SNVS676I August 2010 – April 2018 LM5119
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 High Voltage Start-Up Regulator
- 7.3.2 UVLO
- 7.3.3 Enable 2
- 7.3.4 Oscillator and Sync Capability
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifiers and PWM Comparators
- 7.3.6 Ramp Generator
- 7.3.7 Current Limit
- 7.3.8 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting
- 7.3.9 Soft Start
- 7.3.10 HO and LO Output Drivers
- 7.3.11 Maximum Duty Cycle
- 7.3.12 Thermal Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Dual-output Design Example
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Timing Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Inductor
- 8.2.1.2.3 Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.4 Ramp Resistor and Ramp Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitors
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitors
- 8.2.1.2.7 VCC Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.9 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.10 Restart Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.11 Output Voltage Divider
- 8.2.1.2.12 UVLO Divider
- 8.2.1.2.13 MOSFET Snubber
- 8.2.1.2.14 Error Amplifier Compensation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Two-Phase Design Example
- 8.2.1
Dual-output Design Example
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTV|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTV|32
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitors
The output capacitors smooth the inductor ripple current and provide a source of charge during transient loading conditions. For this design example, a 470-µF electrolytic capacitor with 10-mΩ ESR was selected as the main output capacitor. The fundamental component of the output ripple voltage is approximated with Equation 21 as the example (Equation 22 and Equation 23).
Equation 21. 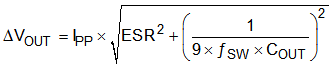
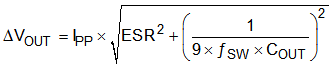
Equation 22. 

Equation 23. 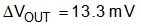
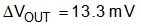
Two 22-µF low ERS or ESL ceramic capacitors are placed in parallel with the 470-µF electrolytic capacitor to further reduce the output voltage ripple and spikes.
Table 1. Performance Variation by K Factor
| K < 1 | 1 <— K —> 3 | K > 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross talk | Sub-harmonic oscillation may occur | Higher | Lower | Introduces additional pole near crossover frequency |
| Peak inductor current with short output condition | Lower | Higher | ||
| Inductor size | Smaller | Larger | ||
| Power dissipation of Rs | Higher | Lower | ||
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher | ||