Unless otherwise specified, the following conditions apply: VIN = 13.5 V,
TA = 25°C. Table 8-3 shows the circuit with the appropriate BOM from Figure 8-26.
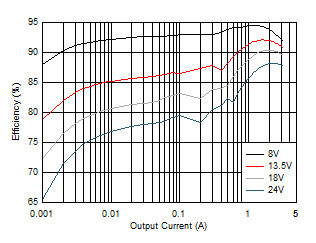
| VOUT = 5 V | ƒSW = 2100 kHz (AUTO) |
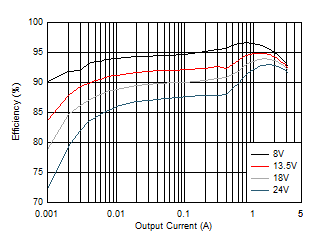
| VOUT = 5
V |
ƒSW = 400 kHz
(AUTO) |
Figure 8-10 Efficiency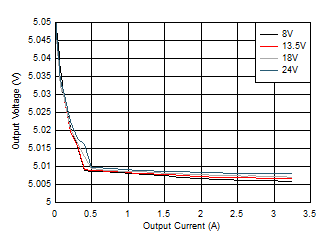
| VOUT = 5
V |
ƒSW = 2100 kHz
(AUTO) |
Figure 8-12 Line and Load Regulation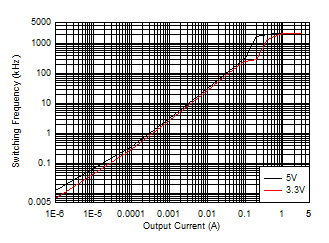
| VIN = 13.5
V |
ƒSW = 2100 kHz
(AUTO) |
Figure 8-14 Switching Frequency versus Output Current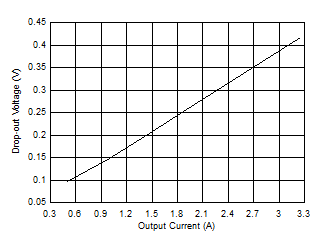 Figure 8-16 Dropout Voltage versus Output Current for -1% Drop
Figure 8-16 Dropout Voltage versus Output Current for -1% Drop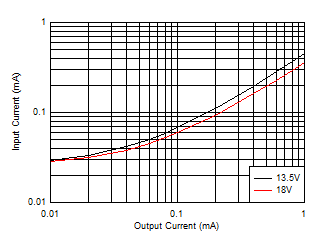 Figure 8-18 Input
Supply Current versus Output Current
Figure 8-18 Input
Supply Current versus Output Current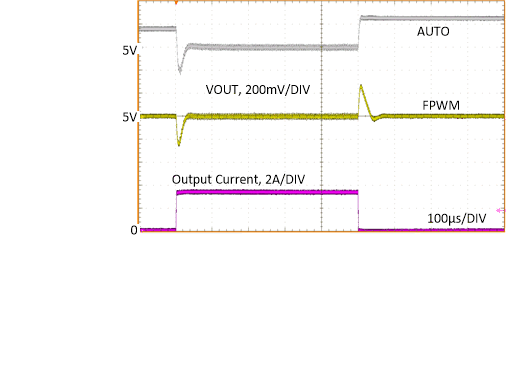
| 0 A to 3.25 A, 2 µs |
VOUT
= 5 V |
ƒSW
= 400 kHz |
Figure 8-20 Load
