SNVS346H November 2007 – October 2024 LM3481
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Applications
- 7.2.1
Boost Converter
- 7.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 7.2.1.2.2 Power Inductor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.3 Programming the Output Voltage and Output Current
- 7.2.1.2.4 Current Limit With Additional Slope Compensation
- 7.2.1.2.5 Power Diode Selection
- 7.2.1.2.6 Power MOSFET Selection
- 7.2.1.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.8 Output Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.9 Driver Supply Capacitor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.10 Compensation
- 7.2.1.3 Application Curve
- 7.2.2 Typical SEPIC Converter
- 7.2.1
Boost Converter
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGS|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.2.1.2.8 Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor in a boost converter provides all the output current when the inductor is charging. As a result it sees very large ripple currents. The output capacitor should be capable of handling the maximum rms current. The rms current in the output capacitor is:
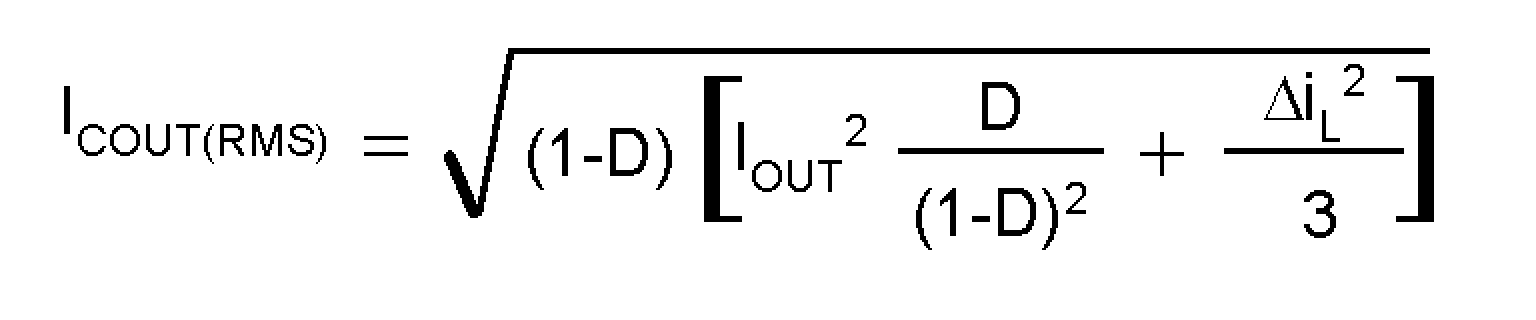
Where
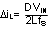
and D, the duty cycle is equal to (VOUT − VIN)/VOUT.
The ESR and ESL of the output capacitor directly control the output ripple. Use capacitors with low ESR and ESL at the output for high efficiency and low ripple voltage. Surface mount tantalums, surface mount polymer electrolytic and polymer tantalum, Sanyo- OSCON, or multi-layer ceramic capacitors are recommended at the output.