SNVS598B August 2010 – March 2018 LM3535
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFQ|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.6 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified: TA = 25°C; VIN = 3.6 V; VHWEN = VIN; CIN= 1 µF, COUT = 1 µF, C1 = C2 = 1 µF.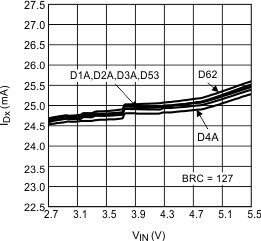
Figure 2. ILED vs Input Voltage 6 LEDs
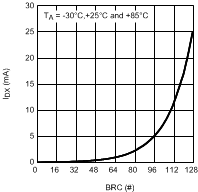
Figure 4. ILED vs Brightness Code Linear Scale
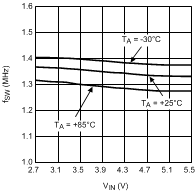
Figure 6. Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage Tri-Temp
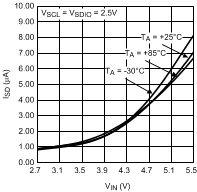
Figure 8. Shutdown Current vs Input Voltage VIO = 2.5 V
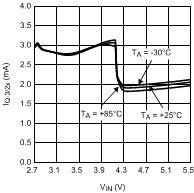
Figure 10. Quiescent Current vs Input Voltage 3/2× Gain
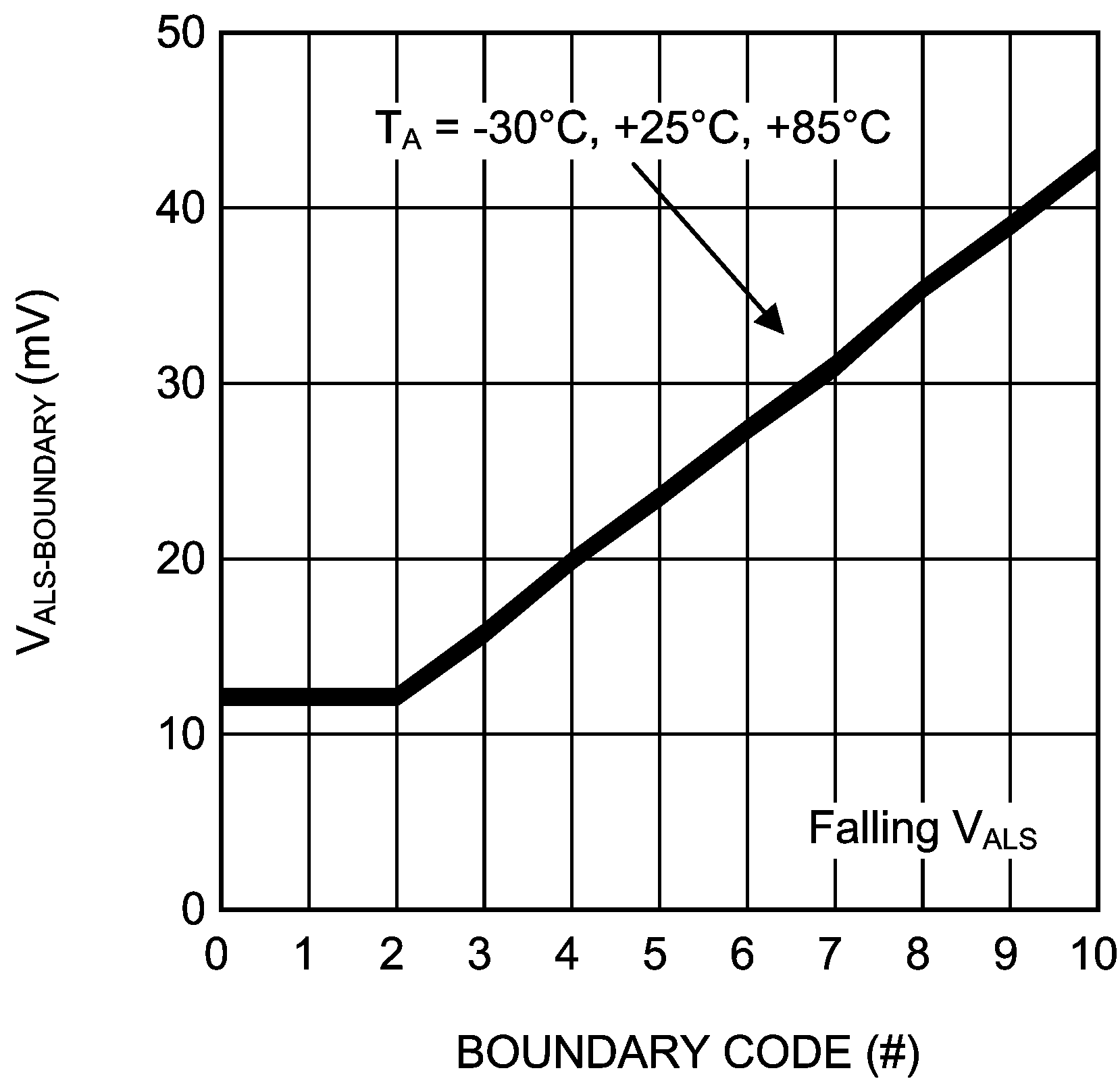