Transient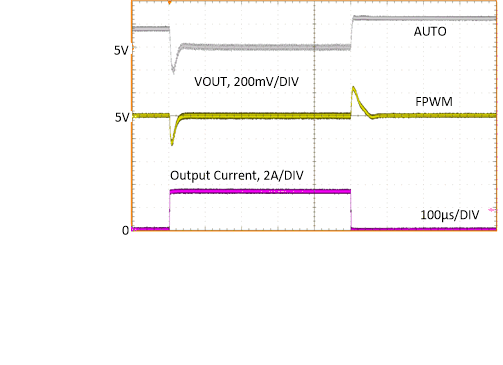
| 0 A to 3.25 A, 2 µs |
VOUT
= 5 V |
ƒSW
= 2100 kHz |
Figure 8-22 Load
Transient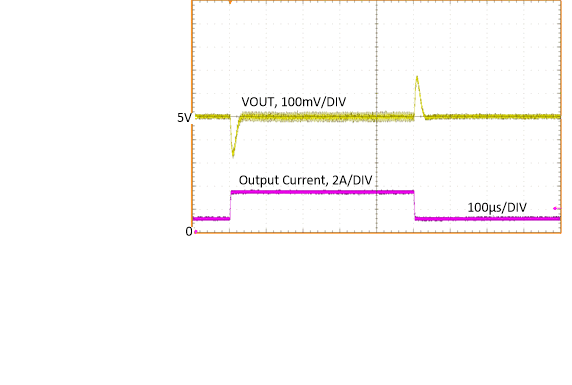
| VOUT
= 5 V |
ƒSW
= 400 kHz |
| AUTO |
1 A to 3.25 A,
2 µs |
Figure 8-24 Load
Transient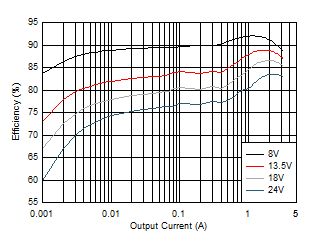
| VOUT = 3.3
V |
ƒSW = 2100 kHz
(AUTO) |
Figure 8-9 Efficiency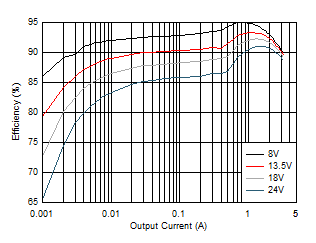
| VOUT = 3.3
V |
ƒSW = 400 kHz
(AUTO) |
Figure 8-11 Efficiency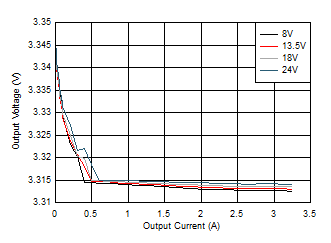
| VOUT = 3.3
V |
ƒSW = 2100 kHz
(AUTO) |
Figure 8-13 Line and Load Regulation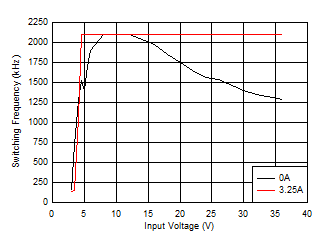
| VOUT = 3.3
V |
ƒSW = 2100 kHz
(FPWM) |
Figure 8-15 Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage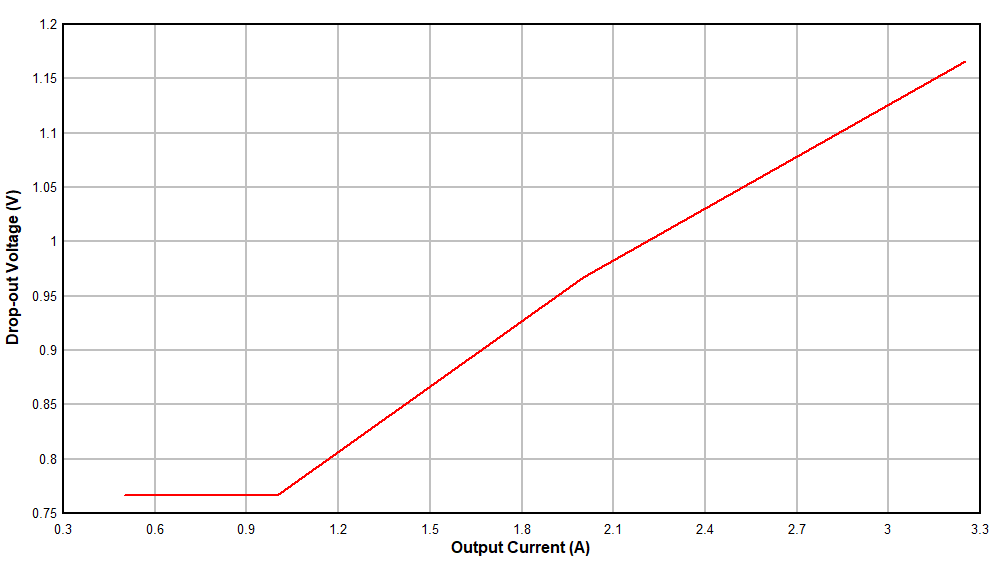 Figure 8-17 Dropout Voltage versus Output Current to 1.85 MHz
Figure 8-17 Dropout Voltage versus Output Current to 1.85 MHz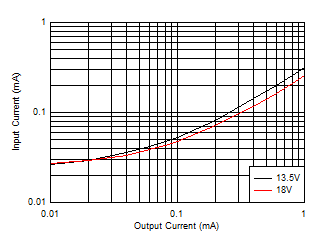 Figure 8-19 Input
Supply Current versus Output Current
Figure 8-19 Input
