SNVS583H March 2009 – October 2018 LM5008A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.7 Typical Characteristics
 Figure 1. Efficiency vs Load Current and VIN
Figure 1. Efficiency vs Load Current and VIN
(Circuit of Figure 10)
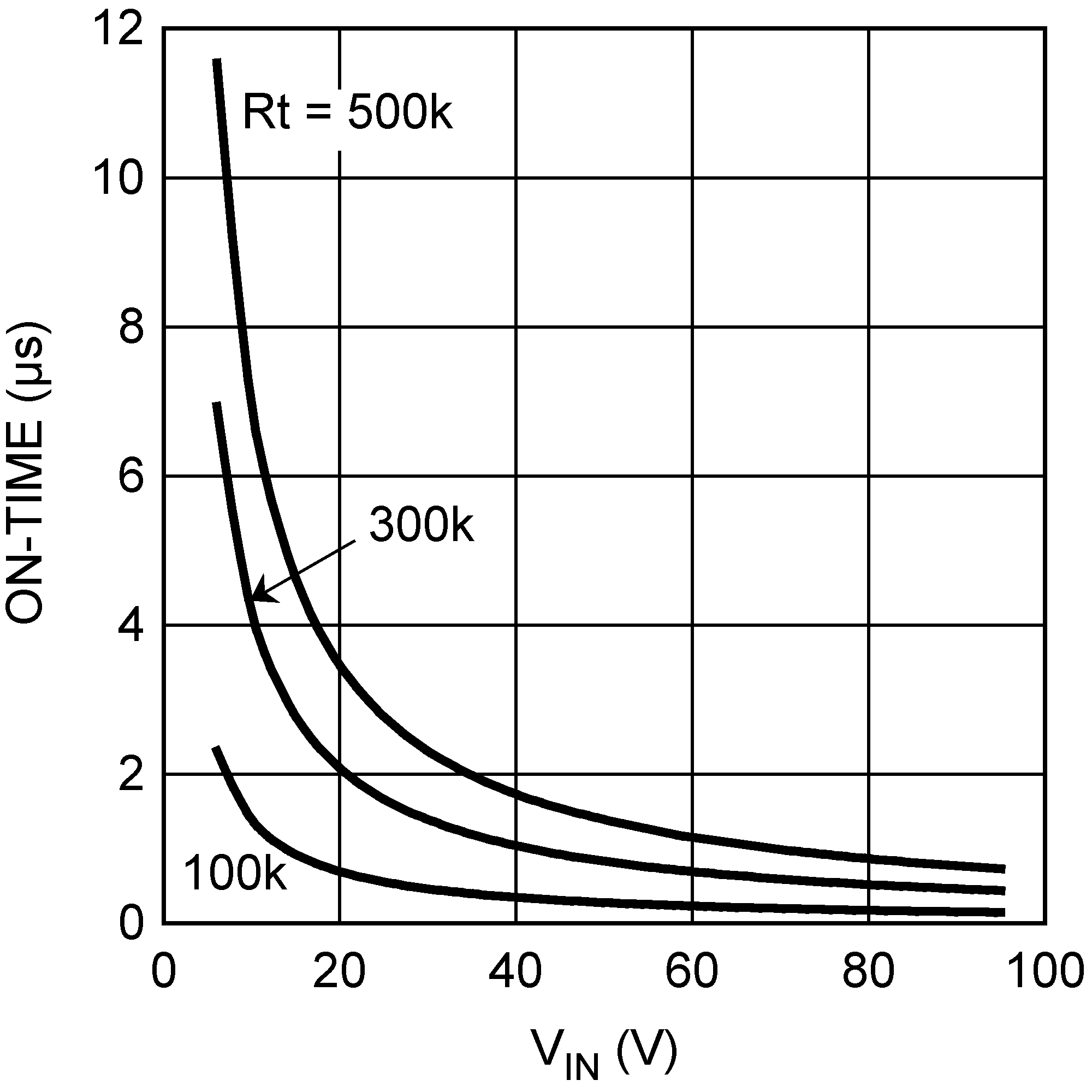 Figure 3. On-Time vs Input Voltage and RT
Figure 3. On-Time vs Input Voltage and RT 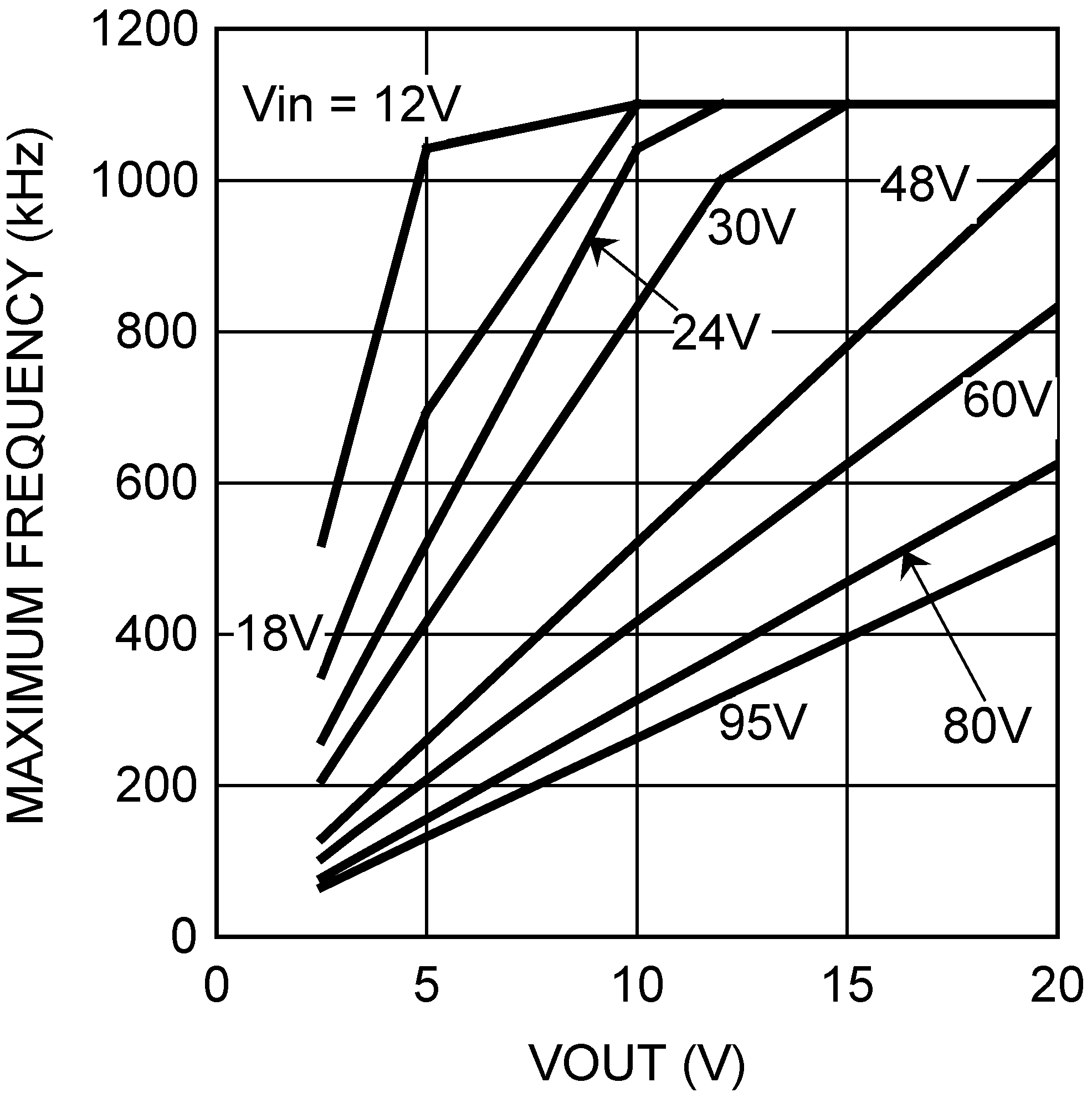 Figure 5. Maximum Frequency vs VOUT and VIN
