SNVSBN5A February 2020 – June 2020 LM60430 , LM60440
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.2.2 Choosing the Switching Frequency
- 9.2.2.3 Setting the Output Voltage
- 9.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.7 CBOOT
- 9.2.2.8 VCC
- 9.2.2.9 CFF Selection
- 9.2.2.10 External UVLO
- 9.2.2.11 Maximum Ambient Temperature
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 EMI
- 9.4 What to Do and What Not to Do
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPK|13
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.2.11 Maximum Ambient Temperature
As with any power conversion device, the LM604x0 dissipates internal power while operating. The effect of this power dissipation is to raise the internal temperature of the converter above ambient. The internal die temperature (TJ) is a function of the ambient temperature, the power loss, and the effective thermal resistance, RθJA, of the device and PCB combination. The maximum internal die temperature for the LM604x0 must be limited to 150°C. This establishes a limit on the maximum device power dissipation and therefore the load current. Equation 10 shows the relationships between the important parameters. It is easy to see that larger ambient temperatures (TA) and larger values of RθJA reduce the maximum available output current. The converter efficiency can be estimated by using the curves provided in this data sheet. If the desired operating conditions cannot be found in one of the curves, then interpolation can be used to estimate the efficiency. Alternatively, the EVM can be adjusted to match the desired application requirements and the efficiency can be measured directly. The correct value of RθJA is more difficult to estimate. As stated in the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics Application Report, the value of RθJA given in the Thermal Information table is not valid for design purposes and must not be used to estimate the thermal performance of the application. The values reported in that table were measured under a specific set of conditions that are rarely obtained in an actual application.
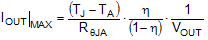
where
- η = efficiency
The effective RθJA is a critical parameter and depends on many factors such as power dissipation, air temperature/flow, PCB area, copper heat-sink area, number of thermal vias under the package, and adjacent component placement, just to mention just a few. The copper area given in the graph is for each layer; the top and bottom layers are 2 oz. copper each, while the inner layers are 1 oz. It must be remembered that the data given in these graphs are for illustration purposes only, and the actual performance in any given application depends on all of the previously mentioned factors.