SNVS783K January 2012 – August 2021 LM5017
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Control Overview
- 7.3.2 VCC Regulator
- 7.3.3 Regulation Comparator
- 7.3.4 Overvoltage Comparator
- 7.3.5 On-Time Generator
- 7.3.6 Current Limit
- 7.3.7 N-Channel Buck Switch and Driver
- 7.3.8 Synchronous Rectifier
- 7.3.9 Undervoltage Detector
- 7.3.10 Thermal Protection
- 7.3.11 Ripple Configuration
- 7.3.12 Soft-Start
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Application Circuit: 12.5-V to 95-V Input and 10-V, 600-mA Output Buck Converter
- 8.2.2
Isolated DC/DC Converter Using LM5017
- 8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.2.1 Transformer Turns Ratio
- 8.2.2.2.2 Total IOUT
- 8.2.2.2.3 RFB1, RFB2
- 8.2.2.2.4 Frequency Selection
- 8.2.2.2.5 Transformer Selection
- 8.2.2.2.6 Primary Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.2.7 Secondary Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.2.8 Type III Feedback Ripple Circuit
- 8.2.2.2.9 Secondary Diode
- 8.2.2.2.10 VCC and Boostrap Capacitor
- 8.2.2.2.11 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.2.12 UVLO Resistors
- 8.2.2.2.13 VCC Diode
- 8.2.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
7.3.12 Soft-Start
A soft-start feature can be implemented with the LM5017 using an external circuit. As shown in Figure 7-3, the soft-start circuit consists of one capacitor, C1, two resistors, R1 and R2, and a diode, D. During the initial start-up, the VCC voltage is established prior to the VOUT voltage. Capacitor C1 is discharged and D is thereby forward biased to pull up the FB voltage. The FB voltage exceeds the reference voltage (1.225 V) and switching is therefore disabled. As capacitor C1 charges, the voltage at node B gradually decreases and switching commences. VOUT will gradually rise to maintain the FB voltage at the reference voltage. Once the voltage at node B is less than a diode drop above FB voltage, the soft-start is finished and D is reverse biased.
During the initial part of the start-up, the FB voltage can be approximated as follows. Please note that the effect of R1 has been ignored to simplify the calculation shown in Equation 8.
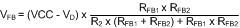
C1 is charged after the first start up. Diode D1 is optional and can be added to discharge C1 when the input voltage experiences a momentary drop to initialize the soft-start sequence.
To achieve the desired soft-start, the following design guidance is recommended:
(1) R2 is selected so that VFB is higher than 1.225 V for a VCC of 4.5 V, but is lower than 5 V when VCC is 8.55 V. If an external VCC is used, VFB should not exceed 5 V at maximum VCC.
(2) C1 is selected to achieve the desired start-up time that can be determined from Equation 9.
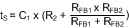
(3) R1 is used to maintain the node B voltage at zero after the soft-start is finished. A value larger than the feedback resistor divider is preferred. Note that the effect of R1 is ignored in the previous equations.
Based on the schematic shown in Figure 8-1, selecting C1 = 1 uF, R2 = 1 kΩ, R1 = 30 kΩ results in a soft-start time of about 2 ms.
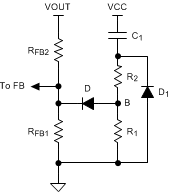 Figure 7-3 Soft-Start Circuit
Figure 7-3 Soft-Start Circuit