-layer ceramic capacitors are recommended at the output.
For applications that require very low output voltage ripple, a second stage LC filter often is a good solution. Most of the time it is lower cost to use a small second Inductor in the power path and an additional final output capacitor than to reduce the output voltage ripple by purely increasing the output capacitor without an additional LC filter.