SNVS499I February 2007 – November 2023 LM5116
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Application
- 7.2.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 7.2.2.2 Timing Resistor
- 7.2.2.3 Output Inductor
- 7.2.2.4 Current Sense Resistor
- 7.2.2.5 Ramp Capacitor
- 7.2.2.6 Output Capacitors
- 7.2.2.7 Input Capacitors
- 7.2.2.8 VCC Capacitor
- 7.2.2.9 Bootstrap Capacitor
- 7.2.2.10 Soft Start Capacitor
- 7.2.2.11 Output Voltage Divider
- 7.2.2.12 UVLO Divider
- 7.2.2.13 MOSFETs
- 7.2.2.14 MOSFET Snubber
- 7.2.2.15 Error Amplifier Compensation
- 7.2.2.16 Comprehensive Equations
- 7.2.3 Application Curves
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
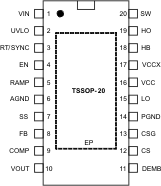 Figure 4-1
PWP Package,
20-Pin HTSSOP
Top View
Figure 4-1
PWP Package,
20-Pin HTSSOP
Top View
Table 4-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| AGND | 6 | G | Analog ground. Connect to PGND through the exposed pad ground connection under the LM5116. |
| COMP | 9 | O | Output of the internal error amplifier. The loop compensation network must be connected between this pin and the FB pin. |
| CS | 12 | I | Current sense amplifier input. Connect to the top of the current sense resistor or the drain of the low-sided MOSFET if RDS(ON) current sensing is used. |
| CSG | 13 | G | Current sense amplifier input. Connect to the bottom of the sense resistor or the source of the low-side MOSFET if RDS(ON) current sensing is used. |
| DEMB | 11 | I | Low-side MOSFET source voltage monitor for diode emulation. For start-up into a pre-biased load, tie this pin to ground at the CSG connection. For fully synchronous operation, use an external series resistor between DEMB and ground to raise the diode emulation threshold above the low-side SW on-voltage. |
| EN | 4 | I | If the EN pin is below 0.5 V, the regulator is in a low-power state, drawing less than 10 µA from VIN. EN must be pulled above 3.3 V for normal operation. The maximum EN transition time for proper operation is one switching period. |
| FB | 8 | I | Feedback signal from the regulated output. This pin is connected to the inverting input of the internal error amplifier. The regulation threshold is 1.215 V. |
| HB | 18 | P | High-side driver supply for bootstrap gate drive. Connect to the cathode of the bootstrap diode and the positive terminal of the bootstrap capacitor. The bootstrap capacitor supplies current to charge the high-side MOSFET gate and must be placed as close to the controller as possible. |
| HO | 19 | O | Connect to the gate of the high-side synchronous MOSFET through a short, low inductance path |
| LO | 15 | O | Connect to the gate of the low-side synchronous MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. |
| PGND | 14 | G | Power ground. Connect to AGND through the exposed pad ground connection under the LM5116 |
| RAMP | 5 | I | Ramp control signal. An external capacitor connected between this pin and the AGND pin sets the ramp slope used for current mode control. |
| RT/SYNC | 3 | I | The internal oscillator is set with a single resistor between this pin and the AGND pin. The recommended frequency range is 50 kHz to 1 MHz. The internal oscillator can be synchronized to an external clock by AC coupling a positive edge onto this node. |
| SS | 7 | I | An external capacitor and an internal 10-µA current source set the soft start time constant for the rise of the error amp reference. The SS pin is held low during VCC < 4.5 V, UVLO < 1.215 V, EN input low, or thermal shutdown. |
| SW | 20 | O | Switch node. Connect to the negative terminal of the bootstrap capacitor and the source terminal of the high-side MOSFET. |
| VIN | 1 | P | Chip supply voltage, input voltage monitor, and input to the VCC regulator. |
| UVLO | 2 | I | If the UVLO pin is below 1.215 V, the regulator is in standby mode (VCC regulator running, switching regulator disabled). If the UVLO pin voltage is above 1.215 V, the regulator is operational. An external voltage divider can set an undervoltage shutdown threshold. There is a fixed 5-µA pullup current on this pin when EN is high. UVLO is pulled to ground when a current limit condition exists for 256 clock cycles. |
| VCC | 16 | P | Locally decouple to PGND using a low ESR/ESL capacitor located as close to the controller as possible. |
| VCCX | 17 | P | Optional input for an externally supplied VCC. If VCCX > 4.5 V, VCCX is internally connected to VCC and the internal VCC regulator is disabled. If VCCX is unused, VCCX must be connected to ground. |
| VOUT | 10 | I | Output monitor. Connect directly to the output voltage. |
| EP | EP | — | Exposed pad. Solder to ground plane. |
(1) G = Ground, I = Input, O = Output, P = Power