SNVSBI7B January 2020 – January 2021 LM5156-Q1 , LM51561-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Line Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO/SYNC/EN Pin)
- 9.3.2 High Voltage VCC Regulator (BIAS, VCC Pin)
- 9.3.3 Soft Start (SS Pin)
- 9.3.4 Switching Frequency (RT Pin)
- 9.3.5 Dual Random Spread Spectrum (DRSS)
- 9.3.6 Clock Synchronization (UVLO/SYNC/EN Pin)
- 9.3.7 Current Sense and Slope Compensation (CS Pin)
- 9.3.8 Current Limit and Minimum On-time (CS Pin)
- 9.3.9 Feedback and Error Amplifier (FB, COMP Pin)
- 9.3.10 Power-Good Indicator (PGOOD pin)
- 9.3.11 Hiccup Mode Overload Protection (LM51561-Q1 Only)
- 9.3.12 Maximum Duty Cycle Limit and Minimum Input Supply Voltage
- 9.3.13 MOSFET Driver (GATE Pin)
- 9.3.14 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 9.3.15 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSS|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSS|12
Orderable Information
9.3.12 Maximum Duty Cycle Limit and Minimum Input Supply Voltage
When designing boost converters, the maximum duty cycle should be reviewed at the minimum supply voltage. The minimum input supply voltage that can achieve the target output voltage is limited by the maximum duty cycle limit, and it can be estimated as follows.
Equation 15. 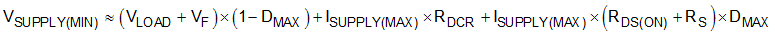
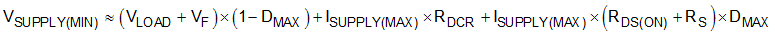
where
- ISUPPLY(MAX) is the maximum input current.
- RDCR is the DC resistance of the inductor.
- RDS(ON) is the on-resistance of the MOSFET.
Equation 16. 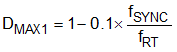
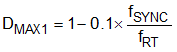
Equation 17. 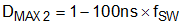
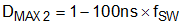
The minimum input supply voltage can be further decreased by supplying fSYNC, which is less than fRT. DMAX is DMAX1 or DMAX2, whichever is lower.