Figure 12. ALS Boundary Voltage vs Boundary Code Falling ALS Voltage (Zoom)
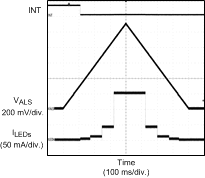
Figure 14. Ambient Light Sensor Response
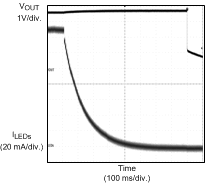
Figure 16. Diode Current Ramp-Down TSTEP = 6 ms
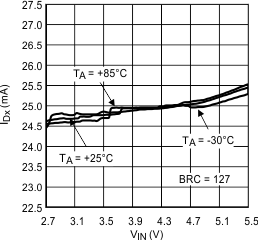
Figure 3. ILED vs Input Voltage
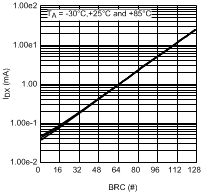
Figure 5. ILED vs Brightness Code Log Scale
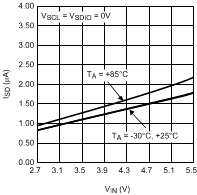
Figure 7. Shutdown Current vs Input Voltage VIO = 0 V
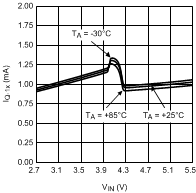
Figure 9. Quiescent Current vs Input Voltage 1× Gain
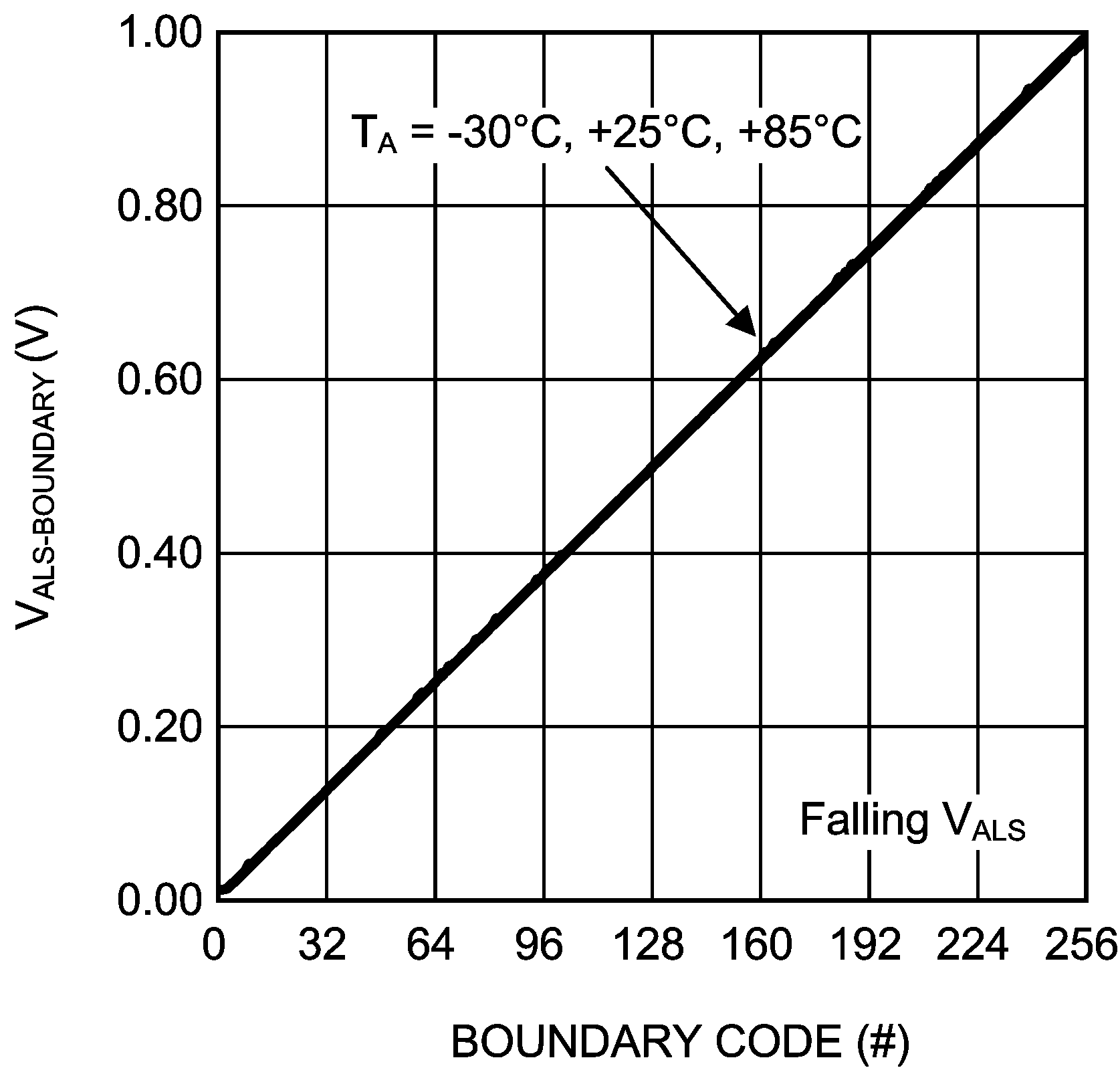
Figure 11. ALS Boundary Voltage vs Boundary Code Falling ALS Voltage
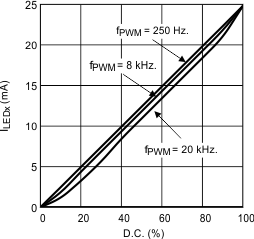
Figure 13. Diode Current vs PWM Duty Cycle
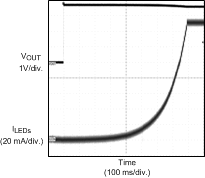
Figure 15. Diode Current Ramp-Up TSTEP = 6 ms