SNVS676I August 2010 – April 2018 LM5119
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 High Voltage Start-Up Regulator
- 7.3.2 UVLO
- 7.3.3 Enable 2
- 7.3.4 Oscillator and Sync Capability
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifiers and PWM Comparators
- 7.3.6 Ramp Generator
- 7.3.7 Current Limit
- 7.3.8 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting
- 7.3.9 Soft Start
- 7.3.10 HO and LO Output Drivers
- 7.3.11 Maximum Duty Cycle
- 7.3.12 Thermal Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Dual-output Design Example
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Timing Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Inductor
- 8.2.1.2.3 Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.4 Ramp Resistor and Ramp Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitors
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitors
- 8.2.1.2.7 VCC Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.9 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.10 Restart Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.11 Output Voltage Divider
- 8.2.1.2.12 UVLO Divider
- 8.2.1.2.13 MOSFET Snubber
- 8.2.1.2.14 Error Amplifier Compensation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Two-Phase Design Example
- 8.2.1
Dual-output Design Example
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTV|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTV|32
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.3 Current Sense Resistor
Before determining the value of current sense resistor (RS), it is valuable to understand the K factor, which is the ramp slope multiple chosen for slope compensation. The K factor can be varied from 1 to 3 in practice and is defined with Equation 12.

The performance of the converter varies depending on the selected K value (see Table 1). For this example, 2.5 was chosen as the K factor to minimize the power loss in sense resistor RS and the crosstalk between channels. Crosstalk between the two regulators under certain conditions may be observed on the output as switch jitter.
The maximum output current capability (IOUT(MAX)) must be approximately 20% to 50% higher than the required output current, (8 A at VOUT2) to account for tolerances and ripple current. For this example, 120% of 8 A was chosen (9.6 A). The current sense resistor value can be calculated with Equation 13 as the example (Equation 14).

where
- VCS(TH) is the current limit threshold voltage (120 mV)

A value of 10 mΩ was chosen for RS. The sense resistor must be rated to handle the power dissipation at maximum input voltage when current flows through the free-wheel MOSFET for the majority of the PWM cycle. The maximum power dissipation of RS can be calculated with Equation 15 as the example (Equation 16).

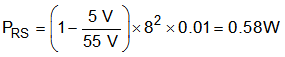
During output short condition, the worst-case peak inductor current is limited to Equation 17 and the example (Equation 18).

where
- tON(MIN) is the minimum HO ON-time which is nominally 100 ns

The chosen inductor must be evaluated for this condition, especially at elevated temperature where the saturation current rating of the inductor may drop significantly. At the maximum input voltage with a shorted output, the valley current must fall below VCS(TH) / RS before the high-side MOSFET is allowed to turn on.