Figure 5. Maximum Frequency vs VOUT and VIN 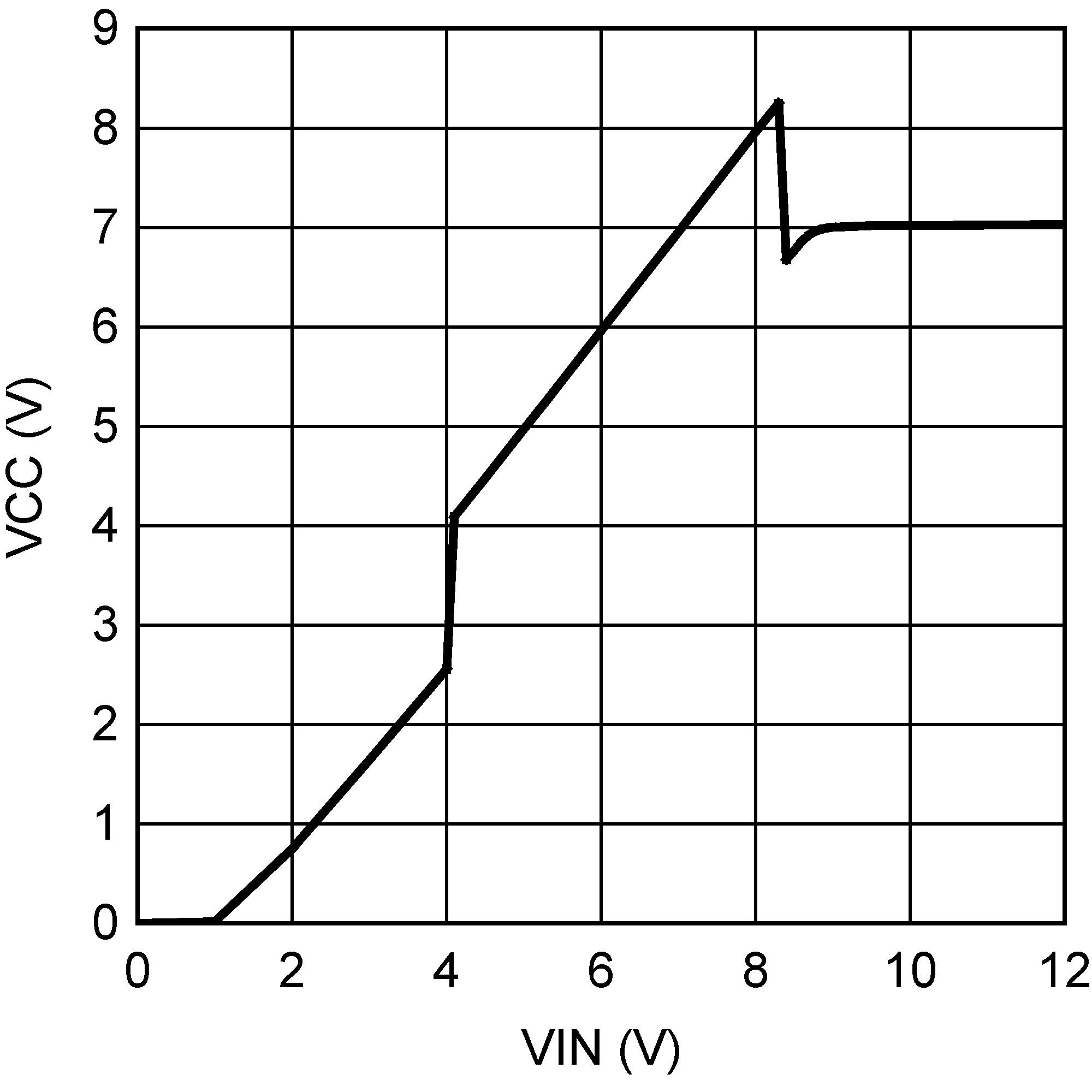 Figure 2. VCC vs VIN
Figure 2. VCC vs VIN 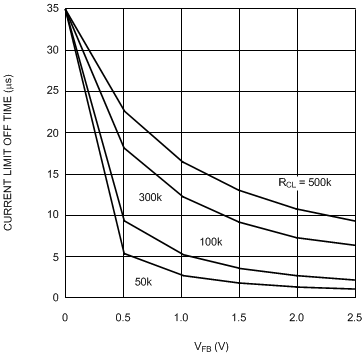 Figure 4. Current