SNVSB54A May 2018 – November 2018 LM5122ZA
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.2 High-Voltage VCC Regulator
- 7.3.3 Oscillator
- 7.3.4 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 PWM Comparator
- 7.3.7 Soft Start
- 7.3.8 HO and LO Drivers
- 7.3.9 Bypass Operation (VOUT = VIN)
- 7.3.10 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
- 7.3.11 Clock Synchronization
- 7.3.12 Maximum Duty Cycle
- 7.3.13 Thermal Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Feedback Compensation
- 8.1.2 Sub-Harmonic Oscillation
- 8.1.3 Interleaved Boost Configuration
- 8.1.4 DCR Sensing
- 8.1.5 Output Overvoltage Protection
- 8.1.6 SEPIC Converter Simplified Schematic
- 8.1.7 Non-Isolated Synchronous Flyback Converter Simplified Schematic
- 8.1.8 Negative to Positive Conversion
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Timing Resistor RT
- 8.2.2.2 UVLO Divider RUV2, RUV1
- 8.2.2.3 Input Inductor LIN
- 8.2.2.4 Current Sense Resistor RS
- 8.2.2.5 Current Sense Filter RCSFP, RCSFN, CCS
- 8.2.2.6 Slope Compensation Resistor RSLOPE
- 8.2.2.7 Output Capacitor COUT
- 8.2.2.8 Input Capacitor CIN
- 8.2.2.9 VIN Filter RVIN, CVIN
- 8.2.2.10 Bootstrap Capacitor CBST and Boost Diode DBST
- 8.2.2.11 VCC Capacitor CVCC
- 8.2.2.12 Output Voltage Divider RFB1, RFB2
- 8.2.2.13 Soft-Start Capacitor CSS
- 8.2.2.14 Restart Capacitor CRES
- 8.2.2.15 Low-Side Power Switch QL
- 8.2.2.16 High-Side Power Switch QH and Additional Parallel Schottky Diode
- 8.2.2.17 Snubber Components
- 8.2.2.18 Loop Compensation Components CCOMP, RCOMP, CHF
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.15 Low-Side Power Switch QL
Selection of the power N-channel MOSFET devices by breaking down the losses is one way to compare the relative efficiencies of different devices. Losses in the low-side N-channel MOSFET device can be separated into conduction loss and switching loss.
Low-side conduction loss is approximately calculated as follows:
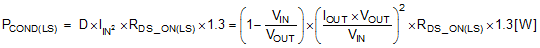
where
- D is the duty cycle
- the factor of 1.3 accounts for the increase in the N-channel MOSFET device on-resistance due to heating
Alternatively, the factor of 1.3 can be eliminated, and the high temperature on-resistance of the N-channel MOSFET device can be estimated using the RDS(ON) vs temperature curves in the N-channel MOSFET datasheet.
Switching loss occurs during the brief transition period as the low-side N-channel MOSFET device turns on and off. During the transition period both current and voltage are present in the channel of the N-channel MOSFET device. The low-side switching loss is approximately calculated as follows:
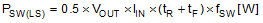
tR and tF are the rise and fall times of the low-side N-channel MOSFET device. The rise and fall times are usually mentioned in the N-channel MOSFET data sheet or can be empirically observed with an oscilloscope.
An additional Schottky diode can be placed in parallel with the low-side N-channel MOSFET switch, with short connections to the source and drain in order to minimize negative voltage spikes at the SW node.