Supply Current versus Output Current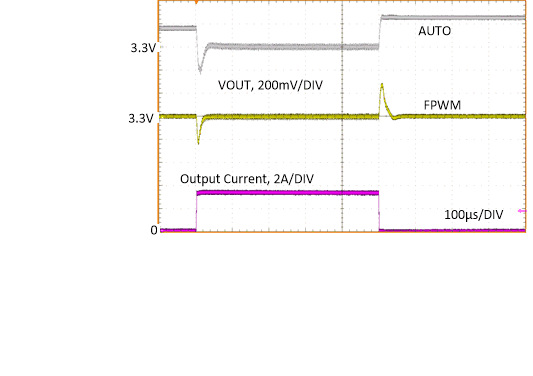
| 0 A to 3.25 A, 2 µs |
VOUT
= 3.3 V |
ƒSW
= 400 kHz |
Figure 8-21 Load
Transient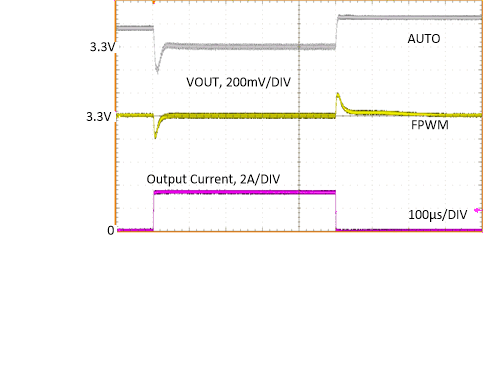
| 0 A to 3.25 A, 2 µs |
VOUT
= 3.3 V |
ƒSW
= 2100 kHz |
Figure 8-23 Load
Transient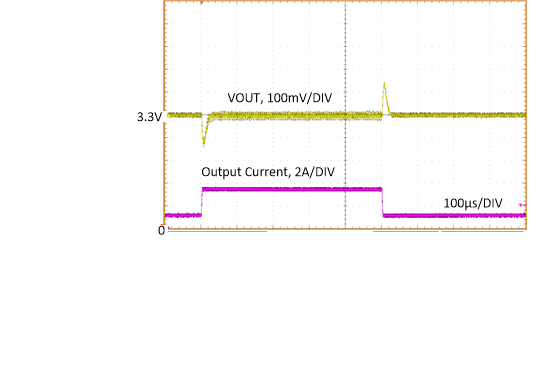
| VOUT
= 3.3 V |
ƒSW
= 400 kHz |
| AUTO |
1 A to 3.25 A,
2 µs |
Figure 8-25 Load
TransientTable 8-3 BOM for Typical Application
Curves
| VOUT(1) |
FREQUENCY |
OUTPUT CURRENT |
COUT |
L |
U1 |
| 3.3 V |
400 kHz |
3.25 A |
3 × 22 µF |
6.8 µH, 22 mΩ |
LM63635D |
| 3.3 V |
2100 kHz |
3.25 A |
3 × 22 µF |
1.5 µH, 10 mΩ |
LM63635D |
| 5 V |
400 kHz |
3.25 A |
3 × 22 µF |
6.8 µH, 22 mΩ |
LM63635D |
| 5 V |
2100 kHz |
3.25 A |
3 × 22 µF |
1.5 µH, 10 mΩ |
LM63635D |
(1) The values
in this table were selected to enhance certain performance criteria and may not
represent typical values.


















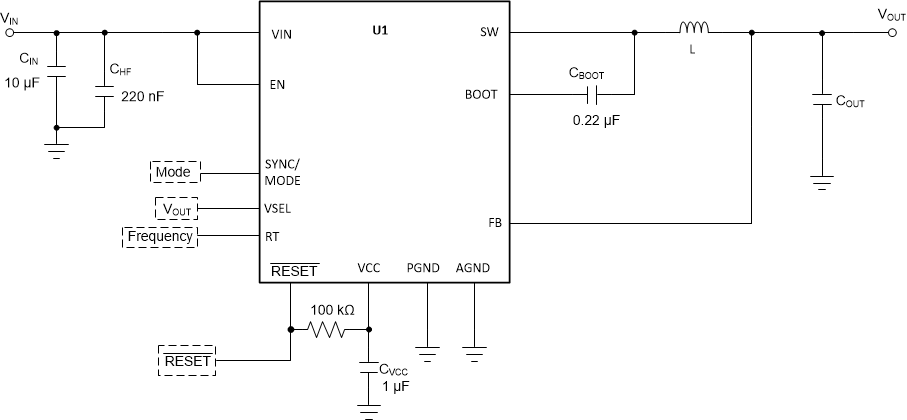 Figure 8-26 Circuit
for Typical Application Curves
Figure 8-26 Circuit
for Typical Application Curves