SNVSAJ7D February 2016 – March 2018 LM36272
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Features Description
- 7.3.1 Enabling the LM36272
- 7.3.2 Backlight
- 7.3.3 LCM Bias
- 7.3.4 Software Reset
- 7.3.5 HWEN Input
- 7.3.6 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Revision Register (Address = 0x01)[Reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2 Backlight Configuration1 Register (Address = 0x02)[Reset = 0x28]
- 7.6.3 Backlight Configuration 2 Register (Address = 0x03)[Reset = 0x8D]
- 7.6.4 Backlight Brightness LSB Register (Address = 0x04)[Reset = 0x07]
- 7.6.5 Backlight Brightness MSB Register (Address = 0x05)[Reset = 0xFF]
- 7.6.6 Backlight Auto-Frequency Low Threshold Register (Address = 0x06)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.7 Backlight Auto-Frequency High Threshold Register (Address = 0x07)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.8 Backlight Enable Register (Address = 0x08)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.9 Bias Configuration 1 Register (Address = 0x09)[Reset = 0x18]
- 7.6.10 Bias Configuration 2 register (Address = 0x0A)[Reset = 0x11]
- 7.6.11 Bias Configuration 3 Register (Address = 0x0B)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.12 LCM Boost Bias Register (Address = 0x0C)[Reset = 0x28]
- 7.6.13 VPOS Bias Register (Address = 0x0D)[Reset = 0x1E]
- 7.6.14 VNEG Bias Register (Address = 0x0E)[Reset = 0x1C]
- 7.6.15 Flags Register (Address = 0x0F)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.16 Option 1 Register (Address = 0x10)[Reset = 0x06]
- 7.6.17 Option 2 Register (Address = 0x11)[Reset = 0x35]
- 7.6.18 PWM-to-Digital Code Readback LSB Register (Address = 0x12)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.19 PWM-to-Digital Code Readback MSB Register (Address = 0x13)[Reset = 0x00]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFF|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.2.7.2 PWM Hysteresis
To prevent jitter at the input PWM signal from feeding through the PWM path and causing oscillations in the LED current, the LM36272 offers 4 selectable hysteresis settings. The hysteresis options for the 1-MHz and 4-MHz PWM sample rate settings are 1, 2, 4, and 6 bits and for the 24-MHz PWM sample rate setting 0, 1, 2, and 3 bits. The hysteresis works by forcing a specific number of 11-bit LSB code transitions to occur in the input duty cycle before the LED current changes. Table 6 describes the hysteresis. The hysteresis only applies during the change in direction of brightness currents. Once a change in the direction of the LED current has taken place, the PWM input must over come the required LSB(s) of the hysteresis setting before the brightness change takes effect. Once the initial hysteresis has been overcome and the direction in brightness change remains the same, the PWM to current response changes with no hysteresis.
Table 6. PWM Input Hysteresis
| HYSTERESIS SETTING (0x03 Bits[1:0]) | MIN CHANGE IN PWM PULSE WIDTH (Δt) REQUIRED TO CHANGE LED CURRENT, AFTER DIRECTION CHANGE (for ƒPWM < 11.7 kHz) | MIN CHANGE IN PWM DUTY CYCLE (ΔD) REQUIRED TO CHANGE LED CURRENT AFTER DIRECTION CHANGE | MIN (ΔILED), INCREASE FOR INITIAL CODE CHANGE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXPONENTIAL MODE | LINEAR MODE | |||
| 0 LSB (24 MHz sample rate only) | 1/(ƒPWM × 2047) | 0.05% | 0.30% | 0.05% |
| 1 LSB | 1/(ƒPWM × 1023) | 0.10% | 0.61% | 0.10% |
| 2 LSBs | 1/(ƒPWM × 511) | 0.20% | 1.21% | 0.20% |
| 3 LSBs (24-MHz sample rate only) | 1/(ƒPWM × 255) | 0.39% | 2.40% | 0.39% |
| 4 LSBs (1-MHz and 4-MHz sample rate only) | 1/(ƒPWM × 127) | 0.78% | 4.74% | 0.78% |
| 6 LSBs (1-MHz and 4-MHz sample rate only ) | 1/(ƒPWM × 31) | 3.12% | 17.66% | 3.12% |
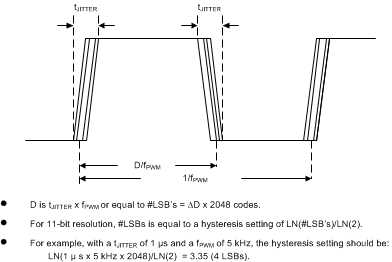 Figure 38. PWM Hysteresis Example
Figure 38. PWM Hysteresis Example