Limit Off-Time vs VFB and RCL
Figure 4. Current Limit Off-Time vs VFB and RCL 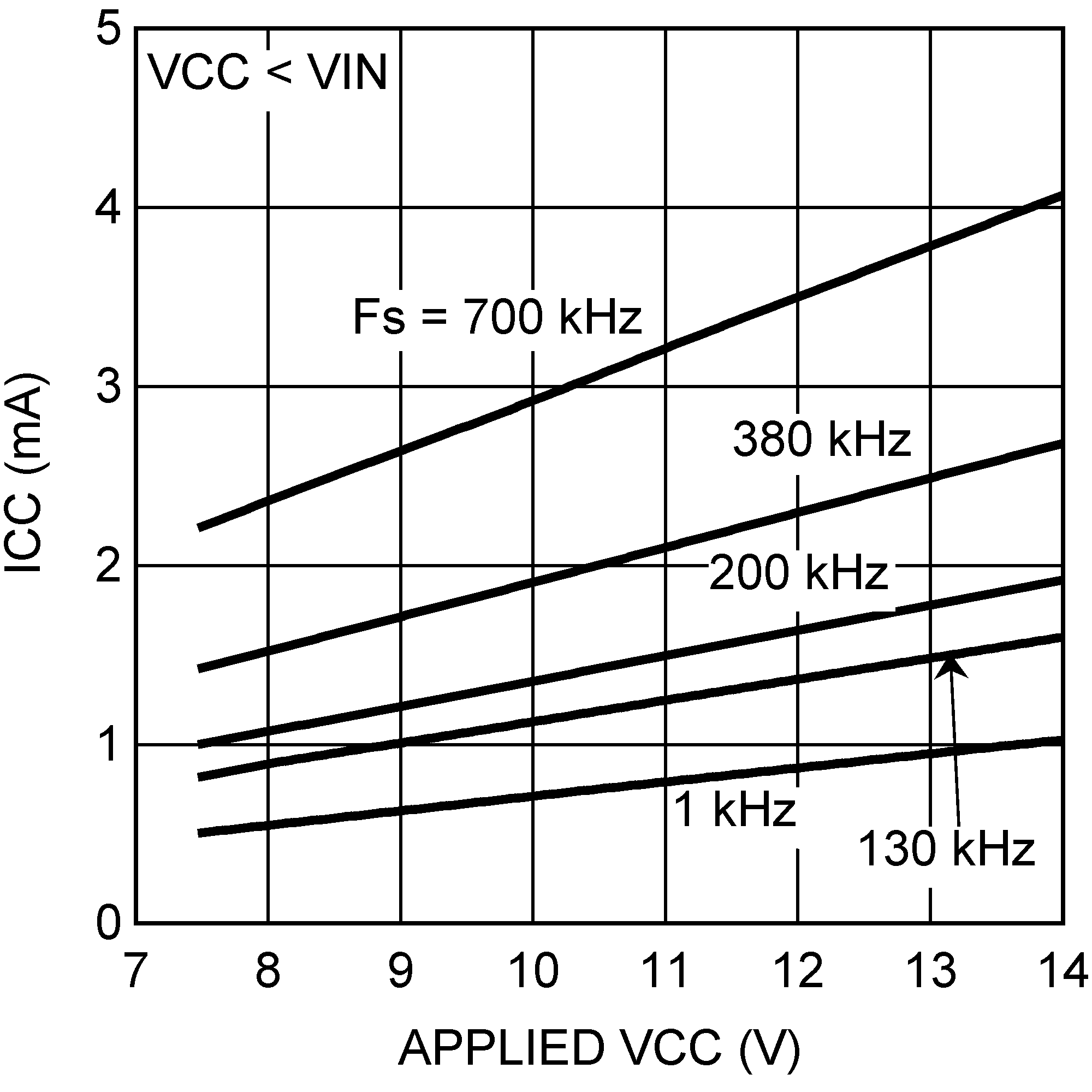 Figure 6. ICC Current vs Applied VCC Voltage
Figure 6. ICC Current vs Applied VCC Voltage